|
Fluorescent Labelling
In molecular biology and biotechnology, a fluorescent tag, also known as a fluorescent label or fluorescent probe, is a molecule that is attached chemically to aid in the detection of a biomolecule such as a protein, antibody, or amino acid. Generally, fluorescent tagging, or labeling, uses a reactive derivative of a fluorescent molecule known as a fluorophore. The fluorophore selectively binds to a specific region or functional group on the target molecule and can be attached chemically or biologically. Various labeling techniques such as enzymatic labeling, protein labeling, and genetic labeling are widely utilized. Ethidium bromide, fluorescein and green fluorescent protein are common tags. The most commonly labelled molecules are antibodies, proteins, amino acids and peptides which are then used as specific probes for detection of a particular target. History The development of methods to detect and identify biomolecules has been motivated by the ability to improve the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Cerevisiae Septins
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''. History Origin Northwest Semitic šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative (as in 'ip'). It originated most likely as a pictogram of a tooth () and represented the phoneme via the acrophonic principle. Ancient Greek did not have a phoneme, so the derived Greek letter sigma () came to represent the voiceless alveolar sibilant . While the letter shape Σ continues Phoenician ''šîn'', its name ''sigma'' is taken from the letter ''samekh'', while the shape and position of ''samekh'' but name of ''šîn'' is continued in the '' xi''. Within Greek, the name of ''sigma'' was influenced by its association with the Greek word (earlier ) "to hiss". The original name of the letter "sigma" may have been ''san'', but due to the complic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
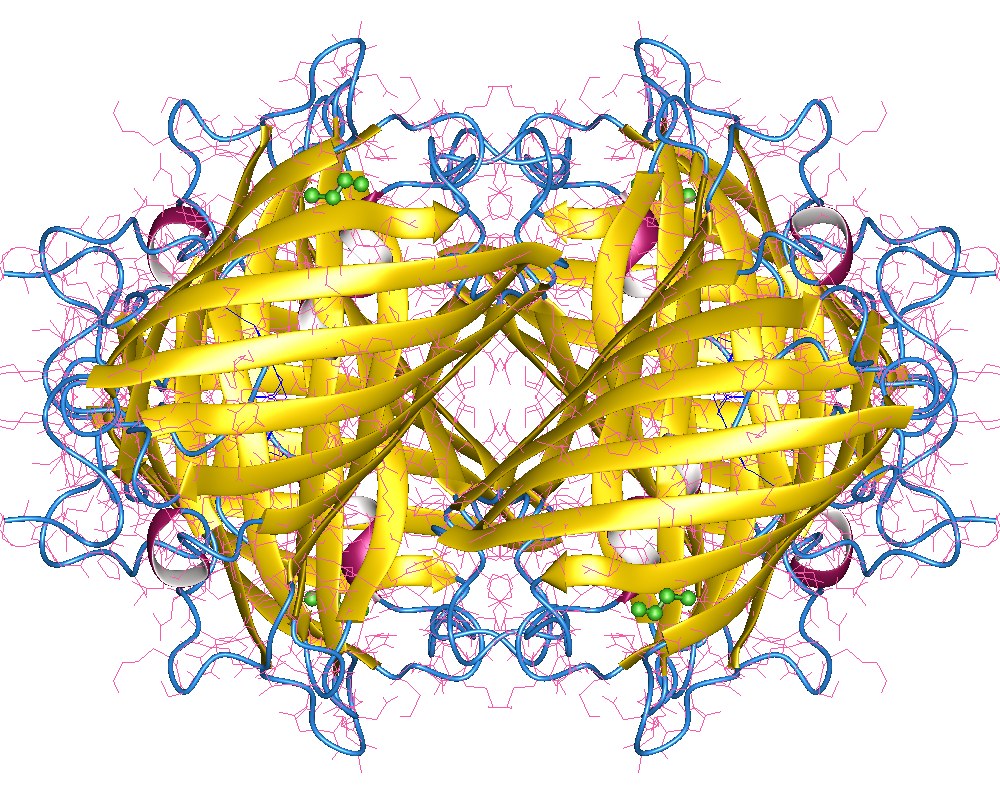
Green Fluorescent Protein
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label ''GFP'' traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish '' Aequorea victoria'' and is sometimes called ''avGFP''. However, GFPs have been found in other organisms including corals, sea anemones, zoanithids, copepods and lancelets. The GFP from ''A. victoria'' has a major excitation peak at a wavelength of 395 nm and a minor one at 475 nm. Its emission peak is at 509 nm, which is in the lower green portion of the visible spectrum. The fluorescence quantum yield (QY) of GFP is 0.79. The GFP from the sea pansy (''Renilla reniformis'') has a single major excitation peak at 498 nm. GFP makes for an excellent tool in many forms of biology due to its ability to form an internal chromophore without requiring any accessory cofactors, gene products, or enzymes / substrates other tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Fluorescent Protein
Yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) is a genetic mutant of green fluorescent protein (GFP) originally derived from the jellyfish ''Aequorea victoria''. Its excitation peak is 513 nm and its emission peak is 527 nm. Like the parent GFP, YFP is a useful tool in cell and molecular biology because the excitation and emission peaks of YFP are distinguishable from GFP which allows for the study of multiple processes/proteins within the same experiment. Three improved versions of YFP are Citrine, Venus, and Ypet. They have reduced chloride sensitivity, faster maturation, and increased brightness (defined as the product of the extinction coefficient and quantum yield). Typically, YFP serves as the acceptor for genetically-encoded FRET sensors of which the most likely donor FP is monomeric cyan fluorescent protein (mCFP). The red-shift relative to GFP is caused by a Pi-Pi stacking interaction as a result of the T203Y substitution introduced by mutation, which essentially increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color that is seen by our eyes is the one not absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavelength spectrum of visible light. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two separate molecular orbitals falls within the range of the visible spectrum. Visible light that hits the chromophore can thus be absorbed by exciting an electron from its ground state into an excited state. In biological molecules that serve to capture or detect light energy, the chromophore is the moiety that causes a conformational change in the molecule when hit by light. Conjugated pi-bond system chromophores Just like how two adjacent p-orbitals in a molecule will form a pi-bond, three or more adjacent p-orbitals in a molecule can form a conjugated pi-system. In a conjugated pi-system, electrons are able to capture certain photons as the electrons resonate along a certain distanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GFP Structure
GFP may refer to: Organisations * Gaelic Football Provence, a French Gaelic Athletic Association club * Geheime Feldpolizei, the German secret military police during the Second World War * French Group for the Study of Polymers and their Application, also called French Polymer Group, a French society for the promotion of polymer science Politics * GFP Ramdir Sena, a militant Hindu nationalist group in Nepal * Goa Forward Party, a political party in Goa, India * Great Fatherland Party, a Russian political party Science and technology * Generic Framing Procedure, a multiplexing technique * Greatest fixed point, in mathematics * Green fluorescent protein * Ground-fault protection, an electrical safety device Other uses * Generalized first-price auction * Government-Furnished Property, a term of art for property furnished by the US Federal government to fulfill contract obligations under Federal Acquisition Regulation The Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) is the principal set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aequorea Victoria
''Aequorea victoria'', also sometimes called the crystal jelly, is a bioluminescent hydrozoan jellyfish, or hydromedusa, that is found off the west coast of North America. The species is best known as the source of two proteins involved in bioluminescence, aequorin, a photoprotein, and green fluorescent protein (GFP). Their discoverers, Osamu Shimomura and colleagues, won the 2008 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their work on GFP. Description Almost entirely transparent and colorless, and sometimes difficult to resolve, ''Aequorea victoria'' possess a highly contractile mouth and manubrium at the center of up to 100 radial canals that extend to the bell margin. The bell margin is surrounded by uneven tentacles, up to 150 of them in fully-grown specimens. The tentacles possess nematocysts that aid in prey capture, although they have no effect on humans. Specimens larger than 3 cm usually possess gonads for sexual reproduction, which run most of the length of the radial canal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarylethene
Diarylethene is the general name of a class of chemical compounds that have aromatic functional groups bonded to each end of a carbon–carbon double bond. The simplest example is stilbene, which has two geometric isomers, E and Z. Under the influence of light, these compounds can generally perform two kinds of reversible isomerizations: * E to Z isomerizations, most common for stilbenes (and azobenzenes). This process goes through an excited state energy minimum where the aromatic rings lie at 90° to each other. This conformation drops to the ground state and generally relaxes to trans and cis forms in a 1:1 ratio, thus the quantum yield for E-Z isomerization is very rarely greater than 0.5. *6π electrocyclizations of the Z form, leading to an additional bond between the two aryl functionalities and a disruption of the aromatic character of these groups.J. March, ''Advanced Organic Chemistry'', 4th ed. (1992). The quantum yield of this reaction is generally less than 0.1, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photochromic
Photochromism is the reversible transformation of a chemical species (photoswitch) between two forms by the absorption of electromagnetic radiation (photoisomerization), where the two forms have different absorption spectra. In plain language, this can be described as a reversible change of color upon exposure to light. Applications Sunglasses One of the most famous reversible photochromic applications is photochromic lens, color changing lenses for sunglasses. The largest limitation in using photochromic technology is that the materials cannot be made stable enough to withstand thousands of hours of outdoor exposure so long-term outdoor applications are not appropriate at this time. The switching speed of photochromic dyes is highly sensitive to the rigidity of the environment around the dye. As a result, they switch most rapidly in solution and slowest in the rigid environment like a polymer lens. In 2005 it was reported that attaching flexible polymers with low glass transit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types Of Biosensors
Type may refer to: Science and technology Computing * Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc. * Data type, collection of values used for computations. * File type * TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file. * Type (Unix), a command in POSIX shells that gives information about commands. * Type safety, the extent to which a programming language discourages or prevents type errors. * Type system, defines a programming language's response to data types. Mathematics * Type (model theory) * Type theory, basis for the study of type systems * Arity or type, the number of operands a function takes * Type, any proposition or set in the intuitionistic type theory * Type, of an entire function ** Exponential type Biology * Type (biology), which fixes a scientific name to a taxon * Dog type, categorization by use or function of domestic dogs Lettering * Type is a design concept for lettering used in typography which helped bring about modern textual printin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSC Advances
''RSC Advances'' is an online-only peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on all aspects of the chemical sciences. It was established in 2011 and is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. The editor-in-chief is Russell J. Cox ( Leibniz University Hannover). In 2014, the journal moved to a very high publication frequency, initially about 100/year (similar to that of '' ChemComm''), but later in the year (and in 2015) turned to even higher frequency—however it did not become a continuous journal. The number of pages published annually had increased dramatically from about 26,500 in 2013 to over 65,000 in 2014, culminating at 116 issues and 115,000+ pages (~1000 pages per issue) in 2016. In late 2016, it was announced that with effect from January 2017, the journal would convert from a subscription based journal to an open access journal. Meanwhile, the journal experienced a cool-down in publication volume, with each issue having only ~500 pages. There were 89 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpeg/1200px-Fall_Leaves_(199582361).jpeg)
.jpg)