|
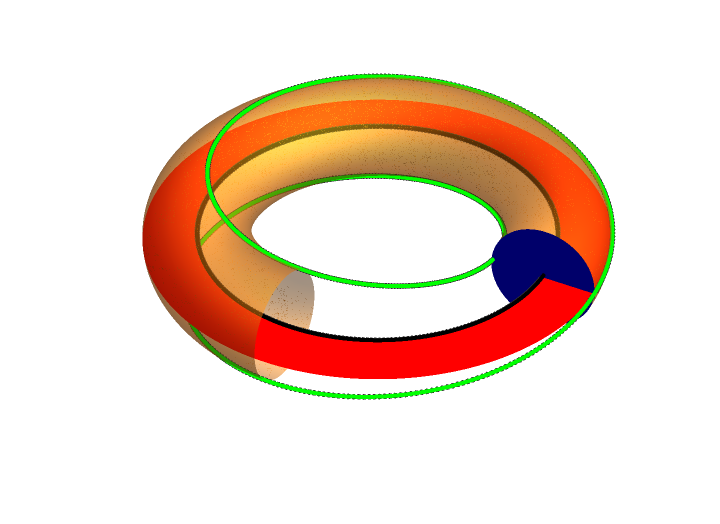
Flux Surface
In magnetic confinement fusion, a flux surface is a surface on which magnetic field lines lie. Since the magnetic field is divergence-free (and magnetic nulls are undesirable), the Poincare-Hopf theorem implies that such a surface must be either a torus, or a knot. In the tokamak and the stellarator flux surfaces have toroidal shapes, whereas the more exotic knotatron has a knotted flux surface. Flux surfaces are typically characterized by the poloidal magnetic flux In physics, specifically electromagnetism, the magnetic flux through a surface is the surface integral of the normal component of the magnetic field B over that surface. It is usually denoted or . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the we ... or the toroidal magnetic flux. The poloidal flux is the magnetic flux passing through a ribbon going from the magnetic axis (the centre of the device) to the flux surface, and the toroidal flux is the magnetic flux passing through a circle which encloses the magnetic axi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Confinement Fusion
Magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma (physics), plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of controlled fusion research, along with inertial confinement fusion. Deuterium–tritium fusion, Fusion reactions for reactors usually combine light Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei of deuterium and tritium to form an alpha particle (helium-4 nucleus) and a neutron, where the energy is released in the form of the kinetic energy of the reaction products. In order to overcome the Coulomb barrier, electrostatic repulsion between the nuclei, the fuel must have a temperature of hundreds of millions of kelvin, at which the fuel is fully Ionization, ionized and becomes a Plasma (physics), plasma. In addition, the plasma must be at a sufficient density, and the energy must remain in the reacting region for a sufficient time, as specified by the Lawson criterion (tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, electric currents, and electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function (mathematics), function assigning a Euclidean vector, vector to each point of space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poincaré–Hopf Theorem
In mathematics, the Poincaré–Hopf theorem (also known as the Poincaré–Hopf index formula, Poincaré–Hopf index theorem, or Hopf index theorem) is an important theorem that is used in differential topology. It is named after Henri Poincaré and Heinz Hopf. The Poincaré–Hopf theorem is often illustrated by the special case of the hairy ball theorem, which simply states that there is no smooth vector field on an even-dimensional n-sphere having no sources or sinks. Formal statement Let M be a differentiable manifold, of dimension n, and v a vector field on M. Suppose that x is an isolated zero of v, and fix some local coordinates near x. Pick a closed ball D centered at x, so that x is the only zero of v in D. Then the index of v at x, \operatorname_x(v), can be defined as the degree of the map u : \partial D \to \mathbb S^ from the boundary of D to the (n-1)-sphere given by u(z)=v(z)/\, v(z)\, . Theorem. Let M be a compact differentiable manifold. Let v be a vecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torus
In geometry, a torus (: tori or toruses) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space one full revolution about an axis that is coplanarity, coplanar with the circle. The main types of toruses include ring toruses, horn toruses, and spindle toruses. A ring torus is sometimes colloquially referred to as a donut or doughnut. If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a ring shape and is called a torus of revolution, also known as a ring torus. If the axis of revolution is tangent to the circle, the surface is a horn torus. If the axis of revolution passes twice through the circle, the surface is a Lemon (geometry), spindle torus (or ''self-crossing torus'' or ''self-intersecting torus''). If the axis of revolution passes through the center of the circle, the surface is a degenerate torus, a double-covered sphere. If the revolved curve is not a circle, the surface is called a ''toroid'', as in a square toroid. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot (mathematics)
In mathematics, a knot is an embedding of the circle () into three-dimensional Euclidean space, (also known as ). Often two knots are considered equivalent if they are ambient isotopic, that is, if there exists a continuous deformation of which takes one knot to the other. A crucial difference between the standard mathematical and conventional notions of a knot is that mathematical knots are closed — there are no ends to tie or untie on a mathematical knot. Physical properties such as friction and thickness also do not apply, although there are mathematical definitions of a knot that take such properties into account. The term ''knot'' is also applied to embeddings of in , especially in the case . The branch of mathematics that studies knots is known as knot theory and has many relations to graph theory. Formal definition A knot is an embedding of the circle () into three-dimensional Euclidean space (), or the 3-sphere (), since the 3-sphere is compact. Two knots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma (physics), plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement fusion, magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor for providing minimally polluting electrical power. The proposal to use controlled thermonuclear fusion for industrial purposes and a specific scheme using thermal insulation of high-temperature plasma by an electric field was first formulated by the Soviet physicist Oleg Lavrentiev in a mid-1950 paper. In 1951, Andrei Sakharov and Igor Tamm modified the scheme by proposing a theoretical basis for a thermonuclear reactor, where the plasma would have the shape of a torus and be held by a magnetic field. The first tokamak was built in the Soviet Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellarator
A stellarator confines Plasma (physics), plasma using external magnets. Scientists aim to use stellarators to generate fusion power. It is one of many types of magnetic confinement fusion devices. The name "stellarator" refers to stars because fusion mostly occurs in stars such as the Sun. It is one of the earliest human-designed fusion power devices. The stellarator was invented by American scientist Lyman Spitzer in 1951. Much of its early development was carried out by Spitzer's team at what became the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL). Spitzer's Model A began operation in 1953 and demonstrated plasma confinement. Larger models followed, but demonstrated poor performance, losing plasma at rates far worse than theoretical predictions. By the early 1960s, hopes of producing a commercial machine faded, and attention turned to studying fundamental theory. By the mid-1960s, Spitzer was convinced that the stellarator was matching the Bohm diffusion rate, which suggested i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Flux
In physics, specifically electromagnetism, the magnetic flux through a surface is the surface integral of the normal component of the magnetic field B over that surface. It is usually denoted or . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber (Wb; in derived units, volt–seconds or V⋅s), and the CGS unit is the maxwell. Magnetic flux is usually measured with a fluxmeter, which contains measuring coils, and it calculates the magnetic flux from the change of voltage on the coils. Description The magnetic interaction is described in terms of a vector field, where each point in space is associated with a vector that determines what force a moving charge would experience at that point (see Lorentz force). Since a vector field is quite difficult to visualize, introductory physics instruction often uses field lines to visualize this field. The magnetic flux, through some surface, in this simplified picture, is proportional to the number of field lines passing through that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Theory
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of Scientific method, scientific study and branch of mathematics. It focuses on underlying patterns and Deterministic system, deterministic Scientific law, laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. These were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state (meaning there is sensitive dependence on initial conditions). A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause or prevent a tornado in Texas. Text was copied from this source, which is avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamiltonian System
A Hamiltonian system is a dynamical system governed by Hamilton's equations. In physics, this dynamical system describes the evolution of a physical system such as a planetary system or an electron in an electromagnetic field. These systems can be studied in both Hamiltonian mechanics and dynamical systems theory. Overview Informally, a Hamiltonian system is a mathematical formalism developed by William Rowan Hamilton, Hamilton to describe the evolution equation, evolution equations of a physical system. The advantage of this description is that it gives important insights into the dynamics, even if the initial value problem cannot be solved analytically. One example is the Three-body problem, planetary movement of three bodies: while there is no closed-form solution to the general problem, Henri Poincaré, Poincaré showed for the first time that it exhibits deterministic chaos. Formally, a Hamiltonian system is a dynamical system characterised by the scalar function H(\bol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |