|
Electric Sail
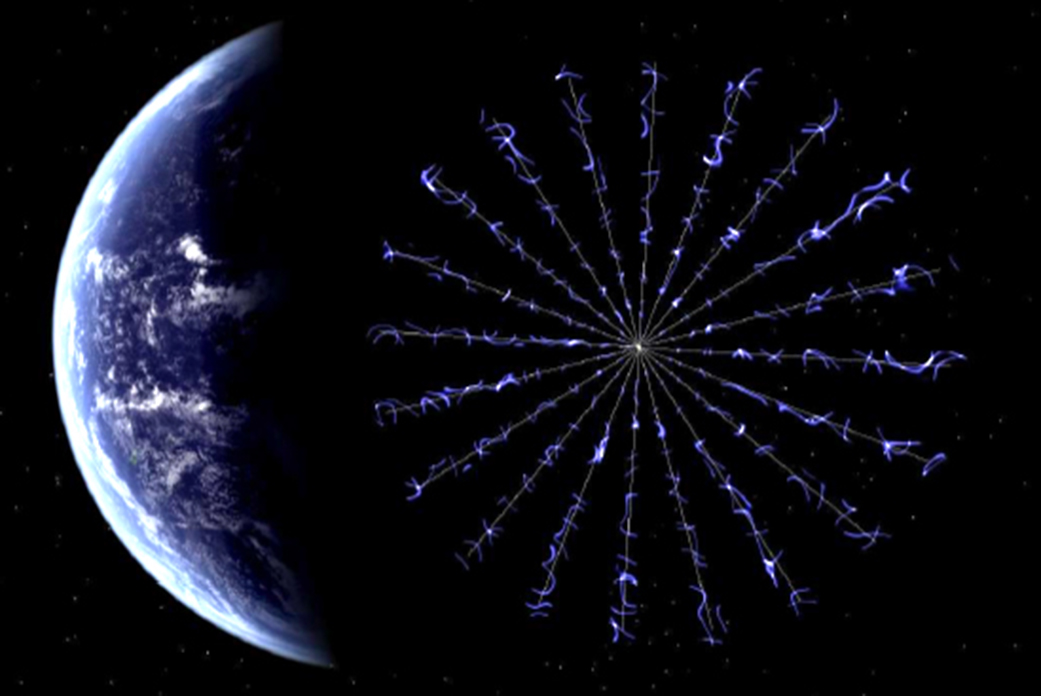
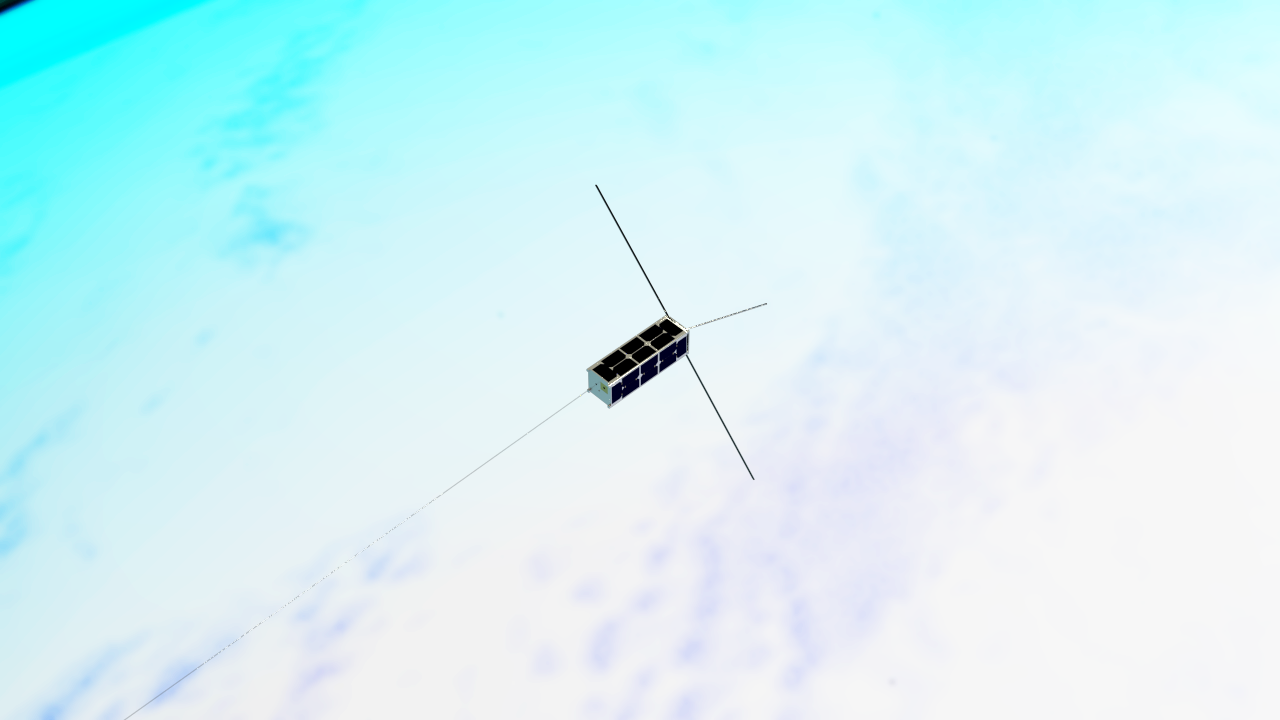
An electric sail (also known as an electric solar wind sail or an E-sail) is a proposed form of spacecraft propulsion using the dynamic pressure of the solar wind as a source of thrust. It creates a "virtual" sail by using small wires to form an electric field that deflects solar wind protons and extracts their momentum. The idea was first conceptualised by Pekka Janhunen in 2006 at the Finnish Meteorological Institute. Principles of operation and design The electric sail consists of a number of thin, long and conducting tethers which are kept in a high positive potential by an onboard electron gun. The positively charged tethers deflect solar wind protons, thus extracting momentum from them. Simultaneously they attract electrons from the solar wind plasma, producing an electron current. The electron gun compensates for the arriving electric current. One way to deploy the tethers is to rotate the spacecraft, using centrifugal force to keep them stretched. By fine-tuning the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliopause Electrostatic Rapid Transit System - HERTS
Heliopause may refer to: * Heliopause (astronomy), the theoretical boundary where the Sun's solar wind is stopped by the interstellar medium. * Heliopause (band) Heliopause are a U.K. band based in Belfast and Brighton Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London. Archaeological ..., a U.K. band * ''Heliopause'' (album), a 2011 album by The Resonance Association {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune. In astrophysics and planetary science the term "ices" refers to volatile chemical compounds with freezing points above about 100 K, such as water, ammonia, or methane, with freezing points of 273 K (0°C), 195 K (−78°C), and 91 K (−182°C), respectively (see Volatiles). In the 1990s, it was determined that Uranus and Neptune are a distinct class of giant planet, separate from the other giant planets, Jupiter and Saturn, which are gas giants predominantly composed of hydrogen and helium. As such, Neptune and Uranus are now referred to as ''ice giants''. Lacking well defined solid surfaces, they are primarily composed of gases and liquids. Their constituent compounds were solids when they were primarily incorporated into the planets during their formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetospheres
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body, the magnetic field resembles a magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation, that also protects all living organisms from potentially detrimental and dangerous consequences. This is studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert discovered that the magnetic field on the surface of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanosatellite
A small satellite, miniaturized satellite, or smallsat is a satellite of low mass and size, usually under . While all such satellites can be referred to as "small", different classifications are used to categorize them based on mass. Satellites can be built small to reduce the large economic cost of launch vehicles and the costs associated with construction. Miniature satellites, especially in large numbers, may be more useful than fewer, larger ones for some purposes – for example, gathering of scientific data and radio relay. Technical challenges in the construction of small satellites may include the lack of sufficient power storage or of room for a propulsion system. Rationales One rationale for miniaturizing satellites is to reduce the cost; heavier satellites require larger rockets with greater thrust that also have greater cost to finance. In contrast, smaller and lighter satellites require smaller and cheaper launch vehicles and can sometimes be launched in mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aalto-1
Aalto-1 is a Finnish research nanosatellite, created by students of Aalto University. Based on the CubeSat architecture, it was originally scheduled to be launched in 2013, it was launched on 23 June 2017. It is Finland's first student satellite project and indigenously-produced satellite. As of 2021, the satellite is operational. Project history The Aalto-1 project began in 2010 with a feasibility study, which was conducted as part of a university course on space technology. The study was followed by the publication of a preliminary design in 2011. A critical design review (CDR) of the satellite was conducted in 2012. In all, over 80 students of Aalto University's School of Electrical Engineering were involved in the project. Design The solar-powered CubeSat - based satellite will weigh approximately , and has 3 main payloads: a miniature Fabry-Pérot spectrometer, designed by VTT Technical Research Centre, a RADMON-radiation detector developed by University of Helsin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland across Estonia to the south. Finland covers an area of with a population of 5.6 million. Helsinki is the capital and largest city, forming a larger metropolitan area with the neighbouring cities of Espoo, Kauniainen, and Vantaa. The vast majority of the population are ethnic Finns. Finnish, alongside Swedish, are the official languages. Swedish is the native language of 5.2% of the population. Finland's climate varies from humid continental in the south to the boreal in the north. The land cover is primarily a boreal forest biome, with more than 180,000 recorded lakes. Finland was first inhabited around 9000 BC after the Last Glacial Period. The Stone Age introduced several different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aalto University
Aalto University ( fi, Aalto-yliopisto; sv, Aalto-universitetet) is a public research university located in Espoo, Finland. It was established in 2010 as a merger of three major Finnish universities: the Helsinki University of Technology, the Helsinki School of Economics and the University of Art and Design Helsinki. The close collaboration between the scientific, business and arts communities is intended to foster multi-disciplinary education and research. The Finnish government, in 2010, set out to create a university that fosters innovation, merging the three institutions into one. The university is composed of six schools with close to 17,500 students and 4,000 staff members, making it Finland's second largest university. The main campus of Aalto University is located in Otaniemi, Espoo. Aalto University Executive Education operates in the district of Töölö, Helsinki. In addition to the Greater Helsinki area, the university also operates its Bachelor's Programme in In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits the Sun, from a maximum ( aphelion) to a minimum ( perihelion) and back again once each year. The astronomical unit was originally conceived as the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion; however, since 2012 it has been defined as exactly (see below for several conversions). The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec. History of symbol usage A variety of unit symbols and abbreviations have been in use for the astronomical unit. In a 1976 resolution, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) had used the symbol ''A'' to denote a length equal to the ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESTCube-1
ESTCube-1 is the first Estonian satellite and first satellite in the world to attempt to use an electric solar wind sail (E-sail). It was launched on 7 May 2013 aboard Vega VV02 carrier rocket and successfully deployed into orbit. The CubeSat standard for nanosatellites was followed during the engineering of ESTCube-1, resulting in a 10×10×11.35 cm cube, with a volume of 1 liter and a mass of 1.048 kg. The mission ended officially on 17 February 2015 and it was said that during this time it resulted in 29 bachelor's and 19 master's dissertations, 5 doctoral theses and 4 start-ups. The deployment of the E-sail tether was unsuccessful, and thus no measurements were taken of the E-sail or of the plasma braking deployment system. The last signal from ESTCube-1 was received on 19 May 2015. Scientific purpose Developed as part of the Estonian Student Satellite Program, ESTCube-1 was an educational project in which university and high school students participated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,200 other islands and islets on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, covering a total area of . The capital city Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest urban areas of the country. The Estonian language is the autochthonous and the official language of Estonia; it is the first language of the majority of its population, as well as the world's second most spoken Finnic language. The land of what is now modern Estonia has been inhabited by '' Homo sapiens'' since at least 9,000 BC. The medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last "pagan" civilisations in Europe to adop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been described as a ''sui generis'' political entity (without precedent or comparison) combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.8per cent of the world population in 2020, the EU generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around trillion in 2021, constituting approximately 18per cent of global nominal GDP. Additionally, all EU states but Bulgaria have a very high Human Development Index according to the United Nations Development Programme. Its cornerstone, the Customs Union, paved the way to establishing an internal single market based on standardised legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states have agree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of Finland
The Academy of Finland ( fi, Suomen Akatemia, sv, Finlands Akademi) is a governmental funding body for scientific research in Finland. It is based in Helsinki. Yearly, the Academy administers over 260 million euros to Finnish research activities. Over 5000 researchers are working on projects supported by the academy. The Academy functions as a funding body only and is not a school. However, personnel funded by the Academy can use the title referring to it, e.g. professors will be called ''akatemiaprofessori''. Academy Professor funding has a term of 5 years. The Academy of Finland should not be confused with the Finnish arts and science school learned societies, The Finnish Academy of Science and Letters (''Suomalainen tiedeakatemia'') and The Finnish Society of Science and Letters (''Finska Vetenskaps-Societeten'') which are the two Finnish national honorary academies, for Finnish and Swedish-speaking scientists and scholars, respectively. For engineers, the two language-based h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |