|
Fan-out
In digital electronics, the fan-out is the number of gate inputs driven by the output of another single logic gate. In most designs, logic gates are connected to form more complex circuits. While no logic gate input can be fed by more than one output at a time without causing contention, it is common for one output to be connected to several inputs. The technology used to implement logic gates usually allows a certain number of gate inputs to be wired directly together without additional interfacing circuitry. The maximum fan-out of an output measures its load-driving capability: it is the greatest number of inputs of gates of the same type to which the output can be safely connected. Logical practice Maximum limits on fan-out are usually stated for a given logic family or device in the manufacturer's datasheets. These limits assume that the driven devices are members of the same family. More complex analysis than fan-in and fan-out is required when two different logic fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals. Digital electronic circuits are usually made from large assemblies of logic gates, often packaged in integrated circuits. Complex devices may have simple electronic representations of Boolean logic functions. History The binary number system was refined by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (published in 1705) and he also established that by using the binary system, the principles of arithmetic and logic could be joined. Digital logic as we know it was the brain-child of George Boole in the mid 19th century. In an 1886 letter, Charles Sanders Peirce described how logical operations could be carried out by electrical switching circuits.Peirce, C. S., "Letter, Peirce to A. Marquand", dated 1886, '' Writings of Charles S. Peirce'', v. 5, 1993, pp. 541–3. GooglPreview See Burks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
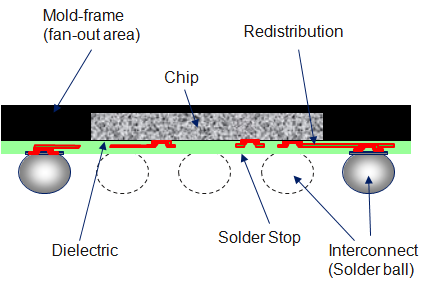
Fan-out Wafer-level Packaging
Fan-out wafer-level packaging (also known as wafer-level fan-out packaging, fan-out WLP, FOWL packaging, FO-WLP, FOWLP, etc.) is an integrated circuit packaging technology, and an enhancement of standard wafer-level packaging (WLP) solutions. In conventional technologies, a wafer is diced first, and then individual dies are packaged; package size is usually considerably larger than the die size. By contrast, in standard WLP flows integrated circuits are packaged while still part of the wafer, and the wafer (with outer layers of packaging already attached) is diced afterwards; the resulting package is practically of the same size as the die itself. However, the advantage of having a small package comes with a downside of limiting the number of external contacts that can be accommodated in the limited package footprint; this may become a significant limitation when complex semiconductor devices requiring a large number of contacts are considered. Fan-out WLP was developed to relax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan-in
Fan-in is the number of inputs a logic gate can handle. For instance the fan-in for the AND gate shown in the figure is 3. Physical logic gates with a large fan-in tend to be slower than those with a small fan-in. This is because the complexity of the input circuitry increases the input capacitance of the device. Using logic gates with higher fan-in will help in reducing the depth of a logic circuit; this is because circuit design is realized by the target logic family at a digital level, meaning any large fan-in logic gates are simply the smaller fan-in gates chained together in series at a given depth to widen the circuit instead. Fan-in tree of a node refers to a collection of signals that contribute to the input signal of that node. In quantum logic gates the fan-in always has to be equal to the number of outputs, the Fan-out. Gates for which the numbers of inputs and outputs differ would not be reversible (unitary) and are therefore not allowed. See also * Fan-out In d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconvergent Fan-out
Reconvergent fan-out is a technique to make VLSI logic simulation less pessimistic. Static timing analysis tries to figure out the best and worst case time estimate for each signal as they pass through an electronic device. Whenever a signal passes through a node, a bit of uncertainty must be added to the time required for the signal to transit that device. These uncertain delays add up so, after passing through many devices, the worst-case timing for a signal could be unreasonably pessimistic. It is common for two signals to share an identical path, branch and follow different paths for a while, then converge back to the same point to produce a result. When this happens, you can remove a fair amount of uncertainty from the total delay because you know that they shared a common path for a while. Even though each signal has an uncertain delay, because their delays were identical for part of the journey the total uncertainty can be reduced. This tightens up the worst-case estimat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Design (electronics)
In integrated circuit design, physical design is a step in the standard design cycle which follows after the circuit design. At this step, circuit representations of the components (devices and interconnects) of the design are converted into geometric representations of shapes which, when manufactured in the corresponding layers of materials, will ensure the required functioning of the components. This geometric representation is called integrated circuit layout. This step is usually split into several sub-steps, which include both design and verification and validation of the layout. Modern day Integrated Circuit (IC) design is split up into ''Front-end Design using HDLs'' and ''Back-end Design'' or ''Physical Design''. The inputs to physical design are (i) a netlist, (ii) library information on the basic devices in the design, and (iii) a technology file containing the manufacturing constraints. Physical design is usually concluded by ''Layout Post Processing'', in which amendmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input Output Buffer Information Specification
Input/output Buffer Information Specification (IBIS) is a specification of a method for integrated circuit vendors to provide information about the input/output buffers of their product to their prospective customers without revealing the intellectual property of their implementation and without requiring proprietary encryption keys. From version 5.0, specification contains two separate types of models, "traditional IBIS" and "IBIS-AMI." The traditional model is generated in text format and consists of a number of tables that captures current vs. voltage (IV) and voltage vs. time (Vt) characteristics of the buffer, as well as the values of certain parasitic components. It is a standard data exchange format for exchanging modeling information among semiconductor device suppliers, simulation software suppliers, and end users. Traditional IBIS models are generally used instead of SPICE models to perform various board level signal integrity (SI) simulations and timing analyses. IBIS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radix Economy
The radix economy of a number in a particular base (or radix) is the number of digits needed to express it in that base, multiplied by the base (the number of possible values each digit could have). This is one of various proposals that have been made to quantify the relative costs of using different radices in representing numbers, especially in computer systems. Radix economy also has implications for organizational structure, networking, and other fields. Definition The radix economy ''E''(''b'',''N'') for any particular number ''N'' in a given base ''b'' is defined as : E(b,N) = b \lfloor \log_b (N) +1 \rfloor \, where we use the floor function \lfloor \rfloor and the base-b logarithm \log_. If both ''b'' and ''N'' are positive integers, then the radix economy E(b,N) is equal to the number of digits needed to express the number ''N'' in base ''b'', multiplied by base ''b''. The radix economy thus measures the cost of storing or processing the number ''N'' in base ''b'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero Flag
The zero flag is a single bit flag that is a central feature on most conventional CPU architectures (including x86, ARM, PDP-11, 68000, 6502, and numerous others). It is often stored in a dedicated register, typically called status register or flag register, along with other flags. The zero flag is typically abbreviated Z or ZF or similar in most documentation and assembly languages. Along with a carry flag, a sign flag and an overflow flag, the zero flag is used to check the result of an arithmetic operation, including bitwise logical instructions. It is set to 1, or true, if an arithmetic result is zero, and reset otherwise. This includes results which are not stored, as most traditional instruction sets implement the compare instruction as a subtract where the result is discarded. It is also common that processors have a bitwise AND-instruction that does not store the result. The logical formula of the zero flag for a twos-complement binary operand is NOT(OR(all bits of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Closure
Design Closure is a part of the digital electronic design automation workflow by which an integrated circuit (i.e. VLSI) design is modified from its initial description to meet a growing list of design constraints and objectives. Every step in the IC design (such as static timing analysis, placement, routing, and so on) is already complex and often forms its own field of study. This article, however, looks at the overall design closure process, which takes a chip from its initial design state to the final form in which all of its design constraints are met. Introduction Every chip starts off as someone’s idea of a good thing: "If we can make a part that performs function X, we will all be rich!" Once the concept is established, someone from marketing says "To make this chip profitably, it must cost $C and run at frequency F." Someone from manufacturing says "To meet this chip’s targets, it must have a yield of Y%." Someone from packaging says “It must fit in the P pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Integrity
Signal integrity or SI is a set of measures of the quality of an electrical signal. In digital electronics, a stream of binary values is represented by a voltage (or current) waveform. However, digital signals are fundamentally analog in nature, and all signals are subject to effects such as noise, distortion, and loss. Over short distances and at low bit rates, a simple conductor can transmit this with sufficient fidelity. At high bit rates and over longer distances or through various mediums, various effects can degrade the electrical signal to the point where errors occur and the system or device fails. Signal integrity engineering is the task of analyzing and mitigating these effects. It is an important activity at all levels of electronics packaging and assembly, from internal connections of an integrated circuit (IC), A survey of the field of electronic design automation. Portions of IC section of this article were derived (with permission) from Vol II, Chapter 21, ''Noise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Tree
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') oscillates between a high and a low state and is used like a metronome to coordinate actions of digital circuits. A clock signal is produced by a clock generator. Although more complex arrangements are used, the most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle, usually with a fixed, constant frequency. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of sufficient complexity use a clock signal in order to synchronize different parts of the circuit, cycling at a rate slower than the worst-case internal propagation delays. In some cases, more than one clock cycle is required to perform a predictable action. As ICs become more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input Impedance
The input impedance of an electrical network is the measure of the opposition to current ( impedance), both static ( resistance) and dynamic ( reactance), into the load network that is ''external'' to the electrical source. The input admittance (the reciprocal of impedance) is a measure of the load's propensity to draw current. The source network is the portion of the network that transmits power, and the load network is the portion of the network that consumes power. Input impedance If the load network were replaced by a device with an output impedance equal to the input impedance of the load network (equivalent circuit), the characteristics of the source-load network would be the same from the perspective of the connection point. So, the voltage across and the current through the input terminals would be identical to the chosen load network. Therefore, the input impedance of the load and the output impedance of the source determine how the source current and voltage change. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |