|
Edict Of Theodoric
The ''Edictum Theodorici'' is a set of laws that date from the 5th or 6th-century and that is one of the codes emanated by Germanic kings to settle issues between Romans and Germans in their kingdoms. It is composed of a preface, 155 chapters and a conclusion. Its dispositions are mostly taken from Roman Law, such as the ''Codex Gregorianus'', the ''Codex Hermogenianus'' and the '' Codex Theodosianus''. Its authenticity, differently from before, is no longer in doubt. As for its character the edict is for the most part a restatement and a reworking of Roman legislation; its chief interest stands in implying, differently from most Romano-barbaric codes, a territorial rather than a personal form of power as its provisions treat Romans and Barbarians equally. Explicit differences are made only for Jews, who are to have their own judges. The problem of the author of the code is one of the most complicated: since when the '' editio princeps'' was printed in 1579 due to Pierre Pithou t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the ''Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I. Roman law forms the basic framework for Civil law (legal system), civil law, the most widely used legal system today, and the terms are sometimes used synonymously. The historical importance of Roman law is reflected by the continued use of List of legal Latin terms, Latin legal terminology in many legal systems influenced by it, including common law. After the dissolution of the Western Roman Empire, the Roman law remained in effect in the Eastern Roman Empire. From the 7th century onward, the legal language in the East was Greek. ''Roman law'' also denoted the legal system applied in most of Western Europe until the end of the 18th century. In Germany, Roman law practice remained in place longer under the Holy Roman Empire ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
, established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus (legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption = The territory of the ''comune'' (''Roma Capitale'', in red) inside the Metropolitan City of Rome (''Città Metropolitana di Roma'', in yellow). The white spot in the centre is Vatican City. , pushpin_map = Italy#Europe , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Italy##Location within Europe , pushpin_relief = yes , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type2 = Region , subdivision_name2 = Lazio , subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan city , subdivision_name3 = Rome Capital , government_footnotes= , government_type = Strong Mayor–Council , leader_title2 = Legislature , leader_name2 = Capitoline Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Legal Codes
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern history, modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Law Codes
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television * Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. In his book '' Getica'' (c. 551), the historian Jordanes writes that the Goths originated in southern Scandinavia, but the accuracy of this account is unclear. A people called the ''Gutones''possibly early Gothsare documented living near the lower Vistula River in the 1st century, where they are associated with the archaeological Wielbark culture. From the 2nd century, the Wielbark culture expanded southwards towards the Black Sea in what has been associated with Gothic migration, and by the late 3rd century it contributed to the formation of the Chernyakhov culture. By the 4th century at the latest, several Gothic groups were distinguishable, among whom the Thervingi and Greuthungi were the most powerful. During this time, Wulfila bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odoacer
Odoacer ( ; – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a soldier and statesman of barbarian background, who deposed the child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became Rex/Dux (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus Augustulus is traditionally seen as marking the end of the Western Roman Empire as well as Ancient Rome. Though the real power in Italy was in his hands, he represented himself as the client of the emperor in Constantinople, Zeno. Odoacer often used the Roman honorific patrician, granted by Zeno, but was referred to as a king ( la, rex) or duke ( la, dux) in many documents, so is not clear which was his actual charge. He himself used the title of king in the only surviving official document that emanated from his chancery, and it was also used by the consul Basilius. Odoacer introduced few important changes into the administrative system of Italy. He had the support of the Roman Senate and was able to distribute land to his followers without muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoric II
Theodoric II, ''Teodorico'' in Spanish and Portuguese, ( 426 – early 466) was the eighth King of the Visigoths, from 453 to 466. Biography Theoderic II, son of Theodoric I, obtained the throne by killing his elder brother Thorismund. The English historian Edward Gibbon writes that "he justified this atrocious deed by the design which his predecessor had formed of violating his alliance with the empire." In late 458 the Western Roman Emperor, Majorian entered Septimania to attack Theodoric and reclaim the province for the empire. Majorian defeated Theodoric at the Battle of Arelate, forcing the Visigoths to abandon Septimania and withdraw west to Aquitania. Under the new treaty with the Romans, the Visigoths had to relinquish their recent conquests in Hispania and return to federate status. However, after the assassination of Majorian in 461, Theodoric recaptured Septimania and invaded Hispania again. Theodoric sided with Ricimer and the new emperor Libius Severus against Majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is known as the Migration Period. The Visigoths emerged from earlier Gothic groups, including a large group of Thervingi, who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and the Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under their first leader, Alaric I, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sacked Rome in August 410. Afterwards, they began settling down, first in southern Gaul and eventually in Hispania, where they founded the Visigothic Kingdom and maintained a presence from the 5th to the 8th centuries AD. The Visigoths first settled in southern Gaul as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
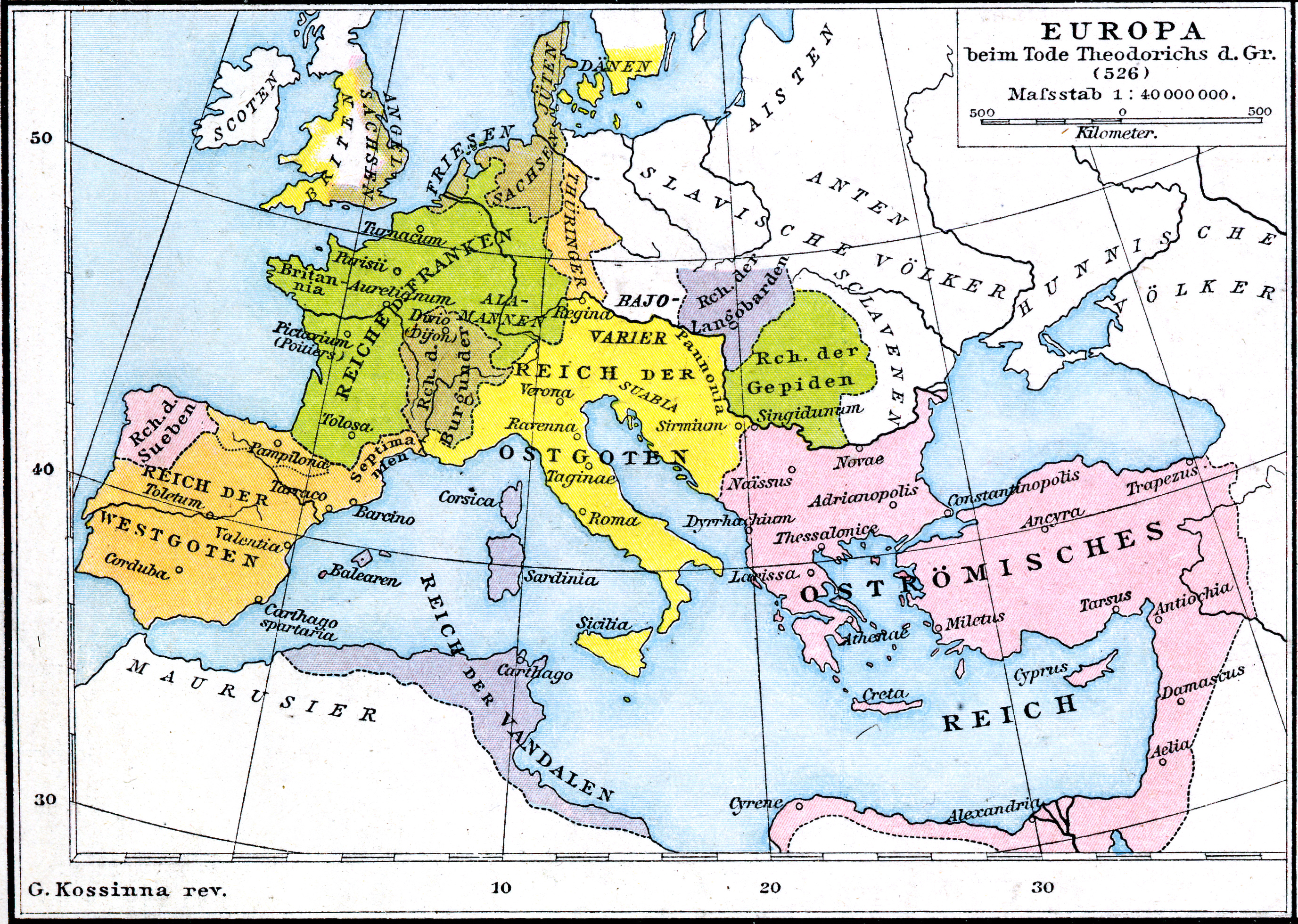
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Gregorianus
The ''Codex Gregorianus'' (Eng. Gregorian Code) is the title of a collection of constitutions (legal pronouncements) of Roman emperors over a century and a half from the 130s to 290s AD. It is believed to have been produced around 291–4 but the exact date is unknown."Codex Gregorianus" in ''The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'', Oxford University Press, New York & Oxford, 1991, p. 474. History The Codex takes its name from its author, a certain Gregorius (or Gregorianus), about whom nothing is known for certain, though it has been suggested that he acted as the ''magister libellorum'' (drafter of responses to petitions) to the emperors Carinus and Diocletian in the 280s and early 290s. The work does not survive intact and much about its original form remains obscure, though from the surviving references and excerpts it is clear that it was a multi-book work, subdivided into thematic headings (''tituli'') that contained a mixture of rescripts to private petitioners, letters to off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century, having crossed the Lower Danube. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under the influence of the Amal dynasty, the family of Theodoric the Great. After the death of Attila and collapse of the Hunnic empire represented by the Battle of Nedao in 453, the Amal family began to form their kingdom in Pannonia. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths, but instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Pithou
Pierre Pithou (1 November 1539 – 1 November 1596) was a French lawyer and scholar. He is also known as Petrus Pithoeus. Life He was born at Troyes. From childhood he loved literature, and his father Pierre encouraged this interest. Young Pithou was called to the Paris bar in 1560. On the outbreak of the second war of religion in 1567, Pithou, who was a Calvinist, withdrew to Sedan, France and afterwards to Basel, returning to France on the publication of the edict of pacification. Soon afterwards he accompanied the duc de Montmorency on his embassy to England, returning shortly before the massacre of St Bartholomew, in which he narrowly escaped with his life. Next year he followed the example of the future Henry IV of France Henry IV (french: Henri IV; 13 December 1553 – 14 May 1610), also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre (as Henry III) from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monarc ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)