|
Enterocin
Enterocin and its derivatives are bacteriocins synthesized by the lactic acid bacteria, ''Enterococcus''. This class of polyketide antibiotics are effective against foodborne pathogens including '' L. monocytogenes, Listeria,'' and ''Bacillus.'' Due to its proteolytic degradability in the gastrointestinal tract, enterocin is used for controlling foodborne pathogens via human consumption. History Enterocin was discovered from soil and marine '' Streptomyces'' strains as well as from marine ascidians of '' Didemnum'' and it has also been found in a mangrove strains '' Streptomyces qinglanensis'' and '' Salinispora pacifica''. Total synthesis The total synthesis of enterocin has been reported. Biosynthesis Enterocin has a caged, tricyclic, nonaromatic core and its formation undergoes a flavoenzyme (EncM) catalyzed Favorskii-like rearrangement of a poly(beta-carbonyl). Studies done on enterocin have shown that it is biosynthesized from a type II polyketide synthase (PKS) pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterocin Biosynthesis
Enterocin and its derivatives are bacteriocins synthesized by the lactic acid bacteria, ''Enterococcus''. This class of polyketide antibiotics are effective against foodborne pathogens including ''Listeria monocytogenes, L. monocytogenes, Listeria,'' and ''Bacillus.'' Due to its proteolytic degradability in the gastrointestinal tract, enterocin is used for controlling foodborne pathogens via human consumption. History Enterocin was discovered from soil and marine ''Streptomyces'' strains as well as from marine ascidians of ''Didemnum'' and it has also been found in a mangrove strains ''Streptomyces qinglanensis'' and ''Salinispora pacifica''. Total synthesis The total synthesis of enterocin has been reported. Biosynthesis Enterocin has a caged, tricyclic, Aromaticity, nonaromatic core and its formation undergoes a flavoenzyme (EncM) catalyzed Favorskii rearrangement, Favorskii-like rearrangement of a poly(beta-carbonyl). Studies done on enterocin have shown that it is biosy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriocin
Bacteriocins are proteinaceous or peptidic toxins produced by bacteria to inhibit the growth of similar or closely related bacterial strain(s). They are similar to yeast and paramecium killing factors, and are structurally, functionally, and ecologically diverse. Applications of bacteriocins are being tested to assess their application as narrow-spectrum antibiotics. Bacteriocins were first discovered by André Gratia in 1925. He was involved in the process of searching for ways to kill bacteria, which also resulted in the development of antibiotics and the discovery of bacteriophage, all within a span of a few years. He called his first discovery a ''colicine'' because it killed ''E. coli.'' Classification Bacteriocins are categorized in several ways, including producing strain, common resistance mechanisms, and mechanism of killing. There are several large categories of bacteriocin which are only phenomenologically related. These include the bacteriocins from gram-posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoic Acid
Benzoic acid is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, which was for a long time its only source. Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many secondary metabolites. Salts of benzoic acid are used as food preservatives. Benzoic acid is an important precursor for the industrial synthesis of many other organic substances. The salts and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates . History Benzoic acid was discovered in the sixteenth century. The dry distillation of gum benzoin was first described by Nostradamus (1556), and then by Alexius Pedemontanus (1560) and Blaise de Vigenère (1596). Justus von Liebig and Friedrich Wöhler determined the composition of benzoic acid. These latter also investigated how hippuric acid is related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
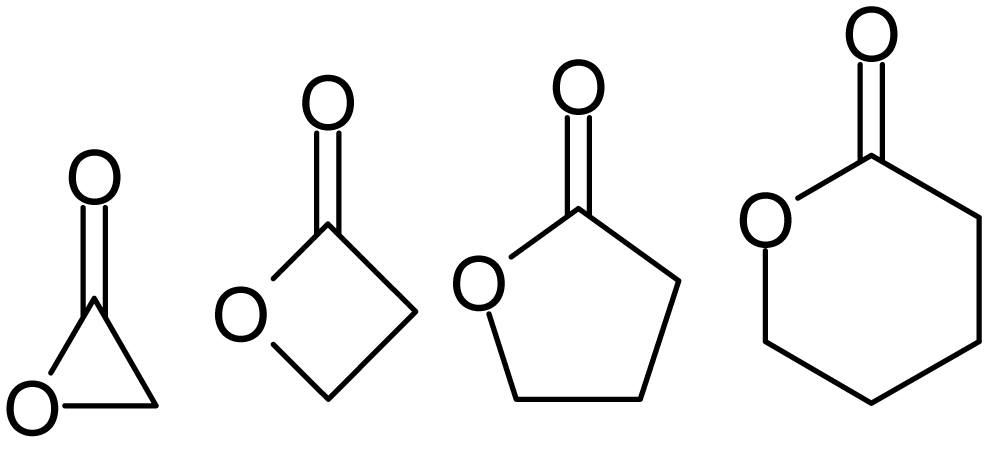
Lactones
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Heterocycles
Oxygen is the chemical element with the chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen Group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly Chemical reaction, reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is Earth's Abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element chemical bond, bind to form Allotropes of oxygen#Dioxygen, dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic molecule, diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has Geological history of oxygen, changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antisep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance (pharmacology), clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In 1963, Ronald W. Estabrook, Estabrook, David Y. Cooper, Cooper, and Otto Rosenthal, Rosenthal described the role of CYP as a catalyst in steroid hormone synthesis and drug metabolism. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of secondary metabolite, defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones. CYP enzymes have been identified in all kingdom (biology), kingdoms of life: animals, plants, fungus, fungi, protists, bacteria, and archaea, as well as in viruses. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherichia coli''. , more than 300,000 distinct CYP proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-methyltransferase
An O-methyltransferase (OMT) is a type of methyltransferase enzyme transferring a methyl group on a molecule. Examples are : * Acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase * Apigenin 4'-O-methyltransferase * Caffeate O-methyltransferase * Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase * Catechol O-methyltransferase * Chlorophenol O-methyltransferase * Columbamine O-methyltransferase * Demethylmacrocin O-methyltransferase * 3'-demethylstaurosporine O-methyltransferase * Demethylsterigmatocystin 6-O-methyltransferase * 3-demethylubiquinone-9 3-O-methyltransferase * 3,7-dimethylquercetin 4'-O-methyltransferase * Fatty-acid O-methyltransferase * Glucuronoxylan 4-O-methyltransferase * 10-hydroxydihydrosanguinarine 10-O-methyltransferase * 12-hydroxydihydrochelirubine 12-O-methyltransferase * 6-hydroxymellein O-methyltransferase * 3'-hydroxy-N-methyl-(S)-coclaurine 4'-O-methyltransferase * 8-hydroxyquercetin 8-O-methyltransferase * Iodophenol O-methyltransferase * Isobutyraldoxime O-methyltra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claisen Condensation
The Claisen condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in a β-keto ester or a β-diketone. It is named after Rainer Ludwig Claisen, who first published his work on the reaction in 1887. Requirements At least one of the reagents must be enolizable (have an α-proton and be able to undergo deprotonation to form the enolate anion). There are a number of different combinations of enolizable and nonenolizable carbonyl compounds that form a few different types of Claisen. The base used must not interfere with the reaction by undergoing nucleophilic substitution or addition with a carbonyl carbon. For this reason, the conjugate sodium alkoxide base of the alcohol formed (e.g. sodium ethoxide if ethanol is formed) is often used, since the alkoxide is regenerated. In mixed Claisen condensations, a non-nucleophilic base such as lithium diisopropylamide, or L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malonyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid. Functions It plays a key role in chain elongation in fatty acid biosynthesis and polyketide biosynthesis. Fatty acid biosynthesis Malonyl-CoA provides 2-carbon units to fatty acids and commits them to fatty acid chain synthesis. Malonyl-CoA is formed by carboxylating acetyl-CoA using the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase. One molecule of acetyl-CoA joins with a molecule of bicarbonate,Nelson D, Cox M (2008) ''Lehninger principles of biochemistry''. 5th Ed: p. 806 requiring energy rendered from ATP. Malonyl-CoA is utilised in fatty acid biosynthesis by the enzyme malonyl coenzyme A:acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT). MCAT serves to transfer malonate from malonyl-CoA to the terminal thiol of ''holo''-acyl carrier protein (ACP). Polyketide biosynthesis MCAT is also involved in bacterial polyketide biosynthesis. The enzyme MCAT together with an acyl carrier protein (ACP), and a polyketide synthase (PKS) and chain-length f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
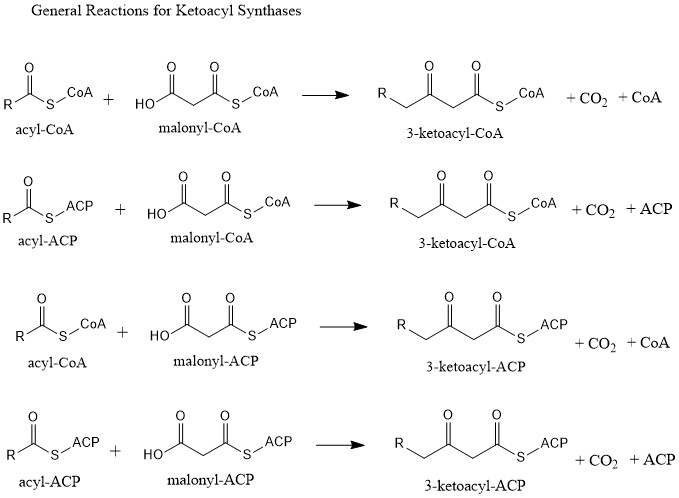
Ketoacyl Synthase
Ketoacyl synthases (KSs) catalyze the condensation reaction of acyl-CoA or acyl-acyl ACP with malonyl-CoA to form 3-ketoacyl-CoA or with malonyl-ACP to form 3-ketoacyl-ACP. This reaction is a key step in the fatty acid synthesis cycle, as the resulting acyl chain is two carbon atoms longer than before. KSs exist as individual enzymes, as they do in type II fatty acid synthesis and type II polyketide synthesis, or as domains in large multidomain enzymes, such as type I fatty acid synthases (FASs) and polyketide synthases (PKSs). KSs are divided into five families: KS1, KS2, KS3, KS4, and KS5. Multidomain enzyme systems Fatty acid synthase Fatty acid synthase (FAS) is the enzyme system involved in de novo fatty acid synthesis. FAS is an iterative multienzyme consisting of several component enzymes, one of which is ketoacyl synthase. There are two types of FASs: type I and type II. Type I FASs are highly integrated multidomain enzymes. They contain discrete functional domains resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyl Carrier Protein
The acyl carrier protein (ACP) is a cofactor of both fatty acid and polyketide biosynthesis machinery. It is one of the most abundant proteins in cells of ''E. coli.'' In both cases, the growing chain is bound to the ACP via a thioester derived from the distal thiol of a 4'-phosphopantetheine moiety. Structure The ACPs are small negatively charged α-helical bundle proteins with a high degree of structural and amino acid similarity. The structures of a number of acyl carrier proteins have been solved using various NMR and crystallography techniques. The ACPs are related in structure and mechanism to the peptidyl carrier proteins (PCP) from nonribosomal peptide synthases. Biosynthesis Subsequent to the expression of the inactive ''apo'' ACP, the 4'-phosphopantetheine moiety is attached to a serine residue. This coupling is mediated by acyl carrier protein synthase (ACPS), a 4'-phosphopantetheinyl transferase. 4'-Phosphopantetheine is a prosthetic group of several acyl carrier pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |