|
Fractional Flow Reserve
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is a diagnostic technique used in coronary catheterization. FFR measures pressure differences across a coronary artery stenosis (narrowing, usually due to atherosclerosis) to determine the likelihood that the stenosis impedes oxygen delivery to the heart muscle (myocardial ischemia). Fractional flow reserve is defined as the pressure after (distal to) a stenosis relative to the pressure before the stenosis. The result is an absolute number; an FFR of 0.80 means that a given stenosis causes a 20% drop in blood pressure. In other words, FFR expresses the maximal flow down a vessel in the presence of a stenosis compared to the maximal flow in the hypothetical absence of the stenosis. Procedure During coronary catheterization, a catheter is inserted into the femoral (groin) or radial arteries (wrist) using a sheath and guidewire. FFR uses a small sensor on the tip of the wire (commonly a transducer) to measure pressure, temperature and flow to determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
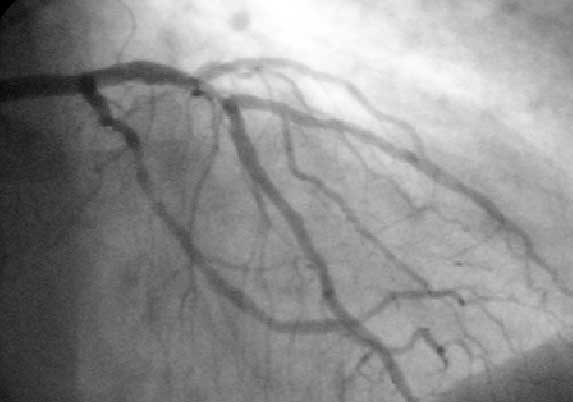
Coronary Catheterization
A coronary catheterization is a minimally invasive procedure to access the coronary circulation and blood filled chambers of the heart using a catheter. It is performed for both diagnostic and interventional (treatment) purposes. Coronary catheterization is one of the several cardiology diagnostic tests and procedures. Specifically, through the injection of a liquid radiocontrast agent and illumination with X-rays, angiocardiography allows the recognition of Vascular occlusion, occlusion, stenosis, restenosis, thrombosis or aneurysmal enlargement of the coronary artery lumen (anatomy), lumens; heart chamber size; heart muscle contraction performance; and some aspects of heart valve function. Important internal heart and lung blood pressures, not measurable from outside the body, can be accurately measured during the test. The relevant problems that the test deals with most commonly occur as a result of advanced atherosclerosis – atheroma activity within the wall of the coronary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papaverine
Papaverine (Latin ''papaver'', "poppy") is an opium alkaloid antispasmodic drug, used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasms and vasospasms (especially those involving the intestines, heart, or brain), occasionally in the treatment of erectile dysfunction and acute mesenteric ischemia. While it is found in the opium poppy, papaverine differs in both structure and pharmacological action from the analgesic morphine and its derivatives (such as codeine). History Papaverine was discovered in 1848 by Georg Merck (1825–1873). Merck was a student of the German chemists Justus von Liebig and August Hofmann, and he was the son of Emanuel Merck (1794–1855), founder of the Merck corporation, a major German chemical and pharmaceutical company. Uses Papaverine is approved to treat spasms of the gastrointestinal tract, bile ducts and ureter and for use as a cerebral and coronary vasodilator in subarachnoid hemorrhage (combined with balloon angioplasty) and coronary artery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revascularization
In medical and surgical therapy, revascularization is the restoration of perfusion to a body part or organ that has had ischemia. It is typically accomplished by surgical means. Vascular bypass and angioplasty are the two primary means of revascularization. The term derives from the prefix re-, in this case meaning "restoration" and vasculature, which refers to the circulatory structures of an organ. It is often combined with "urgent" to form urgent vascularization. Revascularization involves a thorough analysis and diagnosis and treatment of the existing diseased vasculature of the affected organ, and can be aided by the use of different imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging, PET scan, CT scan, and X-ray fluoroscopy. Applications For coronary artery disease (ischemic heart disease), coronary artery bypass surgery and percutaneous coronary intervention (coronary balloon angioplasty) are the two primary means of revascularization. When those cannot be done, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Eluting Stent
A drug-eluting stent (DES) is a peripheral or coronary stent (a scaffold) placed into narrowed, diseased peripheral or coronary arteries that slowly release a drug to block cell proliferation. This prevents fibrosis that, together with clots (thrombi), could otherwise block the stented artery, a process called restenosis. The stent is usually placed within the peripheral or coronary artery by an interventional cardiologist or interventional radiologist during an angioplasty procedure. Drug-eluting stents in current clinical use were approved by the FDA after clinical trials showed they were statistically superior to bare-metal stents for the treatment of native coronary artery narrowings, having lower rates of major adverse cardiac events (usually defined as a composite clinical endpoint of death + myocardial infarction + repeat intervention because of restenosis). The first drug-eluting stents to be approved in Europe and the U.S. were coated with paclitaxel or an mTOR inhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Imaging
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is " radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emitting from within the body rather than radiation that is generated by external sources like X-rays. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on the function. For such reason, it is called a physiological imaging modality. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are the two most common imaging modalities in nuclear medicine. Diagnostic medical imaging Diagnostic In nuclear medicine imaging, radiopharmaceuticals are taken internally, for example, through inhalation, intravenously or orally. Then, external detectors ( gamma cameras) capture and form images from the radiation emitted by the radiopharmaceuticals. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |