|
Employee Motivation
Employee motivation is an intrinsic and internal drive to put forth the necessary effort and action towards work-related activities. It has been broadly defined as the "psychological forces that determine the direction of a person's behavior in an organisation, a person's level of effort and a person's level of persistence". Also, "Motivation can be thought of as the willingness to expend energy to achieve a goal or a reward. Motivation at work has been defined as 'the sum of the processes that influence the arousal, direction, and maintenance of behaviors relevant to work settings'." Motivated employees are essential to the success of an organization as motivated employees are generally more productive at the work place. Motivational techniques Motivation is the impulse that an individual has in a job or activity to reaching an end goal. There are multiple theories of how best to motivate workers, but all agree that a well-motivated work force means a more productive work force. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effortfulness
In psychology, effortfulness is the subjective experience of exertion when performing an activity, especially the mental concentration and energy required. In many applications, effortfulness is simply reported by a patient, client, or experimental subject. There has been some work establishing an association among reported effortfulness and objective measures, such as in brain imaging. Effortfulness is used as a diagnostic indicator in medical and psychological diagnosis and assessment. It is also used as an indicator in psychological experimentation, especially in the field of memory. In the study of aging, Patrick Rabbitt proposed an effortfulness hypothesis in the 1960s: that as their hearing became less acute with age, people would require additional effort to make out what was said and that this effort made it harder to remember it. Neuroscience of Effortfulness A study suggests that the neurotransmitter dopamine may be play a role in enhancing an animal’s motivatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Item
Action Item is a four-piece pop rock band based out of Bergen County, NJ. History Action Item started off as a five-piece consisting of Cag, Li, Brozek, Buczkowski, and Politz. After self-releasing numerous songs via their Myspace page, the four current members of Action Item parted way with Joe Politz, their first vocalist, and started a nearly year-long search for a new permanent vocalist. Eventually, Brian Cag and Anthony Li would take over the vocal duties, oftentimes both singing on the same songs. In early 2008, Action Item headed to Chicago, IL to record their debut EP with Tom Schleiter of Powerspace. The songs recorded during this session would become Action Item's debut EP The World And I. After the recording of The World And I, Action Item recruited a guitarist/keyboardist/vocalist by the name of Mark Shami, formerly of the Bergen County, NJ band Off Broadway. Shortly thereafter The World And I was released on June 14, 2008. The band spent the summer of 2008 doing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Job Security
Job security is the probability that an individual will keep their job; a job with a high level of security is such that a person with the job would have a small chance of losing it. Many factors threaten job security: globalization, outsourcing, downsizing, recession, and new technology, to name a few. Basic economic theory holds that during periods of economic expansion businesses experience increased demand, which in turn necessitates investment in more capital or labor. When businesses are experiencing growth, job confidence and security typically increase. The opposite often holds true during a recession: businesses experience reduced demand and look to downsize their workforces in the short term. Governments and individuals are both motivated to achieve higher levels of job security. Governments attempt to do this by passing laws (such as the U.S. Civil Rights Act of 1964) which make it illegal to fire employees for certain reasons. Individuals can influence their degree o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their unique metabolisms, often evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts. Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtain food in many different ecosystems. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food with intensive agriculture and distributes it through complex food processing and food distribution systems. This system of conventional agriculture relies heavily on fossil fuels, which means that the food and agricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. Water co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
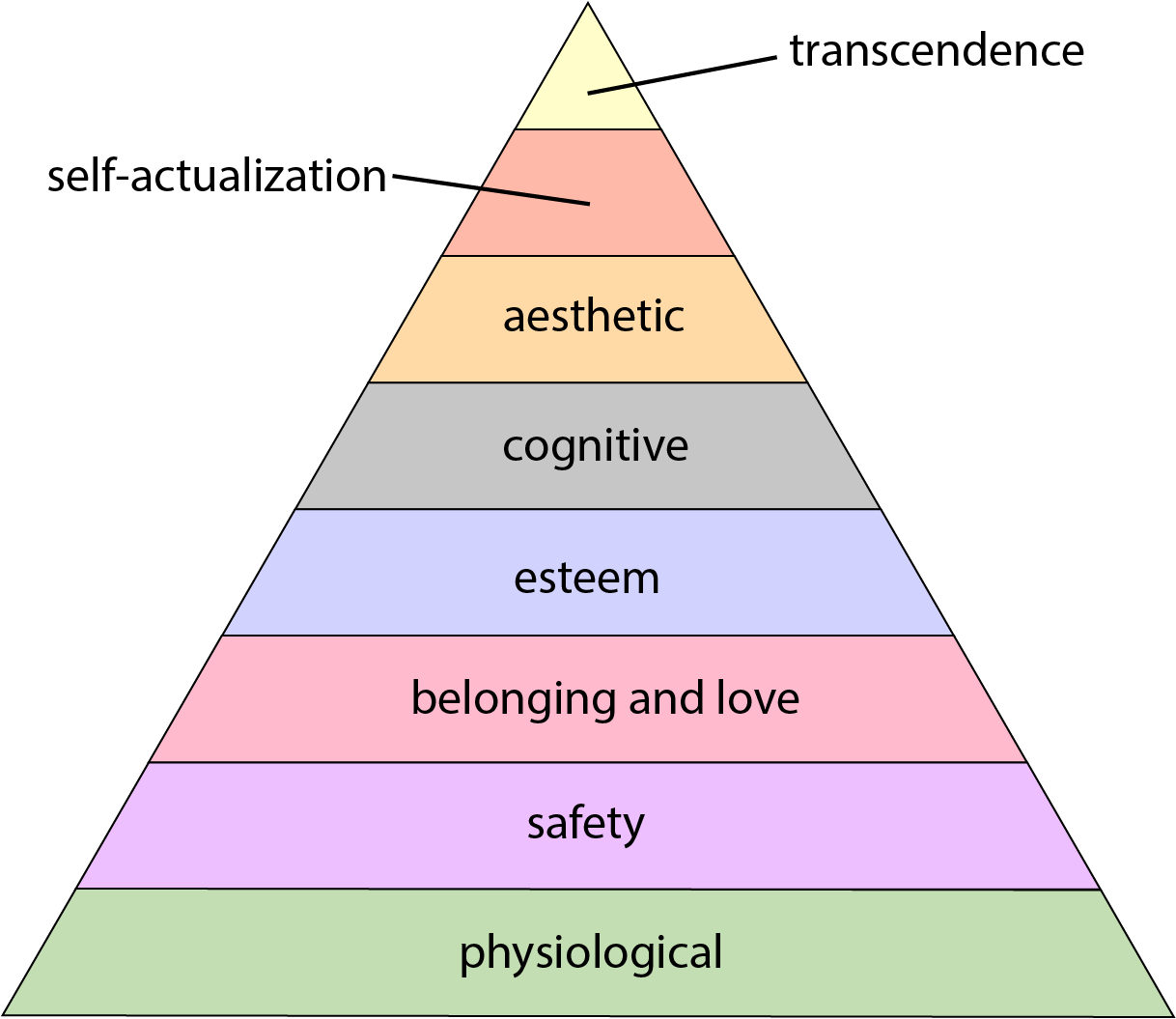
Maslow's Hierarchy Of Needs
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is an idea in psychology proposed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation" in the journal ''Psychological Review''. Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans' innate curiosity. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology, some of which focus on describing the stages of growth in humans. The theory is a classification system intended to reflect the universal needs of society as its base, then proceeding to more acquired emotions. The hierarchy of needs is split between deficiency needs and growth needs, with two key themes involved within the theory being individualism and the prioritization of needs. While the theory is usually shown as a pyramid in illustrations, Maslow himself never created a pyramid to represent the hierarchy of needs. The hierarchy of needs is a psychological idea and also an assessment tool, particularly in education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Maslow
Abraham Harold Maslow (; April 1, 1908 – June 8, 1970) was an American psychologist who was best known for creating Maslow's hierarchy of needs, a theory of psychological health predicated on fulfilling innate human needs in priority, culminating in self-actualization. Maslow was a psychology professor at Brandeis University, Brooklyn College, New School for Social Research, and Columbia University. He stressed the importance of focusing on the positive qualities in people, as opposed to treating them as a "bag of symptoms". Hoffmann (1988), p. 109. A ''Review of General Psychology'' survey, published in 2002, ranked Maslow as the tenth most cited psychologist of the 20th century. Biography Youth Born in 1908 and raised in Brooklyn, New York, Maslow was the oldest of seven children. His parents were first-generation Jewish immigrants from Kiev, then part of the Russian Empire (now Kyiv, Ukraine), who fled from Czarist persecution in the early 20th century. They had deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absenteeism
Absenteeism is a habitual pattern of absence from a duty or obligation without good reason. Generally, absenteeism is unplanned absences. Absenteeism has been viewed as an indicator of poor individual performance, as well as a breach of an implicit contract between employee and employer. It is seen as a management problem, and framed in economic or quasi-economic terms. More recent scholarship seeks to understand absenteeism as an indicator of psychological, medical, or social adjustment to work. Workplace High absenteeism in the workplace may be indicative of poor morale, but absences can also be caused by workplace hazards or sick building syndrome. Measurements such as the Bradford factor, a measurement tool to analyze absenteeism which believes short, unplanned absences effect the work group more than long term absences, do not distinguish between absence for genuine illness reasons and absence for non-illness related reasons. In 2013, the UK CIPD estimated that the average ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employee Engagement
Employee engagement is a fundamental concept in the effort to understand and describe, both qualitatively and quantitatively, the nature of the relationship between an organization and its employees. An "engaged employee" is defined as one who is fully absorbed by and enthusiastic about their work and so takes positive action to further the organization's reputation and interests. An engaged employee has a positive attitude towards the organization and its values. In contrast, a disengaged employee may range from someone doing the bare minimum at work (aka 'coasting'), up to an employee who is actively damaging the company's work output and reputation. An organization with "high" employee engagement might therefore be expected to outperform those with "low" employee engagement. Employee engagement first appeared as a concept in management theory in the 1990s, becoming widespread in management practice in the 2000s, but it remains contested. It stands in an unspecified relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workplace Wellness
Workplace wellness, also known as corporate wellbeing outside the United States, is a broad term used to describe activities, programs, and/or organizational policies designed to support healthy behavior in the workplace. This often involves health education, medical screenings, weight management programs, and onsite fitness programs or facilities. Recent developments in wearable health technology have led to a rise in self-tracking devices as workplace wellness. Other common examples of workplace wellness organizational policies include allowing flex-time for exercise, providing onsite kitchen and eating areas, offering healthy food options in vending machines, holding "walk and talk" meetings, and offering financial and other incentives for participation. Over time, workplace wellness has expanded from single health promotion interventions to describe a larger project intended to create a healthier working environment. Companies most commonly subsidize workplace wellness program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flextime
Flextime (also spelled flexitime ( BE) or flex-time) is a flexible hours schedule that allows workers to alter their workday and decide/adjust their start and finish times. In contrast to traditional work arrangements that require employees to work a standard 9a.m. to 5p.m. day, flextime typically involves a "core" period of the day during which employees are required to be at work (e.g., between 11a.m. and 3p.m.), and a "bandwidth" period within which all required hours must be worked (e.g., between 5:30 a.m. and 7:30 p.m.). The working day outside of the "core" period is "flexible time", in which employees can choose when they work, subject to achieving total daily, weekly or monthly hours within the "bandwidth" period set by employers, and subject to the necessary work being done. The total working time required of employees on flextime schedules is the same as that required under traditional work schedules. A flextime policy allows staff to determine when they will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |