|
Half-transitive Graph
In the mathematics, mathematical field of graph theory, a half-transitive graph is a Graph (discrete mathematics), graph that is both Vertex-transitive graph, vertex-transitive and Edge-transitive graph, edge-transitive, but not symmetric graph, symmetric. In other words, a graph is half-transitive if its automorphism group acts Group action (mathematics), transitively upon both its vertices and its edges, but not on ordered pairs of linked vertices. Every connected symmetric graph must be Vertex-transitive graph, vertex-transitive and Edge-transitive graph, edge-transitive, and the converse is true for graphs of odd degree, so that half-transitive graphs of odd degree do not exist. However, there do exist half-transitive graphs of even degree. The smallest half-transitive graph is the Holt graph, with degree 4 and 27 vertices.. References {{reflist Graph families Algebraic graph theory Regular graphs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of ''graph (discrete mathematics), graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of ''Vertex (graph theory), vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') which are connected by ''Glossary of graph theory terms#edge, edges'' (also called ''arcs'', ''links'' or ''lines''). A distinction is made between undirected graphs, where edges link two vertices symmetrically, and directed graphs, where edges link two vertices asymmetrically. Graphs are one of the principal objects of study in discrete mathematics. Definitions Definitions in graph theory vary. The following are some of the more basic ways of defining graphs and related mathematical structures. Graph In one restricted but very common sense of the term, a graph is an ordered pair G=(V,E) comprising: * V, a Set (mathematics), set of vertices (also called nodes or points); * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph (discrete Mathematics)
In discrete mathematics, particularly in graph theory, a graph is a structure consisting of a Set (mathematics), set of objects where some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects are represented by abstractions called ''Vertex (graph theory), vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an ''edge'' (also called ''link'' or ''line''). Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges. The edges may be directed or undirected. For example, if the vertices represent people at a party, and there is an edge between two people if they shake hands, then this graph is undirected because any person ''A'' can shake hands with a person ''B'' only if ''B'' also shakes hands with ''A''. In contrast, if an edge from a person ''A'' to a person ''B'' means that ''A'' owes money to ''B'', then this graph is directed, because owing mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex-transitive Graph
In the mathematics, mathematical field of graph theory, an Graph automorphism, automorphism is a permutation of the Vertex (graph theory), vertices such that edges are mapped to edges and non-edges are mapped to non-edges. A graph is a vertex-transitive graph if, given any two vertices and of , there is an automorphism such that :f(v_1) = v_2.\ In other words, a graph is vertex-transitive if its automorphism group Group action (mathematics), acts Group_action#Remarkable properties of actions, transitively on its vertices.. A graph is vertex-transitive if and only if its graph complement is, since the group actions are identical. Every symmetric graph without isolated vertex, isolated vertices is vertex-transitive, and every vertex-transitive graph is Regular graph, regular. However, not all vertex-transitive graphs are symmetric (for example, the edges of the truncated tetrahedron), and not all regular graphs are vertex-transitive (for example, the Frucht graph and Tietze's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge-transitive Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, an edge-transitive graph is a graph such that, given any two edges and of , there is an automorphism of that maps to . In other words, a graph is edge-transitive if its automorphism group acts transitively on its edges. Examples and properties The number of connected simple edge-transitive graphs on n vertices is 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 8, 9, 13, 7, 19, 10, 16, 25, 26, 12, 28 ... Edge-transitive graphs include all symmetric graphs, such as the vertices and edges of the cube. Symmetric graphs are also vertex-transitive (if they are connected), but in general edge-transitive graphs need not be vertex-transitive. Every connected edge-transitive graph that is not vertex-transitive must be bipartite, (and hence can be colored with only two colors), and either semi-symmetric or biregular.. Examples of edge but not vertex transitive graphs include the complete bipartite graph In the mathematical field of graph theory, a comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetric Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a graph is symmetric or arc-transitive if, given any two ordered pairs of adjacent vertices (u_1,v_1) and (u_2,v_2) of , there is an automorphism :f : V(G) \rightarrow V(G) such that :f(u_1) = u_2 and f(v_1) = v_2. In other words, a graph is symmetric if its automorphism group acts transitively on ordered pairs of adjacent vertices (that is, upon edges considered as having a direction). Such a graph is sometimes also called -transitive or flag-transitive. By definition (ignoring and ), a symmetric graph without isolated vertices must also be vertex-transitive. Since the definition above maps one edge to another, a symmetric graph must also be edge-transitive. However, an edge-transitive graph need not be symmetric, since might map to , but not to . Star graphs are a simple example of being edge-transitive without being vertex-transitive or symmetric. As a further example, semi-symmetric graphs are edge-transitive and regular, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automorphism Group
In mathematics, the automorphism group of an object ''X'' is the group consisting of automorphisms of ''X'' under composition of morphisms. For example, if ''X'' is a finite-dimensional vector space, then the automorphism group of ''X'' is the group of invertible linear transformations from ''X'' to itself (the general linear group of ''X''). If instead ''X'' is a group, then its automorphism group \operatorname(X) is the group consisting of all group automorphisms of ''X''. Especially in geometric contexts, an automorphism group is also called a symmetry group. A subgroup of an automorphism group is sometimes called a transformation group. Automorphism groups are studied in a general way in the field of category theory. Examples If ''X'' is a set with no additional structure, then any bijection from ''X'' to itself is an automorphism, and hence the automorphism group of ''X'' in this case is precisely the symmetric group of ''X''. If the set ''X'' has additional structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Action (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group action of a group G on a set (mathematics), set S is a group homomorphism from G to some group (under function composition) of functions from S to itself. It is said that G acts on S. Many sets of transformation (function), transformations form a group (mathematics), group under function composition; for example, the rotation (mathematics), rotations around a point in the plane. It is often useful to consider the group as an abstract group, and to say that one has a group action of the abstract group that consists of performing the transformations of the group of transformations. The reason for distinguishing the group from the transformations is that, generally, a group of transformations of a mathematical structure, structure acts also on various related structures; for example, the above rotation group also acts on triangles by transforming triangles into triangles. If a group acts on a structure, it will usually also act on objects built from that st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
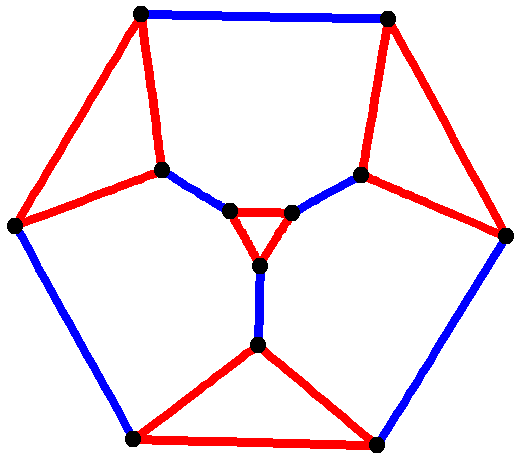
Holt Graph
In graph theory, the Holt graph or Doyle graph is the smallest half-transitive graph, that is, the smallest example of a vertex-transitive and edge-transitive graph which is not also symmetric. Such graphs are not common. It is named after Peter G. Doyle and Derek F. Holt, who discovered the same graph independently in 1976 and 1981. respectively. The Holt graph has diameter 3, radius 3 and girth 5, chromatic number 3, chromatic index 5 and is Hamiltonian with distinct Hamiltonian cycles. It is also a 4- vertex-connected and a 4- edge-connected graph. It has book thickness 3 and queue number 3.Jessica Wolz, ''Engineering Linear Layouts with SAT''. Master Thesis, University of Tübingen, 2018 It has an automorphism group of order 54. This is a smaller group than a symmetric graph with the same number of vertices and edges would have. The graph drawing on the right highlights this, in that it lacks reflectional symmetry. The characteristic polynomial of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Mathematical Bulletin
The ''Canadian Mathematical Bulletin'' () is a mathematics journal, established in 1958 and published quarterly by the Canadian Mathematical Society. The current editors-in-chief of the journal are Antonio Lei and Javad Mashreghi. The journal publishes short articles in all areas of mathematics that are of sufficient interest to the general mathematical public. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted in: for the Canadian Mathematical Bulletin. * '''' * '' |
Journal Of Graph Theory
The ''Journal of Graph Theory'' is a peer-reviewed mathematics journal specializing in graph theory and related areas, such as structural results about graphs, graph algorithms with theoretical emphasis, and discrete optimization on graphs. The scope of the journal also includes related areas in combinatorics and the interaction of graph theory with other mathematical sciences. It is published by John Wiley & Sons. The journal was established in 1977 by Frank Harary.Frank Harary a biographical sketch at the ACM site The are [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Families
Graph may refer to: Mathematics *Graph (discrete mathematics), a structure made of vertices and edges **Graph theory, the study of such graphs and their properties *Graph (topology), a topological space resembling a graph in the sense of discrete mathematics *Graph of a function *Graph of a relation *Graph paper *Chart, a means of representing data (also called a graph) Computing *Graph (abstract data type), an abstract data type representing relations or connections *graph (Unix), Unix command-line utility *Conceptual graph, a model for knowledge representation and reasoning *Microsoft Graph, a Microsoft API developer platform that connects multiple services and devices Other uses *HMS Graph, HMS ''Graph'', a submarine of the UK Royal Navy See also *Complex network *Graf *Graff (other) *Graph database *Grapheme, in linguistics *Graphemics *Graphic (other) *-graphy (suffix from the Greek for "describe," "write" or "draw") *List of information graphics soft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |