|
End-systolic Volume
End-systolic volume (ESV) is the volume of blood in a ventricle at the end of contraction, or systole, and the beginning of filling, or diastole. ESV is the lowest volume of blood in the ventricle at any point in the cardiac cycle. The main factors that affect the end-systolic volume are afterload and the contractility of the heart. __TOC__ Uses End systolic volume can be used clinically as a measurement of the adequacy of cardiac emptying, related to systolic function. On an electrocardiogram, or ECG, the end-systolic volume will be seen at the end of the T wave. Clinically, ESV can be measured using two-dimensional echocardiography, MRI ( magnetic resonance tomography) or cardiac CT (computed tomography A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...) or SPECT (single photo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricle (heart)
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium (heart), atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
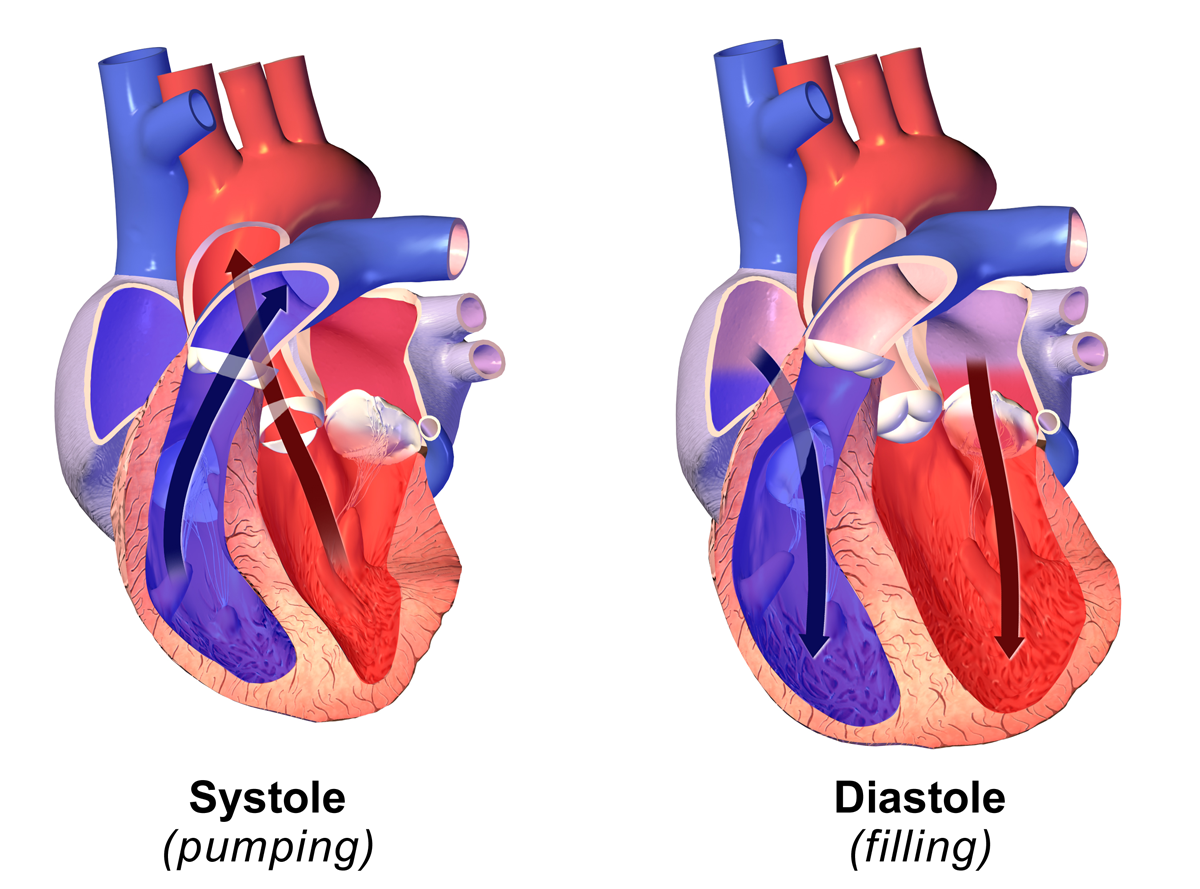
Systole (medicine)
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and send blood to the larger, lower ventricle chambers. This flow fills the ventricles with blood, and the resulting pressure closes the valves to the atria. The ventricles now perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles. The term originates from the Greek word (''diastolē''), meaning "dilation", from (''diá'', "apart") + (''stéllein'', "to send"). Role in cardiac cycle A typical heart rate is 75 beats per minute (bpm), which means that the cardiac cycle that produces one heartbeat, lasts for less than one second. The cycle requires 0.3 sec in ventricular systole (contraction)—pumping blood to all body systems from the two ventricles; and 0.5 sec in diastole (dilation), re-filling the four chambers of the heart, for a total of 0.8 sec to complete the cycle. Early ventricular diastole During early ventricular diastole, pressure in the two ventricles begins to drop from the peak reached during syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following a period of robust contraction and pumping of blood, called systole. After emptying, the heart immediately relaxes and expands to receive another influx of blood returning from the lungs and other systems of the body, before again contracting to pump blood to the lungs and those systems. A normally performing heart must be fully expanded before it can efficiently pump again. Assuming a healthy heart and a typical rate of 70 to 75 beats per minute, each cardiac cycle, or heartbeat, takes about 0.8 second to complete the cycle. There are two atrial and two ventricle chambers of the heart; they are paired as the left heart and the right heart—that is, the left atrium with the left ventricle, the right atrium with the right ventricle—an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterload
Afterload is the pressure that the heart must work against to eject blood during systole (ventricular contraction). Afterload is proportional to the average arterial pressure. As aortic and pulmonary pressures increase, the afterload increases on the left and right ventricles respectively. Afterload changes to adapt to the continually changing demands on an animal's cardiovascular system. Afterload is proportional to mean systolic blood pressure and is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). Hemodynamics Afterload is a determinant of cardiac output. Cardiac output is the product of stroke volume and heart rate. Afterload is a determinant of stroke volume (in addition to preload, and strength of myocardial contraction). Following Laplace's law, the tension upon the muscle fibers in the heart wall is the pressure within the ventricle multiplied by the volume within the ventricle divided by the wall thickness (this ratio is the other factor in setting the afterload). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnormality in patients with suspected cardiac disease. It is a tool which helps in reaching an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Tomography
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although "open" MRI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computed Tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End-diastolic Volume
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume (EDV) is the volume of blood in the right or left ventricle at end of filling in diastole which is ammount of blood present in ventricle at the end of diastole systole. Because greater EDVs cause greater distention of the ventricle, ''EDV'' is often used synonymously with '' preload'', which refers to the length of the sarcomeres in cardiac muscle prior to contraction (systole). An increase in EDV increases the preload on the heart and, through the Frank-Starling mechanism of the heart, increases the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle during systole (stroke volume). __TOC__ Sample values The right ventricular end-diastolic volume (RVEDV) ranges between 100 and 160 mL. The right ventricular end-diastolic volume index (RVEDVI) is calculated by RVEDV/ BSA and ranges between 60 and 100 mL/m2. See also * End-systolic volume * Stroke volume In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke Volume
In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat. Stroke volume is calculated using measurements of ventricle volumes from an echocardiogram and subtracting the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of a beat (called end-systolic volume) from the volume of blood just prior to the beat (called end-diastolic volume). The term ''stroke volume'' can apply to each of the two ventricles of the heart, although it usually refers to the left ventricle. The stroke volumes for each ventricle are generally equal, both being approximately 70 mL in a healthy 70-kg man. Stroke volume is an important determinant of cardiac output, which is the product of stroke volume and heart rate, and is also used to calculate ejection fraction, which is stroke volume divided by end-diastolic volume. Because stroke volume decreases in certain conditions and disease states, stroke volume itself correlates with cardiac function. Calcul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |