|
Fluridone
Fluridone is an organic compound that is used as aquatic herbicide often used to control invasive plants. It is used in the United States to control hydrilla and Eurasian watermilfoil among other species. Fluridone is sold as a solution and as a slow release solid because the herbicide level must be maintained for several weeks. The compound is a colorless solid.Franz Müller and Arnold P. Applebyki "Weed Control, 2. Individual Herbicides" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2010 The compound was first reported as a possible herbicide for cotton fields in 1976. It was registered with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency in 1986 and has low toxicity to animals with no restrictions on swimming or drinking in treated water bodies. Fluridone breaks down in the environment over days or weeks with the major degradation product being N-methyl formamide. The half-life of fluridone in soils and sediments has been estimated at nine months. Fluridone degradation in soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrilla
''Hydrilla'' (waterthyme) is a genus of aquatic plant Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments (saltwater or freshwater). They are also referred to as hydrophytes or macrophytes to distinguish them from algae and other microphytes. A macrophyte is a plant that ..., usually treated as containing just one species, ''Hydrilla verticillata'', though some botanists divide it into several species. It is native to the cool and warm waters of the Old World in Asia, Africa and Australia, with a sparse, scattered distribution; in Australia from Northern Territory, Queensland, and New South Wales.Flora Europaea''Hydrilla''/ref>Flora of Taiwan''Hydrilla''Australian Plant Name Index''Hydrilla''/ref> The stems grow up to 1–2m long. The leaf, leaves are arranged in whorls of two to eight around the stem, each leaf 5–20 mm long and 0.7–2 mm broad, with serrations or small spines along the leaf margins; the leaf midrib is often reddish whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15-Cis-phytoene Desaturase
15-''cis''-phytoene desaturases (''PDS'', ''plant-type phytoene desaturases'') (, ''15-cis-phytoene:plastoquinone oxidoreductase''), are enzymes involved in the carotenoid biosynthesis in plants and cyanobacteria. Phytoene desaturases are membrane-bound enzymes localized in plastids and introduce two double bonds into their colorless substrate phytoene by dehydrogenation and isomerize two additional double bonds. This reaction starts a biochemical pathway involving three further enzymes ( zeta-carotene isomerase, zeta-carotene desaturase and carotene cis-trans isomerase) called the poly-cis pathway and leads to the red colored lycopene. The homologous phytoene desaturase found in bacteria and fungi ( CrtI) converts phytoene directly to lycopene by an all-trans pathway. Biochemistry PDS converts 15-''cis''-phytoene into 9,15,9'-tri-''cis''-ζ-carotene through reduction of the enzymes non-covalently bound FAD cofactor. This conversion introduces two additional double bonds at p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stormy Lake (Alaska)
Stormy Lake is a lake on the Kenai Peninsula of Alaska, also known as Three Bay Lake. It is located north of the town of Kenai. The lake has been the target of two efforts to eradicate invasive species and re-introduce native flora and fish. Name and location Stormy Lake is a lake on the Kenai Peninsula. It is located within the Captain Cook State Recreation Area. The prevailing winds can sometimes produce whitecaps on the lake, giving it its name. It is also known as ''Three Bay Lake'' because it consists of three nearly separate areas connected by channels. Access to the lake is via the Kenai Spur Highway, about north of Kenai. Facilities include a boat launch, overlook, picnic area, wading/swimming area, and a small, boat-in only campground. |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
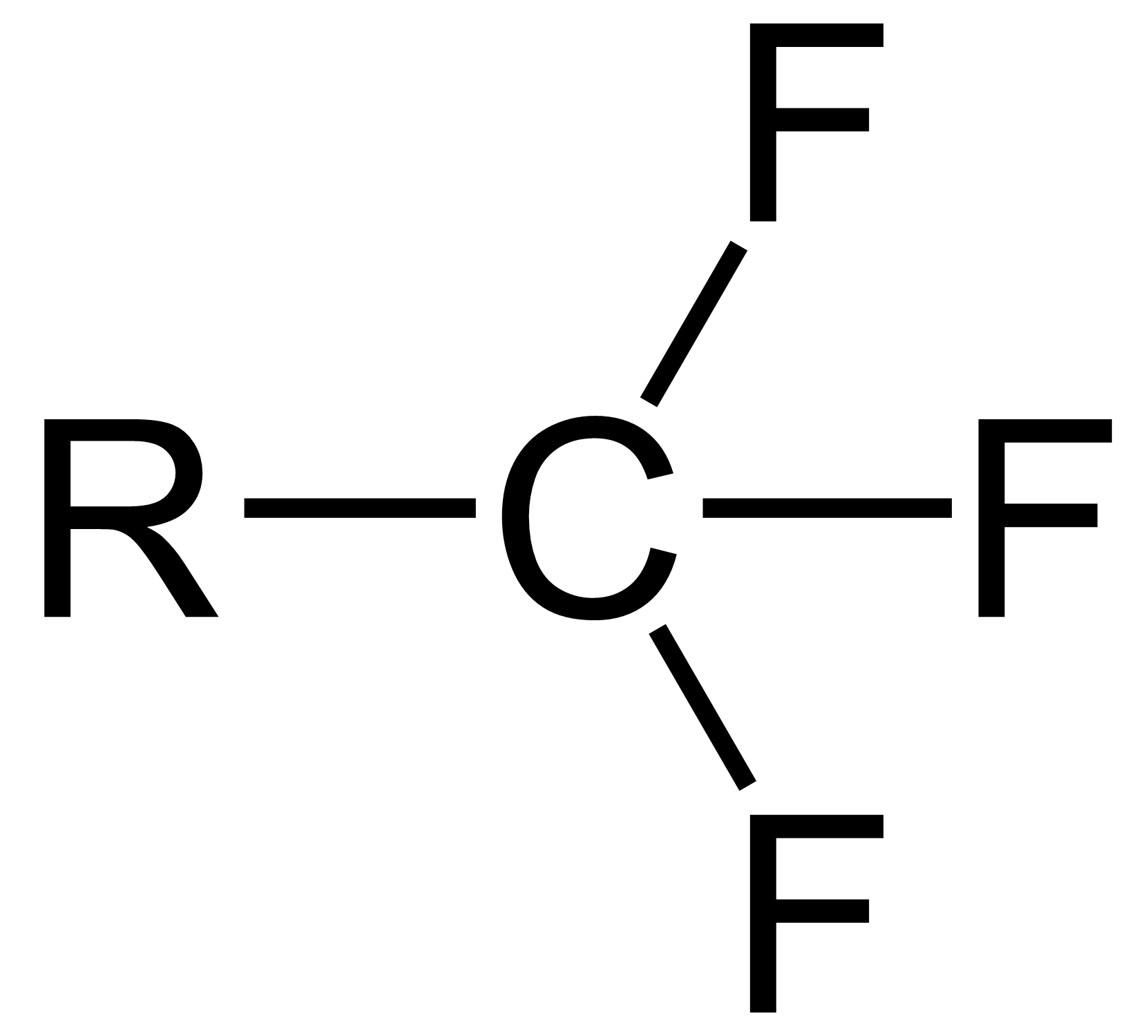
Trifluoromethyl Compounds
The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula -CF3. The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula -CH3), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a fluorine atom. Some common examples are trifluoromethane H–, 1,1,1-trifluoroethane –, and hexafluoroacetone –CO–. Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organofluorines. Properties The trifluoromethyl group has a significant electronegativity that is often described as being intermediate between the electronegativities of fluorine and chlorine. For this reason, trifluoromethyl-substituted compounds are often strong acids, such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and trifluoroacetic acid. Conversely, the trifluoromethyl group lowers the basicity of compounds like trifluoroethanol. Uses The trifluoromethyl group occurs in certain pharmaceuticals, drugs, and abiotically synthesized natural fluorocarbon based compounds. The medicinal use of the trifloromethyl group dates from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicides
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page for EPA reports on pesticide use ihere Selective herbicides control specific weed species, while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides (sometimes called total weedkillers in commercial products) can be used to clear waste ground, industrial and construction sites, railways and railway embankments as they kill all plant material with which they come into contact. Apart from selective/non-selective, other important distinctions include ''persistence'' (also known as ''residual action'': how long the product stays in place and remains active), ''means of uptake'' (whether it is absorbed by above-ground foliage only, through the roots, or by other means), and ''mechanism of action'' (how it works). Historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elodea
''Elodea'' is a genus of 6 species of aquatic plants often called the waterweeds described as a genus in 1803. Classified in the frog’s-bit family (Hydrocharitaceae), ''Elodea'' is native to the Americas and is also widely used as aquarium vegetation and laboratory demonstrations of cellular activities. It lives in fresh water. An older name for this genus is ''Anacharis'', which serves as a common name in North America. The introduction of some species of ''Elodea'' into waterways in parts of Europe, Australia, Africa, Asia, and New Zealand has created a significant problem and it is now considered a noxious weed in these areas. ''Elodea canadensis'', sometimes called American or Canadian water weed or pond weed, is widely known as the generic water weed. The use of these names causes it to be confused with similar-looking plants, like Brazilian elodea (''Egeria densa'') or hydrilla (''Hydrilla verticillata''). American water weed is an attractive aquarium plant and is a good ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscisic Acid
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone. ABA functions in many plant developmental processes, including seed and bud dormancy, the control of organ size and stomatal closure. It is especially important for plants in the response to environmental stresses, including drought, soil salinity, cold tolerance, freezing tolerance, heat stress and heavy metal ion tolerance. In plants Function ABA was originally believed to be involved in abscission, which is how it received its name. This is now known to be the case only in a small number of plants. ABA-mediated signaling also plays an important part in plant responses to environmental stress and plant pathogens. The plant genes for ABA biosynthesis and sequence of the pathway have been elucidated. ABA is also produced by some plant pathogenic fungi via a biosynthetic route different from ABA biosynthesis in plants. In preparation for winter, ABA is produced in terminal buds. This slows plant growth and directs leaf primordia to devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotenoid
Carotenoids (), also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic compound, organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, and Fungus, fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, maize, corn, tomatoes, Domestic Canary, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Carotenoids can be produced from Lipid, fats and other basic organic metabolic building blocks by all these organisms. It is also produced by Endosymbiont, endosymbiotic bacteria in Whitefly, whiteflies. Carotenoids from the diet are stored in the fatty tissues of animals, and exclusively Carnivore, carnivorous animals obtain the compounds from animal fat. In the human diet, Small intestine#Absorption, absorption of carotenoids is improved when consumed with fat in a meal. Cooking carotenoid-containing vegetables in oil and shredding the vegetable both increase carotenoid bioavailability. There are over 1,100 known c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue-green algae, although they are not usually scientifically classified as algae. They appear to have originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Sericytochromatia, the proposed name of the paraphyletic and most basal group, is the ancestor of both the non-photosynthetic group Melainabacteria and the photosynthetic cyanobacteria, also called Oxyphotobacteria. Cyanobacteria use photosynthetic pigments, such as carotenoids, phycobilins, and various forms of chlorophyll, which absorb energy from light. Unlike heterotrophic prokaryotes, cyanobacteria have internal membranes. These are flattened sacs called thylakoids where photosynthesis is performed. Phototrophic eukaryotes such as green plants perform photosynthesis in plast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page for EPA reports on pesticide use ihere Selective herbicides control specific weed species, while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides (sometimes called total weedkillers in commercial products) can be used to clear waste ground, industrial and construction sites, railways and railway embankments as they kill all plant material with which they come into contact. Apart from selective/non-selective, other important distinctions include ''persistence'' (also known as ''residual action'': how long the product stays in place and remains active), ''means of uptake'' (whether it is absorbed by above-ground foliage only, through the roots, or by other means), and ''mechanism of action'' (how it works). Historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
