|
Fanout Of 4
In digital electronics, Fan-out of 4 is a measure of time used in digital CMOS technologies: the gate delay of a component with a fan-out of 4. Fan out = Cload / Cin, where :Cload = total MOS gate capacitance driven by the logic gate under consideration :Cin = the MOS gate capacitance of the logic gate under consideration As a delay metric, one FO4 is the delay of an inverter, driven by an inverter 4x smaller than itself, and driving an inverter 4x larger than itself. Both conditions are necessary since input signal rise/fall time affects the delay as well as output loading. FO4 is generally used as a delay metric because such a load is generally seen in case of tapered buffers driving large loads, and approximately in any logic gate of a logic path sized for minimum delay. Also, for most technologies the optimum fanout for such buffers generally varies from 2.7 to 5.3. A fan out of 4 is the answer to the canonical problem stated as follows: Given a fixed size inverter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals. Digital electronic circuits are usually made from large assemblies of logic gates, often packaged in integrated circuits. Complex devices may have simple electronic representations of Boolean logic functions. History The binary number system was refined by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (published in 1705) and he also established that by using the binary system, the principles of arithmetic and logic could be joined. Digital logic as we know it was the brain-child of George Boole in the mid 19th century. In an 1886 letter, Charles Sanders Peirce described how logical operations could be carried out by electrical switching circuits.Peirce, C. S., "Letter, Peirce to A. Marquand", dated 1886, '' Writings of Charles S. Peirce'', v. 5, 1993, pp. 541–3. GooglPreview See Burks, Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors ( CMOS sensors), data converters, RF circuits ( RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. The CMOS process was originally conceived by Frank Wanlass at Fairchild Semiconductor and presented by Wanlass and Chih-Tang Sah at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference in 1963. Wanlass later filed US patent 3,356,858 for CMOS circuitry and it was granted in 1967. commercialized the technology with the trademar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propagation Delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics. ''Hold time'' is the minimum interval required for the logic level to remain on the input after triggering edge of the clock pulse. Networking In computer networks, propagation delay is the amount of time it takes for the head of the signal to travel from the sender to the receiver. It can be computed as the ratio between the link length and the propagation speed over the specific medium. Propagation delay is equal to ''d / s'' where ''d'' is the distance and ''s'' is the wave propagation speed. In wireless communication, ''s''=''c'', i.e. the speed of light. In copper wire, the speed ''s'' generally ranges from .59c to .77c. This delay is the major obstacle in the development of high-speed computers and is called the interconnect bottleneck in IC systems. Electronics In electronics, digital circuits and digital electronics, the propaga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan-out
In digital electronics, the fan-out is the number of gate inputs driven by the output of another single logic gate. In most designs, logic gates are connected to form more complex circuits. While no logic gate input can be fed by more than one output at a time without causing contention, it is common for one output to be connected to several inputs. The technology used to implement logic gates usually allows a certain number of gate inputs to be wired directly together without additional interfacing circuitry. The maximum fan-out of an output measures its load-driving capability: it is the greatest number of inputs of gates of the same type to which the output can be safely connected. Logical practice Maximum limits on fan-out are usually stated for a given logic family or device in the manufacturer's datasheets. These limits assume that the driven devices are members of the same family. More complex analysis than fan-in and fan-out is required when two different logic fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
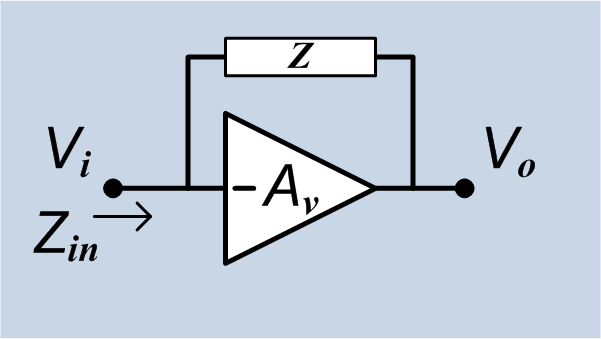
Gate Capacitance
Gate capacitance is the capacitance of the gate terminal of a field-effect transistor. It can be expressed as the absolute capacitance of the gate of a transistor, or as the capacitance per unit area of an integrated circuit technology, or as the capacitance per unit width of minimum-length transistors in a technology. In generations of approximately Dennard scaling of MOSFETs, the capacitance per unit area has increased inversely with device dimensions. Since the gate area has gone down by the square of device dimensions, the gate capacitance of a transistor has gone down in direct proportion with device dimensions. With Dennard scaling, the capacitance per unit of gate width has remained approximately constant; this measurement can include gate–source and gate–drain overlap capacitances. Other scalings are not uncommon; the voltages and gate oxide thicknesses have not always decreased as rapidly as device dimensions, so the gate capacitance per unit area has not increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverter (logic Gate)
In digital logic, an inverter or NOT gate is a logic gate which implements logical negation. It outputs a bit opposite of the bit that is put into it. The bits are typically implemented as two differing voltage levels. Description The NOT gate outputs a zero when given a one, and a one when given a zero. Hence, it inverts its inputs. Colloquially, this inversion of bits is called "flipping" bits. As with all binary logic gates, other pairs of symbols such as true and false, or high and low may be used in lieu of one and zero. It is equivalent to the logical negation operator (¬) in mathematical logic. Because it has only one input, it is a unary operation and has the simplest type of truth table. It is also called the complement gate because it produces the ones' complement of a binary number, swapping 0s and 1s. The NOT gate is one of three basic logic gates from which any Boolean circuit may be built up. Together with the AND gate and the OR gate, any function in bin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Capacitance
Parasitic capacitance is an unavoidable and usually unwanted capacitance that exists between the parts of an electronic component or circuit simply because of their proximity to each other. When two electrical conductors at different voltages are close together, the electric field between them causes electric charge to be stored on them; this effect is capacitance. All practical circuit elements such as inductors, diodes, and transistors have internal capacitance, which can cause their behavior to depart from that of ideal circuit elements. Additionally, there is always non-zero capacitance between any two conductors; this can be significant with closely spaced conductors, such as wires or printed circuit board traces. The parasitic capacitance between the turns of an inductor or other wound component is often described as ''self-capacitance''. However, in electromagnetics, the term self-capacitance more correctly refers to a different phenomenon: the capacitance of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Constant
In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek letter (tau), is the parameter characterizing the response to a step input of a first-order, linear time-invariant (LTI) system.Concretely, a first-order LTI system is a system that can be modeled by a single first order differential equation in time. Examples include the simplest single-stage electrical RC circuits and RL circuits. The time constant is the main characteristic unit of a first-order LTI system. In the time domain, the usual choice to explore the time response is through the step response to a step input, or the impulse response to a Dirac delta function input. In the frequency domain (for example, looking at the Fourier transform of the step response, or using an input that is a simple sinusoidal function of time) the time constant also determines the bandwidth of a first-order time-invariant system, that is, the frequency at which the output signal power drops to half the value it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POWER6
The POWER6 is a microprocessor developed by IBM that implemented the Power ISA v.2.03. When it became available in systems in 2007, it succeeded the POWER5+ as IBM's flagship Power microprocessor. It is claimed to be part of the eCLipz project, said to have a goal of converging IBM's server hardware where practical (hence "ipz" in the acronym: iSeries, pSeries, and zSeries). History POWER6 was described at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) in February 2006, and additional details were added at the Microprocessor Forum in October 2006 and at the next ISSCC in February 2007. It was formally announced on May 21, 2007. It was released on June 8, 2007 at speeds of 3.5, 4.2 and 4.7 GHz, but the company has noted prototypes have reached 6 GHz. POWER6 reached first silicon in the middle of 2005, and was bumped to 5.0 GHz in May 2008 with the introduction of the P595. Description The POWER6 is a dual-core processor. Each core is capable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 is a series of single-core CPUs for desktops, laptops and entry-level servers manufactured by Intel. The processors were shipped from November 20, 2000 until August 8, 2008. The production of Netburst processors was active from 2000 until May 21, 2010. All Pentium 4 CPUs are based on the NetBurst microarchitecture. The Pentium 4 '' Willamette'' (180 nm) introduced SSE2, while the '' Prescott'' (90 nm) introduced SSE3. Later versions introduced Hyper-Threading Technology (HTT). The first Pentium 4-branded processor to implement 64-bit was the ''Prescott'' (90 nm) (February 2004), but this feature was not enabled. Intel subsequently began selling 64-bit Pentium 4s using the ''"E0" revision'' of the Prescotts, being sold on the OEM market as the Pentium 4, model F. The E0 revision also adds eXecute Disable (XD) (Intel's name for the NX bit) to Intel 64. Intel's official launch of Intel 64 (under the name EM64T at that time) in mainstream de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Effort
The method of logical effort, a term coined by Ivan Sutherland and Bob Sproull in 1991, is a straightforward technique used to estimate delay in a CMOS circuit. Used properly, it can aid in selection of gates for a given function (including the number of stages necessary) and sizing gates to achieve the minimum delay possible for a circuit. Derivation of delay in a logic gate Delay is expressed in terms of a basic delay unit, ''τ'' = ''3RC'', the delay of an inverter driving an identical inverter without any additional capacitance added by interconnects or other loads; the unitless number associated with this is known as the normalized delay. (Some authors prefer define the basic delay unit as the fanout of 4 delay—the delay of one inverter driving 4 identical inverters). The absolute delay is then simply defined as the product of the normalized delay of the gate, ''d'', and ''τ'': :d_ = d \cdot \tau In a typical 600-nm process ''τ'' is about 50 ps. For a 250-nm process, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan-in
Fan-in is the number of inputs a logic gate can handle. For instance the fan-in for the AND gate shown in the figure is 3. Physical logic gates with a large fan-in tend to be slower than those with a small fan-in. This is because the complexity of the input circuitry increases the input capacitance Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized a ... of the device. Using logic gates with higher fan-in will help in reducing the depth of a logic circuit; this is because circuit design is realized by the target logic family at a digital level, meaning any large fan-in logic gates are simply the smaller fan-in gates chained together in series at a given depth to widen the circuit instead. Fan-in tree of a node refers to a collection of signals that contribute to the input signal of that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |