|
Flame Can
A flame () is the visible, gaseous part of a fire. It is caused by a highly exothermic chemical reaction made in a thin zone. When flames are hot enough to have ionized gaseous components of sufficient density, they are then considered plasma. Mechanism Color and temperature of a flame are dependent on the type of fuel involved in the combustion. For example, when a lighter is held to a candle, the applied heat causes the fuel molecules in the candle wax to vaporize. In this state they can then readily react with oxygen in the air, which gives off enough heat in the subsequent exothermic reaction to vaporize yet more fuel, thus sustaining a consistent flame. The high temperature of the flame causes the vaporized fuel molecules to decompose, forming various incomplete combustion products and free radicals, and these products then react with each other and with the oxidizer involved in the reaction of the following flame (fire). One may investigate different parts of a candle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
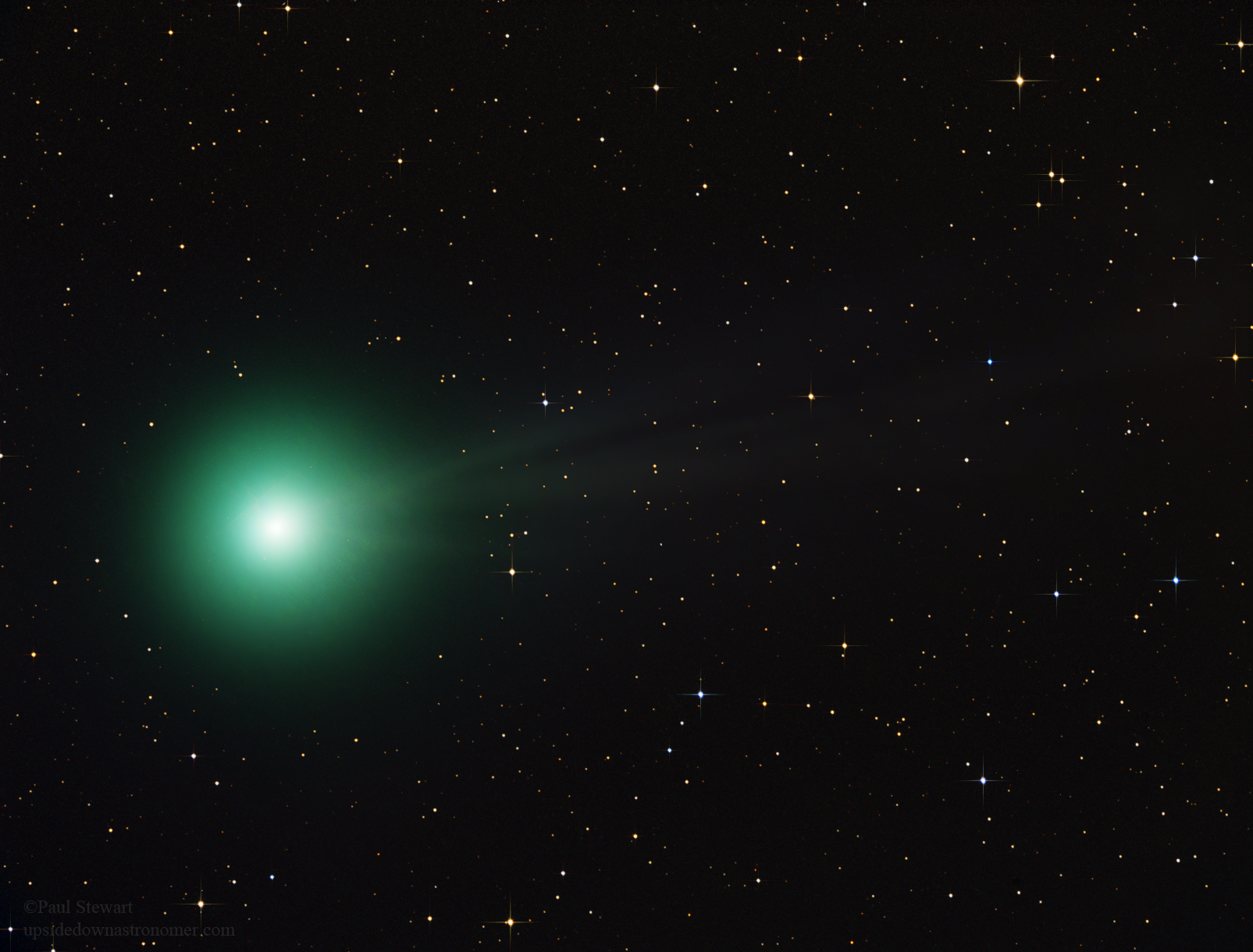
Diatomic Carbon
Diatomic carbon (systematically named dicarbon and 1λ2,2λ2-ethene), is a green, gaseous inorganic chemical with the chemical formula C=C (also written 2or C2). It is kinetically unstable at ambient temperature and pressure, being removed through autopolymerisation. It occurs in carbon vapor, for example in electric arcs; in comet A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...s, stellar atmospheres, and the interstellar medium; and in blue hydrocarbon flames. Diatomic carbon is the second simplest of the allotropes of carbon (after atomic carbon), and is an intermediate participant in the genesis of fullerenes. Properties C2 is a component of carbon vapor. One paper estimates that carbon vapor is around 28% diatomic, but theoretically this depends on the temperature and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
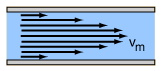
Laminar Flow
Laminar flow () is the property of fluid particles in fluid dynamics to follow smooth paths in layers, with each layer moving smoothly past the adjacent layers with little or no mixing. At low velocities, the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another smoothly. There are no cross-currents perpendicular to the direction of flow, nor eddies or swirls of fluids. In laminar flow, the motion of the particles of the fluid is very orderly with particles close to a solid surface moving in straight lines parallel to that surface. Laminar flow is a flow regime characterized by high momentum diffusion and low momentum convection. When a fluid is flowing through a closed channel such as a pipe or between two flat plates, either of two types of flow may occur depending on the velocity and viscosity of the fluid: laminar flow or turbulent flow. Laminar flow occurs at lower velocities, below a threshold at which the flow becomes turbulent. The thresh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premixed Flame
A premixed flame is a flame formed under certain conditions during the combustion of a premixed charge (also called pre-mixture) of fuel and oxidiser. Since the fuel and oxidiser—the key chemical reactants of combustion—are available throughout a homogeneous stoichiometric premixed charge, the combustion process once initiated sustains itself by way of its own heat release. The majority of the chemical transformation in such a combustion process occurs primarily in a thin interfacial region which separates the unburned and the burned gases. The premixed flame interface propagates through the mixture until the entire charge is depleted. The propagation speed of a premixed flame is known as the flame speed (or burning velocity) which depends on the convection-diffusion-reaction balance within the flame, i.e. on its inner chemical structure. The premixed flame is characterised as laminar or turbulent depending on the velocity distribution in the unburned pre-mixture (which prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
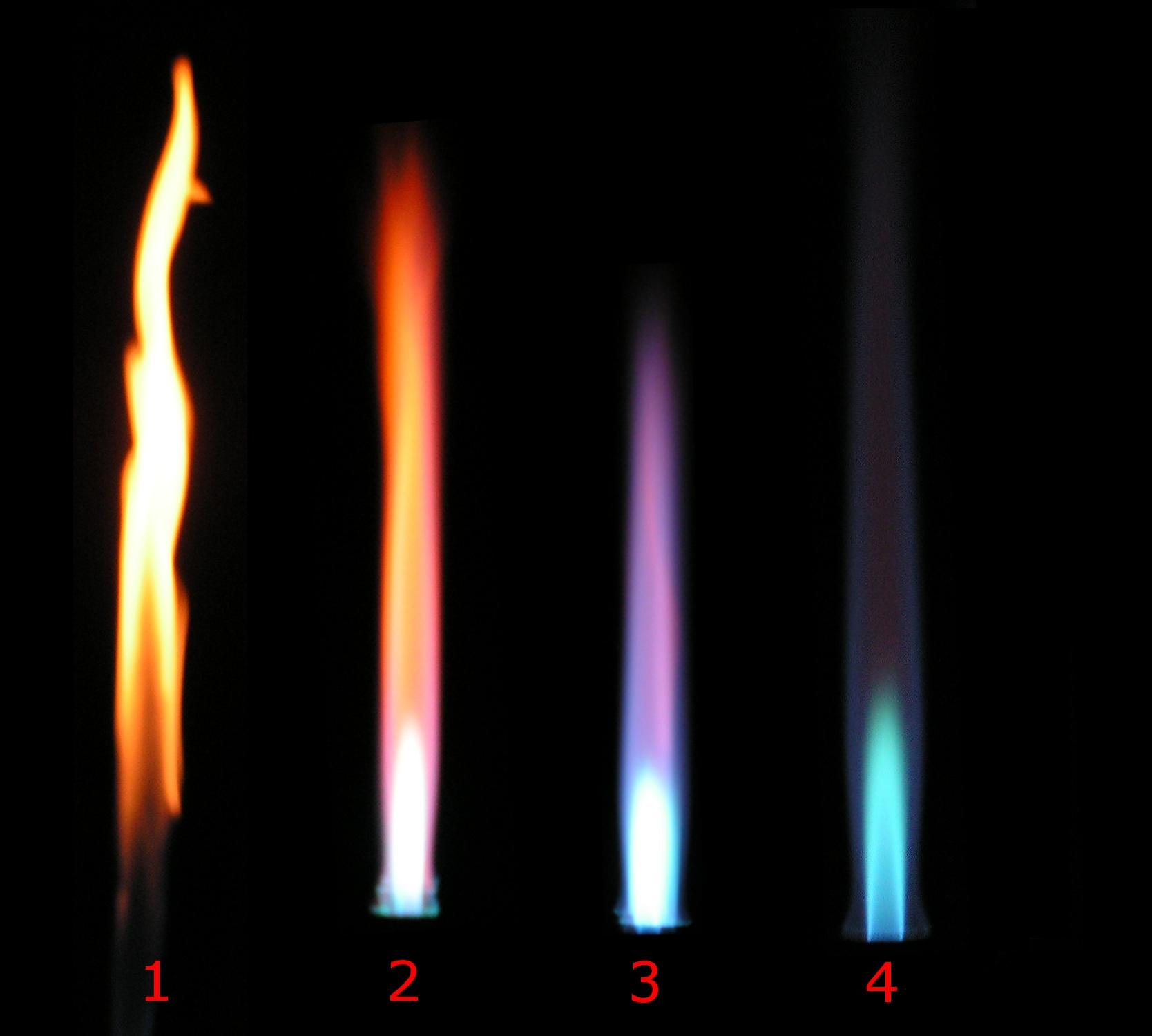
Diffusion Flame
In combustion, a diffusion flame is a flame in which the oxidizer and fuel are separated before burning. Contrary to its name, a diffusion flame involves both diffusion and convection processes. The name diffusion flame was first suggested by S.P. Burke and T.E.W. Schumann in 1928, to differentiate from premixed flame where fuel and oxidizer are premixed prior to burning. The diffusion flame is also referred to as nonpremixed flame. The burning rate is however still limited by the rate of diffusion. Diffusion flames tend to burn slower and to produce more soot than premixed flames because there may not be sufficient oxidizer for the reaction to go to completion, although there are some exceptions to the rule. The soot typically produced in a diffusion flame becomes incandescent from the heat of the flame and lends the flame its readily identifiable orange-yellow color. Diffusion flames tend to have a less-localized flame front than premixed flames. The contexts for diffusion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogas
Biogas is a gaseous renewable energy source produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste, Wastewater treatment, wastewater, and food waste. Biogas is produced by anaerobic digestion with anaerobic organisms or methanogens inside an Anaerobic digestion, anaerobic digester, biodigester or a bioreactor. The gas composition is primarily methane () and carbon dioxide () and may have small amounts of hydrogen sulfide (), moisture and siloxanes. The methane can be combusted or oxidized with oxygen. This energy release allows biogas to be used as a fuel; it can be used in fuel cells and for heating purpose, such as in cooking. It can also be used in a gas engine to convert the energy in the gas into electricity and heat. After removal of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide it can be compressed natural gas, compressed in the same way as natural gas and used to power Alternative fuel vehicle, motor vehicles. In the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the branch of physical chemistry that is concerned with understanding the rates of chemical reactions. It is different from chemical thermodynamics, which deals with the direction in which a reaction occurs but in itself tells nothing about its rate. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how experimental conditions influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition states, as well as the construction of mathematical models that also can describe the characteristics of a chemical reaction. History The pioneering work of chemical kinetics was done by German chemist Ludwig Wilhelmy in 1850. He experimentally studied the rate of inversion of sucrose and he used integrated rate law for the determination of the reaction kinetics of this reaction. His work was noticed 34 years later by Wilhelm Ostwald. In 1864, Peter Waage and Cato Guldberg published the law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extremely Reactivity (chemistry), reactive as it reacts with all other Periodic table, elements except for the light Noble gas, noble gases. It is highly toxicity, toxic. Among the elements, fluorine ranks Abundance of the chemical elements, 24th in cosmic abundance and 13th in crustal abundance. Fluorite, the primary mineral source of fluorine, which gave the element its name, was first described in 1529; as it was added to metal ores to lower their melting points for smelting, the Latin verb meaning gave the mineral its name. Proposed as an element in 1810, fluorine proved difficult and dangerous to separate from its compounds, and several early experimenters died or sustained injuries from their attempts. Only in 1886 did French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoropolymer
A fluoropolymer is a fluorocarbon-based polymer with multiple carbon–fluorine bonds. It is characterized by a high resistance to solvents, acids, and bases. The best known fluoropolymer is polytetrafluoroethylene under the brand name "Teflon," trademarked by the DuPont Company. History In 1938, polytetrafluoroethylene (DuPont brand name Teflon) was discovered by accident by a recently hired DuPont Ph.D., Roy J. Plunkett. While working with tetrafluoroethylene gas to develop refrigerants, he noticed that a previously pressurized cylinder had no pressure remaining. In dissecting the cylinder, he found a mass of white solid in a quantity similar to that of the tetrafluoroethylene gas. It was determined that this material was a new-to-the-world polymer. Tests showed the substance was resistant to corrosion from most acids, bases and solvents and had better high temperature stability than any other plastic. By early 1941, a crash program was making substantial quantities of PT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypergolic
A hypergolic propellant is a rocket propellant combination used in a rocket engine, whose components spontaneously ignite when they come into contact with each other. The two propellant components usually consist of a fuel and an oxidizer. The main advantages of hypergolic propellants are that they can be stored as liquids at room temperature and that engines which are powered by them are easy to ignite reliably and repeatedly. Common hypergolic propellants are extremely toxic or corrosive, making them difficult to handle. In contemporary usage, the terms "hypergol" and "hypergolic propellant" usually mean the most common such propellant combination: dinitrogen tetroxide plus hydrazine. History The fact that turpentine may spontaneously combust when mixed with nitric acid was discovered as early as the late 17th century by Frederick Slare, but it remained a scientific curiosity for centuries until it was proposed to use it for rocket-assisted take off during WWII. In 1935, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Tetroxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russian rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. Its molar mass is 92.011 g/mol. Dinitrogen tetroxide is a powerful oxidizer that is hypergolic (spontaneously reacts) upon contact with various forms of hydrazine, which has made the pair a common bipropellant for rockets. Structure and properties Dinitrogen tetroxide could be regarded as two nitro groups (-NO2) bonded together. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. The molecule is planar with an N-N bond distance of 1.78Å and N-O distances of 1.19Å. The N-N distance corresponds to a weak bond, since it is significantly longer than the average N-N single bond length of 1.45Å. This exceptionally weak σ bond (amounting to overlapping of the ''sp''2 hybrid orbitals of the two NO2 units) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |