flame can on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A flame (from Latin '' flamma'') is the visible, gaseous part of a
A flame (from Latin '' flamma'') is the visible, gaseous part of a
 Color and temperature of a flame are dependent on the type of fuel involved in the combustion, as, for example, when a lighter is held to a
Color and temperature of a flame are dependent on the type of fuel involved in the combustion, as, for example, when a lighter is held to a
 Flame color depends on several factors, the most important typically being
Flame color depends on several factors, the most important typically being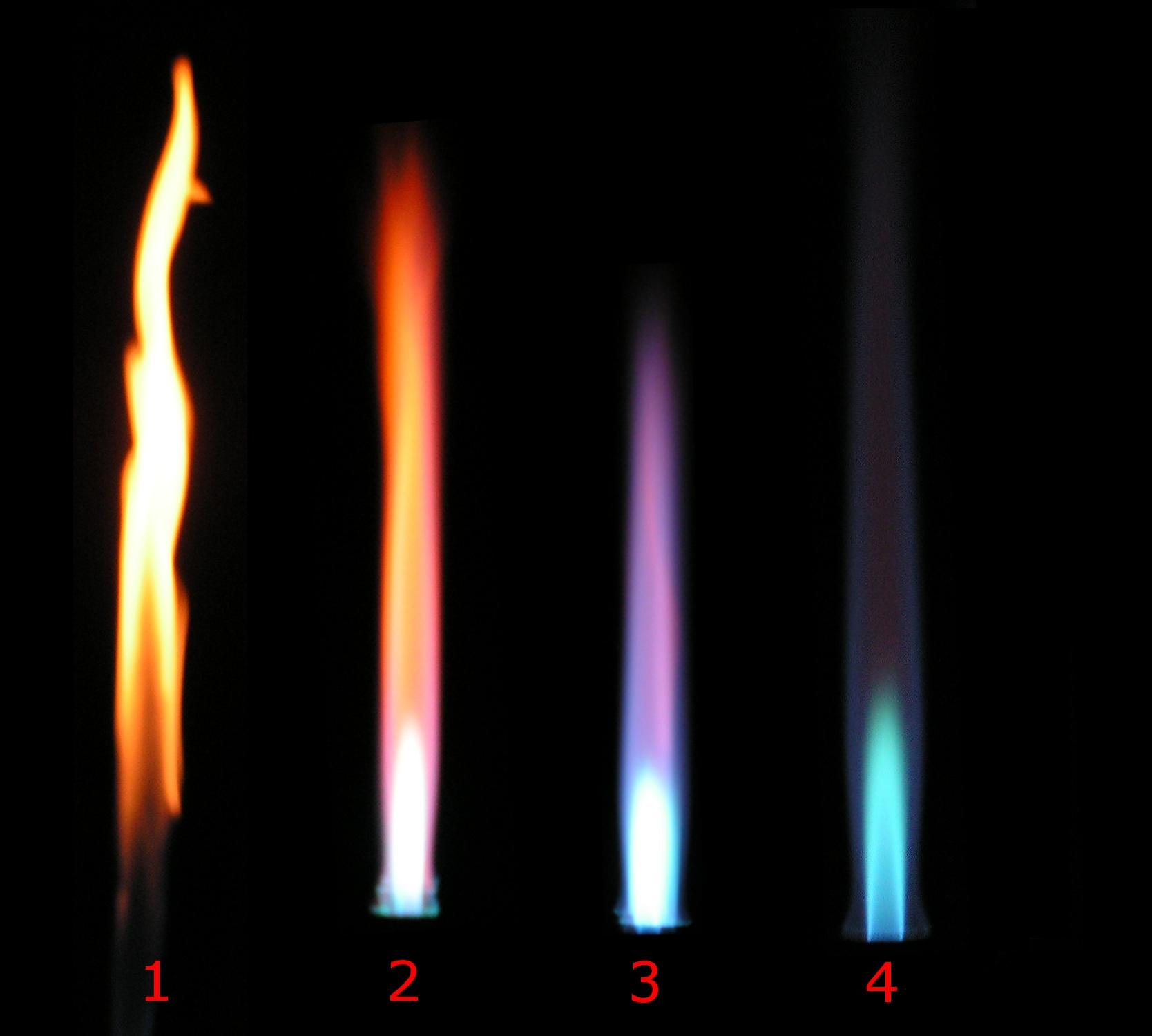  In a laboratory under normal gravity conditions and with a closed air inlet, a Bunsen burner burns with yellow flame (also called a safety flame) with a peak temperature of about . The yellow arises from
In a laboratory under normal gravity conditions and with a closed air inlet, a Bunsen burner burns with yellow flame (also called a safety flame) with a peak temperature of about . The yellow arises from
 When looking at a flame's temperature there are many factors which can change or apply. An important one is that a flame's color does not necessarily determine a temperature comparison because black-body radiation is not the only thing that produces or determines the color seen; therefore it is only an estimation of temperature. Other factors that determine its temperature are:
* In fires (particularly house fires), the cooler flames are often red and produce the most smoke. Here the red color compared to typical yellow color of the flames suggests that the temperature is lower. This is because there is a lack of oxygen in the room and therefore there is incomplete combustion and the flame temperature is low, often just . This means that a lot of
When looking at a flame's temperature there are many factors which can change or apply. An important one is that a flame's color does not necessarily determine a temperature comparison because black-body radiation is not the only thing that produces or determines the color seen; therefore it is only an estimation of temperature. Other factors that determine its temperature are:
* In fires (particularly house fires), the cooler flames are often red and produce the most smoke. Here the red color compared to typical yellow color of the flames suggests that the temperature is lower. This is because there is a lack of oxygen in the room and therefore there is incomplete combustion and the flame temperature is low, often just . This means that a lot of
 In the year 2000, experiments by NASA confirmed that gravity plays an indirect role in flame formation and composition. The common distribution of a flame under normal gravity conditions depends on
In the year 2000, experiments by NASA confirmed that gravity plays an indirect role in flame formation and composition. The common distribution of a flame under normal gravity conditions depends on
A candle flame strongly influenced and moved about by an electric field due to the flame having ions.
Ultra-Low Emissions Low-Swirl Burner
7 Shades of Fire
* {{Authority control Fire lez:ЦӀай
 A flame (from Latin '' flamma'') is the visible, gaseous part of a
A flame (from Latin '' flamma'') is the visible, gaseous part of a fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition ...
. It is caused by a highly exothermic
In thermodynamics, an exothermic process () is a thermodynamic process or reaction that releases energy from the system to its surroundings, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity ...
chemical reaction taking place in a thin zone. When flames are hot enough to have ionize
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule ...
d gaseous components of sufficient density they are then considered plasma.
Mechanism
candle
A candle is an ignitable wick embedded in wax, or another flammable solid substance such as tallow, that provides light, and in some cases, a fragrance. A candle can also provide heat or a method of keeping time.
A person who makes candl ...
. The applied heat causes the fuel molecules in the candle wax to vaporize (if this process happens in inert atmosphere without oxidizer
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxid ...
, it is called pyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''p ...
). In this state they can then readily react with oxygen in the air, which gives off enough heat in the subsequent exothermic reaction to vaporize yet more fuel, thus sustaining a consistent flame. The high temperature of the flame causes the vaporized fuel molecules to decompose
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is ...
, forming various incomplete combustion products and free radicals
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron.
With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spon ...
, and these products then react with each other and with the oxidizer
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxid ...
involved in the reaction of the following flame (fire). One may investigate all the different parts of the flame from a candle with a cold metal spoon: Higher parts are water vapor, the result of combustion; yellow parts in the middle are soot; down just next to the candle wick is unburned wax. Goldsmiths use higher parts of a flame with a metallic blow-pipe for melting gold and silver. Sufficient energy in the flame will excite the electrons in some of the transient reaction intermediates such as the methylidyne radical (CH) and diatomic carbon (C2), which results in the emission of visible light as these substances release their excess energy (see spectrum below for an explanation of which specific radical species produce which specific colors). As the combustion temperature of a flame increases (if the flame contains small particles of unburnt carbon or other material), so does the average energy of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the flame (see Black body
A black body or blackbody is an idealized physical object, physical body that absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence. T ...
).
Other oxidizers besides oxygen can be used to produce a flame. Hydrogen burning in chlorine produces a flame and in the process emits gaseous hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride g ...
(HCl) as the combustion product. Another of many possible chemical combinations is hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazin ...
and nitrogen tetroxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russia rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium ...
which is hypergolic and commonly used in rocket engines. Fluoropolymers can be used to supply fluorine as an oxidizer of metallic fuels, e.g. in the magnesium/teflon/viton composition.
The chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the branch of physical chemistry that is concerned with understanding the rates of chemical reactions. It is to be contrasted with chemical thermodynamics, which deals with the direction in ...
occurring in the flame are very complex and typically involve a large number of chemical reactions and intermediate species, most of them radicals
Radical may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change
*Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and ...
. For instance, a well-known chemical kinetics scheme, GRI-Mech, uses 53 species and 325 elementary reactions to describe combustion of biogas
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste and food waste. I ...
.
There are different methods of distributing the required components of combustion to a flame. In a diffusion flame, oxygen and fuel diffuse into each other; the flame occurs where they meet. In a premixed flame, the oxygen and fuel are premixed beforehand, which results in a different type of flame. Candle flames (a diffusion flame) operate through evaporation of the fuel which rises in a laminar flow of hot gas which then mixes with surrounding oxygen and combusts.
Color
 Flame color depends on several factors, the most important typically being
Flame color depends on several factors, the most important typically being black-body radiation
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific, continuous sp ...
and spectral band emission, with both spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to iden ...
emission and spectral line absorption playing smaller roles. In the most common type of flame, hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
flames, the most important factor determining color is oxygen supply and the extent of fuel-oxygen pre-mixing, which determines the rate of combustion and thus the temperature and reaction paths, thereby producing different color hues.
 In a laboratory under normal gravity conditions and with a closed air inlet, a Bunsen burner burns with yellow flame (also called a safety flame) with a peak temperature of about . The yellow arises from
In a laboratory under normal gravity conditions and with a closed air inlet, a Bunsen burner burns with yellow flame (also called a safety flame) with a peak temperature of about . The yellow arises from incandescence
Incandescence is the emission of electromagnetic radiation (including visible light) from a hot body as a result of its high temperature. The term derives from the Latin verb ''incandescere,'' to glow white. A common use of incandescence is ...
of very fine soot particles that are produced in the flame. Also, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
is produced, and the flame tends to take oxygen from the surfaces it touches. When the air inlet is opened, less soot and carbon monoxide are produced. When enough air is supplied, no soot or carbon monoxide is produced and the flame becomes blue. (Most of this blue had previously been obscured by the bright yellow emissions.) The spectrum of a premixed (complete combustion) butane
Butane () or ''n''-butane is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Butane is a highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gas that quickly vaporizes at room temperature. The name bu ...
flame on the right shows that the blue color arises specifically due to emission of excited molecular radicals
Radical may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change
*Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and ...
in the flame, which emit most of their light well below ≈565 nanometers in the blue and green regions of the visible spectrum.
The colder part of a diffusion (incomplete combustion) flame will be red, transitioning to orange, yellow, and white as the temperature increases as evidenced by changes in the black-body radiation spectrum. For a given flame's region, the closer to white on this scale, the hotter that section of the flame is. The transitions are often apparent in fires, in which the color emitted closest to the fuel is white, with an orange section above it, and reddish flames the highest of all. A blue-colored flame only emerges when the amount of soot decreases and the blue emissions from excited molecular radicals become dominant, though the blue can often be seen near the base of candles where airborne soot is less concentrated.
Specific colors can be imparted to the flame by introduction of excitable species with bright emission spectrum
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an electron making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The photon energy of t ...
lines. In analytical chemistry, this effect is used in flame test
A flame test is an analytical procedure used in chemistry to detect the presence of certain elements, primarily metal ions, based on each element's characteristic flame emission spectrum (which may be affected by the presence of chloride ...
s (or flame emission spectroscopy
A flame (from Latin ''flamma'') is the visible, gaseous part of a fire. It is caused by a highly exothermic chemical reaction taking place in a thin zone. When flames are hot enough to have ionized gaseous components of sufficient density they a ...
) to determine presence of some metal ions. In pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics is the science and craft of creating such things as fireworks, safety matches, oxygen candles, Pyrotechnic fastener, explosive bolts and other fasteners, parts of automotive airbags, as well as gas-pressure blasting in mining, quarry ...
, the pyrotechnic colorants are used to produce brightly colored fireworks.
Temperature
 When looking at a flame's temperature there are many factors which can change or apply. An important one is that a flame's color does not necessarily determine a temperature comparison because black-body radiation is not the only thing that produces or determines the color seen; therefore it is only an estimation of temperature. Other factors that determine its temperature are:
* In fires (particularly house fires), the cooler flames are often red and produce the most smoke. Here the red color compared to typical yellow color of the flames suggests that the temperature is lower. This is because there is a lack of oxygen in the room and therefore there is incomplete combustion and the flame temperature is low, often just . This means that a lot of
When looking at a flame's temperature there are many factors which can change or apply. An important one is that a flame's color does not necessarily determine a temperature comparison because black-body radiation is not the only thing that produces or determines the color seen; therefore it is only an estimation of temperature. Other factors that determine its temperature are:
* In fires (particularly house fires), the cooler flames are often red and produce the most smoke. Here the red color compared to typical yellow color of the flames suggests that the temperature is lower. This is because there is a lack of oxygen in the room and therefore there is incomplete combustion and the flame temperature is low, often just . This means that a lot of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
is formed (which is a flammable gas) which is when there is greatest risk of backdraft. When this occurs, combustible gases at or above the flash point
The flash point of a material is the "lowest liquid temperature at which, under certain standardized conditions, a liquid gives off vapours in a quantity such as to be capable of forming an ignitable vapour/air mixture". (EN 60079-10-1)
The fl ...
of spontaneous combustion are exposed to oxygen, carbon monoxide and superheated hydrocarbons combust, and temporary temperatures of up to occur.
Common flame temperatures
This is a rough guide to flame temperatures for various common substances (in air at 1 atm. pressure):Highest temperature
Dicyanoacetylene
Dicyanoacetylene, also called carbon subnitride or but-2-ynedinitrile (IUPAC), is a compound of carbon and nitrogen with chemical formula . It has a linear molecular structure, (often abbreviated as ), with alternating triple and single covale ...
, a compound of carbon and nitrogen with chemical formula C4N2 burns in oxygen with a bright blue-white flame at a temperature of , and at up to in ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
. This high flame temperature is partially due to the absence of hydrogen in the fuel (dicyanoacetylene is not a hydrocarbon) thus there is no water among the combustion products.
Cyanogen
Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the formula ( C N)2. It is a colorless and highly toxic gas with a pungent odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules consist of two CN groups – analogous to diatomic halogen molec ...
, with the formula (CN)2, produces the second-hottest-known natural flame with a temperature of over when it burns in oxygen.
Cool flames
At temperatures as low as , fuel-air mixtures can react chemically and produce very weak flames called cool flames. The phenomenon was discovered byHumphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for the ...
in 1817. The process depends on a fine balance of temperature and concentration of the reacting mixture, and if conditions are right it can initiate without any external ignition source. Cyclical variations in the balance of chemicals, particularly of intermediate products in the reaction, give oscillations in the flame, with a typical temperature variation of about , or between "cool" and full ignition. Sometimes the variation can lead to an explosion.
In microgravity
 In the year 2000, experiments by NASA confirmed that gravity plays an indirect role in flame formation and composition. The common distribution of a flame under normal gravity conditions depends on
In the year 2000, experiments by NASA confirmed that gravity plays an indirect role in flame formation and composition. The common distribution of a flame under normal gravity conditions depends on convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the c ...
, as soot tends to rise to the top of a flame (such as in a candle in normal gravity conditions), making it yellow. In microgravity
The term micro-g environment (also μg, often referred to by the term microgravity) is more or less synonymous with the terms '' weightlessness'' and ''zero-g'', but emphasising that g-forces are never exactly zero—just very small (on the ...
or zero gravity
Weightlessness is the complete or near-complete absence of the sensation of weight. It is also termed zero gravity, zero G-force, or zero-G.
Weight is a measurement of the force on an object at rest in a relatively strong gravitational fie ...
environment, such as in orbit, natural convection no longer occurs and the flame becomes spherical, with a tendency to become bluer and more efficient. There are several possible explanations for this difference, of which the most likely is the hypothesis that the temperature is sufficiently evenly distributed that soot is not formed and complete combustion occurs. Experiments by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
reveal that diffusion flames in microgravity allow more soot to be completely oxidized after they are produced than do diffusion flames on Earth, because of a series of mechanisms that behave differently in microgravity when compared to normal gravity conditions. These discoveries have potential applications in applied science
Applied science is the use of the scientific method and knowledge obtained via conclusions from the method to attain practical goals. It includes a broad range of disciplines such as engineering and medicine. Applied science is often contrasted ...
and private industry, especially concerning fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, ...
.
Thermonuclear flames
Flames do not need to be driven only by chemical energy release. In stars, subsonic burning fronts driven by burning light nuclei (like carbon or helium) to heavy nuclei (up to iron group) propagate as flames. This is important in some models of Type Ia supernovae. In thermonuclear flames, thermal conduction dominates over species diffusion, so the flame speed and thickness is determined by the thermonuclear energy release andthermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
(often in the form of degenerate electrons).
See also
* Flame detector * International Flame Research Foundation *Oxidizing and reducing flames
In pyrology, flames are affected by the fuel introduced and the oxygen available. A flame with a good oxygen-fuel ratio is called a neutral flame. The color of the flame is semi-transparent purple or blue. This flame is optimal for all intentions, ...
* The Combustion Institute
References
External links
A candle flame strongly influenced and moved about by an electric field due to the flame having ions.
Ultra-Low Emissions Low-Swirl Burner
7 Shades of Fire
* {{Authority control Fire lez:ЦӀай