|
Forced-induction
In an internal combustion engine, forced induction is where turbocharging or supercharging is used to increase the density of the intake air. Engines without forced induction are classified as naturally aspirated. Operating principle Overview Forced induction is often used to increase the power output of an engine. This is achieved by compressing the intake air, to increase the mass of the air-fuel mixture present within the combustion chamber. A naturally aspirated engine is limited to a maximum intake air pressure equal to its surrounding atmosphere; however a forced induction engine produces "boost", whereby the air pressure is higher than the surrounding atmosphere. Since the density of air increases with pressure, this allows a greater mass of air to enter the combustion chamber. Theoretically, the vapour power cycle analysis of the second law of thermodynamics would suggest that increasing the mean effective pressure within the combustion chamber would also increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbo Mini GT (cropped)
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. Turbochargers are distinguished from superchargers in that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases, whereas a is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the inve ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
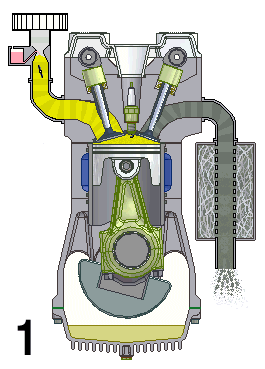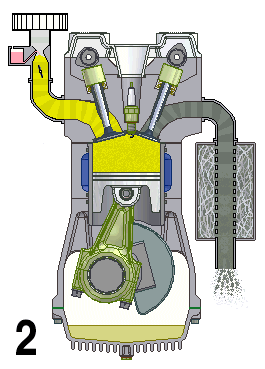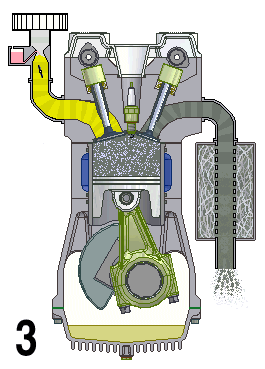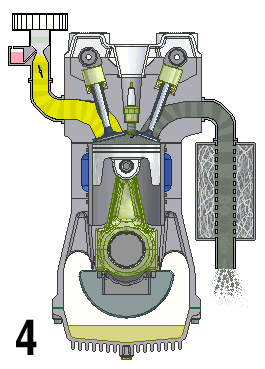
Naturally Aspirated Engine
A naturally aspirated engine, also known as a normally aspirated engine, and abbreviated to N/A or NA, is an internal combustion engine in which air intake depends solely on atmospheric pressure and does not have forced induction through a turbocharger or a supercharger. Description In a naturally aspirated engine, air for combustion ( Diesel cycle in a diesel engine or specific types of Otto cycle in petrol engines, namely petrol direct injection) or an air/fuel mixture (traditional Otto cycle petrol engines), is drawn into the engine's cylinders by atmospheric pressure acting against a partial vacuum that occurs as the piston travels downwards toward bottom dead centre during the intake stroke. Owing to innate restriction in the engine's inlet tract, which includes the intake manifold, a small pressure drop occurs as air is drawn in, resulting in a volumetric efficiency of less than 100 percent—and a less than complete air charge in the cylinder. The density of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines. Internal combustion engines Most commonly used with turbocharged engines, an intercooler is used to counteract the heat of compression and heat soak in the pressurised intake air. By reducing the temperature of the intake air, the air becomes denser (allowing more fuel to be injected, resulting in increased power) and less likely to suffer from pre-ignition or knocking. Additional cooling can be provided by externally spraying a fine mist onto the intercooler surface, or even into the intake air itself, to further reduce intake charge temperature through evaporative cooling. Intercoolers can vary dramatically in size, shape and design, depending on the performance and space requirements of the system. Many passenger cars use either front-mounted intercoolers locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
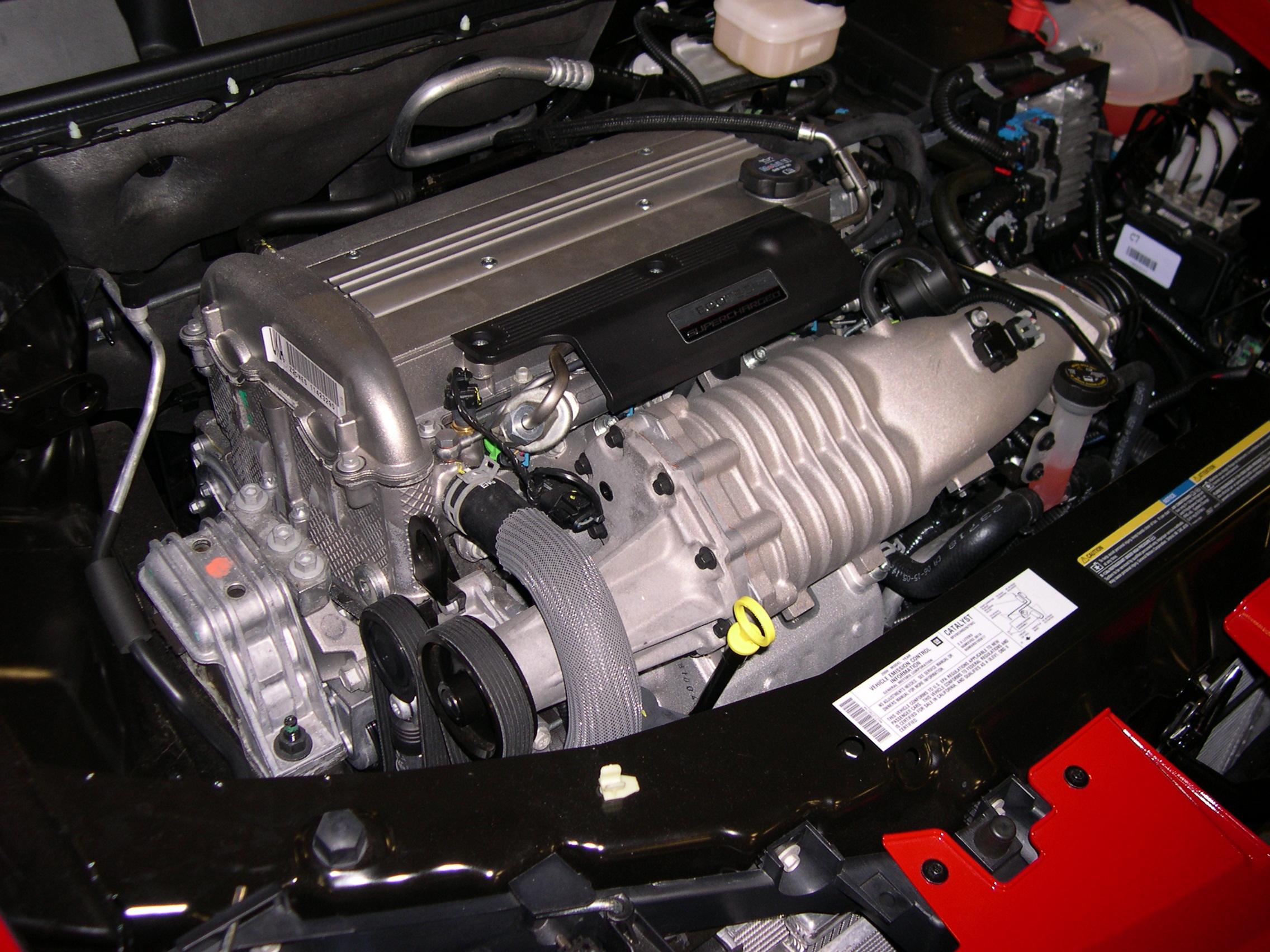
Supercharger Mustang
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. It is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and increase power outputs, especially with reduced engine displacements. Design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superchargers
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. It is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and increase power outputs, especially with reduced engine displacements. Design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement (engine), displacement. It is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and increase power outputs, especially with reduced engine dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. Turbochargers are distinguished from superchargers in that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases, whereas a is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the inv ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
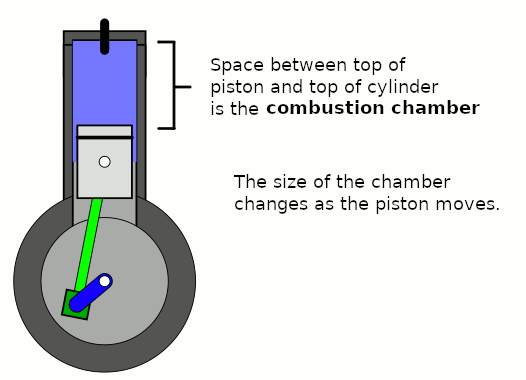
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the air–fuel ratio, fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the Firebox (steam engine), firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol engine, petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696 psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Efficiency
In thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency (\eta_) is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc. For a heat engine, thermal efficiency is the ratio of the net work output to the heat input; in the case of a heat pump, thermal efficiency (known as the '' coefficient of performance'' or COP) is the ratio of net heat output (for heating), or the net heat removed (for cooling) to the energy input (external work). The efficiency of a heat engine is fractional as the output is always less than the input while the COP of a heat pump is more than 1. These values are further restricted by the Carnot theorem. Overview In general, energy conversion efficiency is the ratio between the useful output of a device and the input, in energy terms. For thermal efficiency, the input, Q_, to the device is heat, or the heat-content of a fuel that is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Knock
In Spark-ignition engine, spark-ignition internal combustion engines, knocking (also knock, detonation, spark knock, pinging or pinking) occurs when combustion of some of the air-fuel ratio, air/fuel mixture in the cylinder does not result from propagation of the flame front ignited by the spark plug, but when one or more pockets of air/fuel mixture explode outside the envelope of the normal combustion front. The fuel–air charge is meant to be ignited by the spark plug only, and at a precise point in the piston's stroke. Knock occurs when the peak of the combustion process no longer occurs at the optimum moment for the four-stroke cycle. The shock wave creates the characteristic metallic "pinging" sound, and cylinder pressure increases dramatically. Effects of engine knocking range from inconsequential to completely destructive. Knocking should not be confused with pre-ignition—they are two separate events. However, pre-ignition can be followed by knocking. The phenomenon of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Engine
The diesel engine, named after the German engineer Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which Combustion, ignition of diesel fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to Mechanics, mechanical Compression (physics), compression; thus, the diesel engine is called a compression-ignition engine (CI engine). This contrasts with engines using spark plug-ignition of the air-fuel mixture, such as a petrol engine (gasoline engine) or a gas engine (using a gaseous fuel like natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas). Introduction Diesel engines work by compressing only air, or air combined with residual combustion gases from the exhaust (known as exhaust gas recirculation, "EGR"). Air is inducted into the chamber during the intake stroke, and compressed during the compression stroke. This increases air temperature inside the Cylinder (engine), cylinder so that atomised diesel fuel injected into the combustion chamber ignites. The torque a dies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |