|
Facultative Heterochromatin
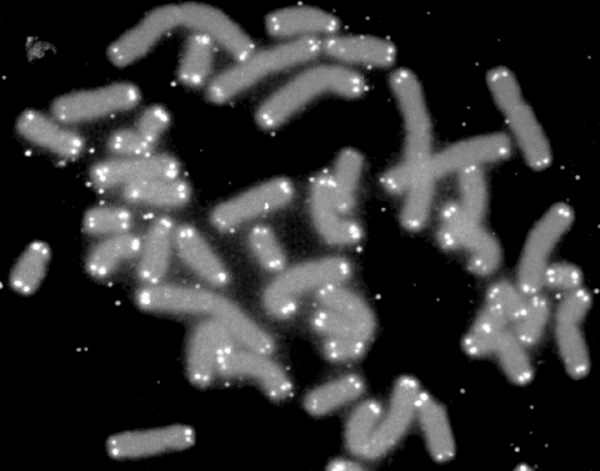
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or '' condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continue between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a role in the expression of genes. Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; however, according to Volpe et al. (2002), and many other papers since, much of this DNA is in fact transcribed, but it is continuously turned over via RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS). Recent studies with electron microscopy and OsO4 staining reveal that the dense packing is not due to the chromatin. Constitutive heterochromatin can affect the genes near itself (e.g. position-effect variegation). It is usually repetitive and forms structural functions such as centromeres or telomeres, in addition to acting as an attractor for other gene-expression or repression signals. Facultative heter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Condensation
DNA condensation refers to the process of compacting DNA molecules ''in vitro'' or ''in vivo''. Mechanistic details of DNA packing are essential for its functioning in the process of gene regulation in living systems. Condensed DNA often has surprising properties, which one would not predict from classical concepts of dilute solutions. Therefore, DNA condensation ''in vitro'' serves as a model system for many processes of physics, biochemistry and biology. In addition, DNA condensation has many potential applications in medicine and biotechnology. DNA diameter is about 2 nm, while the length of a stretched single molecule may be up to several dozens of centimetres depending on the organism. Many features of the DNA double helix contribute to its large stiffness, including the mechanical properties of the sugar-phosphate backbone, electrostatic repulsion between phosphates (DNA bears on average one elementary negative charge per each 0.17 nm of the double helix), stackin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H3K9me3
H3K9me3 is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein Histone H3. It is a mark that indicates the tri-methylation at the 9th lysine residue of the histone H3 protein and is often associated with heterochromatin. Nomenclature H3K9me3 indicates trimethylation of lysine 9 on histone H3 protein subunit: Lysine Methylation This diagram shows the progressive methylation of a lysine residue. The tri-methylation denotes the methylation present in H3K9me3 . Understanding histone modifications The genomic DNA of eukaryotic cells is wrapped around special protein molecules known as Histones. The complexes formed by the looping of the DNA are known as chromatin. The basic structural unit of chromatin is the nucleosome: this consists of the core octamer of histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) as well as a linker histone and about 180 base pairs of DNA. These core histones are rich in lysine and arginine residues. The carboxyl (C) terminal end of these histones contribute to hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barr Body
A Barr body (named after discoverer Murray Barr) or X-chromatin is an inactive X chromosome in a cell with more than one X chromosome, rendered inactive in a process called lyonization, in species with XY sex-determination (including humans). The Lyon hypothesis states that in cells with multiple X chromosomes, all but one are inactivated during mammalian embryogenesis. This happens early in embryonic development at random in mammals,Brown, C.J., Robinson, W.P., (1997), XIST Expression and X-Chromosome Inactivation in Human Preimplantation Embryos ''Am. J. Hum. Genet.'' 61, 5–8Full Text PDF except in marsupials and in some extra-embryonic tissues of some placental mammals, in which the X chromosome from the sperm is always deactivated. In humans with euploidy, a genotypical female (46, XX karyotype) has one Barr body per somatic cell nucleus, while a genotypical male (46, XY) has none. The Barr body can be seen in the interphase nucleus as a darkly staining small mass in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery In the early 1970s, Soviet theorist Alexei Olovnikov first recognized that chromosomes could not completely replicate their ends; this is known as the "end replication problem". Building on this, and accommodating Leonard Hayflick's idea of limited somatic cell division, Olovnikov suggested that DNA sequences are lost every time a cell replicates until the loss reaches a critical level, at which point cell division end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to the centromere via the kinetochore. The physical role of the centromere is to act as the site of assembly of the kinetochores – a highly complex multiprotein structure that is responsible for the actual events of chromosome segregation – i.e. binding microtubules and signaling to the cell cycle machinery when all chromosomes have adopted correct attachments to the spindle, so that it is safe for cell division to proceed to completion and for cells to enter anaphase. There are, broadly speaking, two types of centromeres. "Point centromeres" bind to specific proteins that recognize particular DNA sequences with high efficiency. Any piece of DNA with the point centromere DNA sequence on it will typically form a centromere if pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite DNA
Satellite DNA consists of very large arrays of tandemly repeating, non-coding DNA. Satellite DNA is the main component of functional centromeres, and form the main structural constituent of heterochromatin. The name "satellite DNA" refers to the phenomenon that repetitions of a short DNA sequence tend to produce a different frequency of the bases adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine, and thus have a different density from bulk DNA such that they form a second or "satellite" band(s) when genomic DNA is separated along a cesium chloride density gradient using buoyant density centrifugation. Sequences with a greater ratio of A+T display a lower density while those with a greater ratio of G+C display a higher density than the bulk of genomic DNA. Some repetitive sequences are ~50% G+C/A+T and thus have buoyant densities the same as bulk genomic DNA. These satellites are called "cryptic" satellites because they form a band hidden within the main band of genomic DNA. "Isopycnic" is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in addition to" the traditional genetic basis for inheritance. Epigenetics most often involves changes that affect the regulation of gene expression, but the term can also be used to describe any heritable phenotypic change. Such effects on cellular and physiological phenotypic traits may result from external or environmental factors, or be part of normal development. The term also refers to the mechanism of changes: functionally relevant alterations to the genome that do not involve mutation of the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Gene expression can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Opinion In Genetics & Development
''Current Opinion'' is a collection of review journals on various disciplines of the life sciences. They were acquired by Elsevier in 1997. Each issue of each journal, which all are published bimonthly, contains one or more themed sections edited by scientists who specialise in the field and invite authors to contribute reviews aimed at experts and non-specialists. Each journal aims to cover all the major recent advances in its topic area, and to direct readers to the most important original research. Journals See also * Current Opinion (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins) ''Current Opinion'' is a series of medical journals published by Wolters Kluwer imprint Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Wolters Kluwer acquired the journals from the Thomson Organisation International Thomson Organization (ITO) was a holding comp ... References External links * {{Reed Elsevier Elsevier imprints Elsevier academic journals Publishing companies established in 1990 Review journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
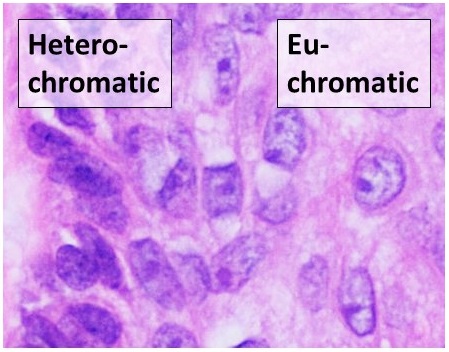
Euchromatin
Euchromatin (also called "open chromatin") is a lightly packed form of chromatin ( DNA, RNA, and protein) that is enriched in genes, and is often (but not always) under active transcription. Euchromatin stands in contrast to heterochromatin, which is tightly packed and less accessible for transcription. 92% of the human genome is euchromatic. In eukaryotes, euchromatin comprises the most active portion of the genome within the cell nucleus. In prokaryotes, euchromatin is the ''only'' form of chromatin present; this indicates that the heterochromatin structure evolved later along with the nucleus, possibly as a mechanism to handle increasing genome size. Structure Euchromatin is composed of repeating subunits known as nucleosomes, reminiscent of an unfolded set of beads on a string, that are approximately 11 nm in diameter. At the core of these nucleosomes are a set of four histone protein pairs: H3, H4, H2A, and H2B. Each core histone protein possesses a 'tail' str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30-nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biology, 58,'' 95–104. https://doi.o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterochromatin Vs
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or ''DNA_condensation, condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continue between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a role in the gene expression, expression of genes. Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; however, according to Volpe et al. (2002), and many other papers since, much of this DNA is in fact transcribed, but it is continuously Messenger RNA#Eukaryotic mRNA turnover, turned over via RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS). Recent studies with Electron microscope, electron microscopy and osmium tetroxide, OsO4 staining reveal that the dense packing is not due to the chromatin. Constitutive heterochromatin can affect the genes near itself (e.g. position-effect variegation). It is usually Repeated sequence (DNA), repetitive and forms structural functions such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |