intercooler on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An intercooler is a
An intercooler is a

 Most commonly used with
Most commonly used with

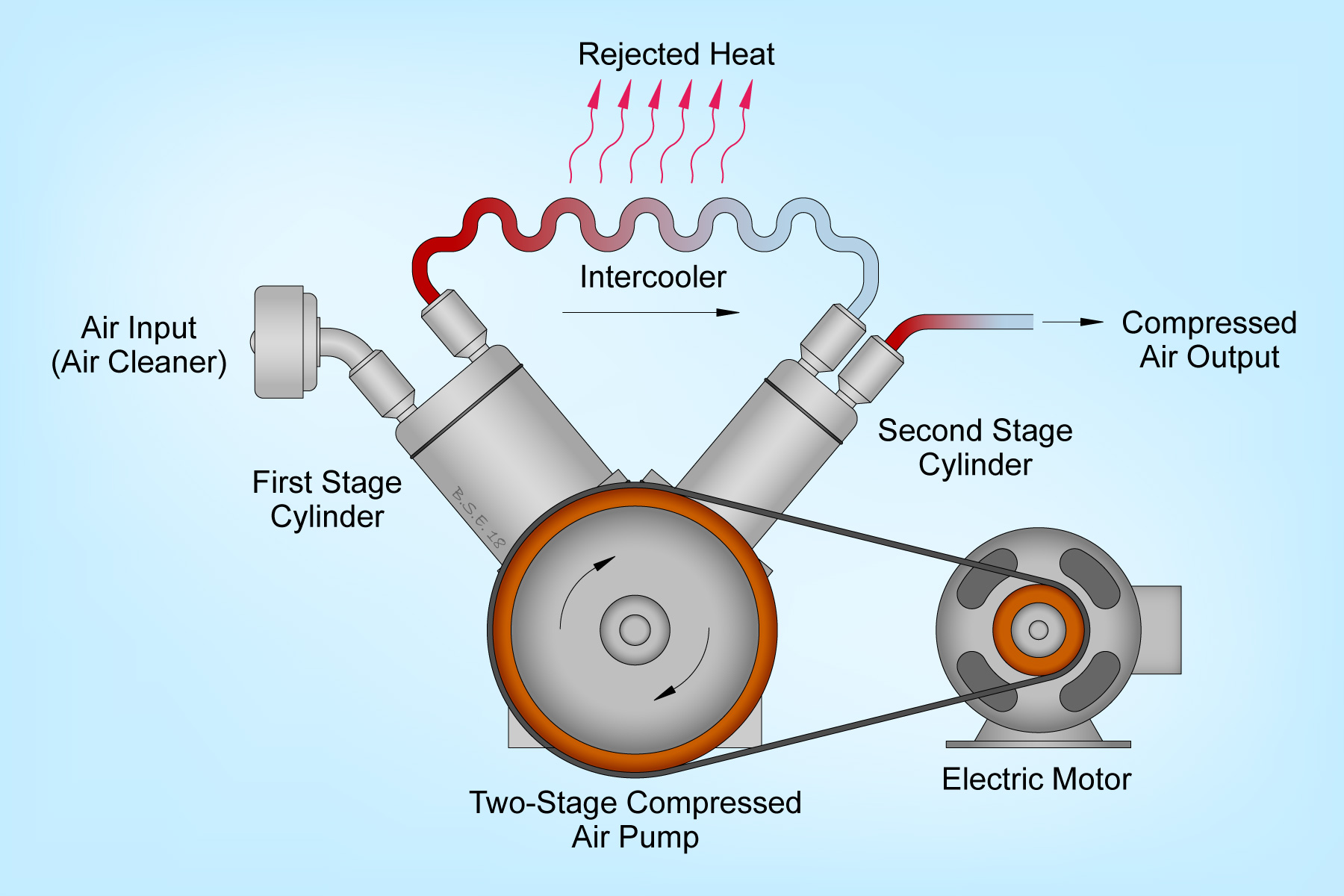 Intercoolers are used to remove the waste heat from the first stage of two-stage air compressors. Two-stage air compressors are manufactured because of their inherent efficiency. The cooling action of the intercooler is principally responsible for this higher efficiency, bringing it closer to Carnot efficiency. Removing the heat-of-compression from the discharge of the first stage has the effect of densifying the air charge. This, in turn, allows the second stage to produce more work from its fixed compression ratio. Adding an intercooler to the setup requires additional investments.
Intercoolers are used to remove the waste heat from the first stage of two-stage air compressors. Two-stage air compressors are manufactured because of their inherent efficiency. The cooling action of the intercooler is principally responsible for this higher efficiency, bringing it closer to Carnot efficiency. Removing the heat-of-compression from the discharge of the first stage has the effect of densifying the air charge. This, in turn, allows the second stage to produce more work from its fixed compression ratio. Adding an intercooler to the setup requires additional investments.
 An intercooler is a
An intercooler is a heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contac ...
used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the ...
engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration
Refrigeration is any of various types of cooling of a space, substance, or system to lower and/or maintain its temperature below the ambient one (while the removed heat is ejected to a place of higher temperature).IIR International Dictionary of ...
and gas turbine
A gas turbine or gas turbine engine is a type of Internal combustion engine#Continuous combustion, continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas gene ...
s.
Internal combustion engines

 Most commonly used with
Most commonly used with turbocharged
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the ...
engines, an intercooler is used to counteract the heat of compression and heat soak in the pressurised intake air. By reducing the temperature of the intake air, the air becomes denser (allowing more fuel to be injected, resulting in increased power) and less likely to suffer from pre-ignition or knocking. Additional cooling can be provided by externally spraying a fine mist onto the intercooler surface, or even into the intake air itself, to further reduce intake charge temperature through evaporative cooling
An evaporative cooler (also known as evaporative air conditioner, swamp cooler, swamp box, desert cooler and wet air cooler) is a device that cools air through the evaporation of water. Evaporative cooling differs from other air conditioning sy ...
.
Intercoolers can vary dramatically in size, shape and design, depending on the performance and space requirements of the system. Many passenger cars use either front-mounted intercoolers located in the front bumper or grill opening, or top-mounted intercoolers located above the engine. An intercooling system can use an air-to-air design, an air-to-liquid design, or a combination of both.
Multiple stages of compression
In automotive engines where multiple stages of forced-induction are used (e.g. a sequential twin-turbo or twin-charged engine), the intercooling usually takes place after the last turbocharger/supercharger. However it is also possible to use separate intercoolers for each stage of the turbocharging/supercharging, such as in the JCB Dieselmax land speed record racing car. Some aircraft engines also use an intercooler for each stage of the forced induction. In engines with two-stage turbocharging, the term ''intercooler'' can specifically refer to the cooler between the two turbochargers and the term ''aftercooler'' is used for the cooler located between the second-stage turbo and the engine. However, the terms ''intercooler'' and ''charge-air cooler'' are also often used regardless of the location in the intake system.Method of heat transfer
Air-to-air intercoolers areheat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contac ...
s that transfer heat from the intake air directly to the atmosphere. Alternatively, air-to-liquid intercoolers transfer the heat from the intake air to intermediate liquid (usually water), which in turn transfers the heat to the atmosphere. The heat exchanger that transfers the heat from the fluid to the atmosphere operates in a similar fashion to the main radiator in a water-cooled engine's cooling system, or in some cases the engine's cooling system is also used for the intercooling system. Air-to-liquid intercoolers are usually heavier than their air-to-air counterparts, due to additional components making up the system (e.g. water circulation pump, radiator, fluid, and plumbing).
The majority of marine engines use air-to-liquid intercoolers, since the water of the lake, river or sea can easily be accessed for cooling purposes. In addition, most marine engines are located in closed compartments where obtaining a good flow of cooling air for an air-to-air unit would be difficult. Marine intercoolers take the form of a tubular heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contac ...
with the air passing around a series of tubes within the cooler casing, and sea water circulating inside the tubes. The main materials used for this kind of application are meant to resist sea water corrosion: Copper-Nickel for the tubes and bronze for the sea water covers.
Alternatives
An alternative to using intercoolers - which is rarely used these days - was to inject excess fuel into the combustion chamber, so that thevaporization
Vaporization (or vapo(u)risation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenome ...
process would cool the cylinders in order to prevent knocking. However the downsides to this method were increased fuel consumption and exhaust gas emissions.
Air compressors

 Intercoolers are used to remove the waste heat from the first stage of two-stage air compressors. Two-stage air compressors are manufactured because of their inherent efficiency. The cooling action of the intercooler is principally responsible for this higher efficiency, bringing it closer to Carnot efficiency. Removing the heat-of-compression from the discharge of the first stage has the effect of densifying the air charge. This, in turn, allows the second stage to produce more work from its fixed compression ratio. Adding an intercooler to the setup requires additional investments.
Intercoolers are used to remove the waste heat from the first stage of two-stage air compressors. Two-stage air compressors are manufactured because of their inherent efficiency. The cooling action of the intercooler is principally responsible for this higher efficiency, bringing it closer to Carnot efficiency. Removing the heat-of-compression from the discharge of the first stage has the effect of densifying the air charge. This, in turn, allows the second stage to produce more work from its fixed compression ratio. Adding an intercooler to the setup requires additional investments.
References
{{Automotive engine, expanded Engine cooling systems Engine technology Turbochargers Engine components Gas technologies Heat exchangers