|
Efficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid making mistakes or wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time while performing a task. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste. In more mathematical or scientific terms, it signifies the level of performance that uses the least amount of inputs to achieve the highest amount of output. It often specifically comprises the capability of a specific application of effort to produce a specific outcome with a minimum amount or quantity of waste, expense, or unnecessary effort.Sickles, R., and Zelenyuk, V. (2019).Measurement of Productivity and Efficiency: Theory and Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . Efficiency refers to very different inputs and outputs in different fields and industries. In 2019, the European Commission said: "Resource efficiency means using the Earth's limited resources in a sustainable procent manner while minimising impacts on the envi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Energy Conversion Efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency (''η'') is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The input, as well as the useful output may be chemical, electric power, mechanical work, light (radiation), or heat. The resulting value, ''η'' (eta), ranges between 0 and 1. Overview Energy conversion efficiency depends on the usefulness of the output. All or part of the heat produced from burning a fuel may become rejected waste heat if, for example, work is the desired output from a thermodynamic cycle. Energy converter is an example of an energy transformation. For example, a light bulb falls into the categories energy converter. \eta = \frac Even though the definition includes the notion of usefulness, efficiency is considered a technical or physical term. Goal or mission oriented terms include effectiveness and efficacy. Generally, energy conversion efficiency is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1.0, or 0% to 100%. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
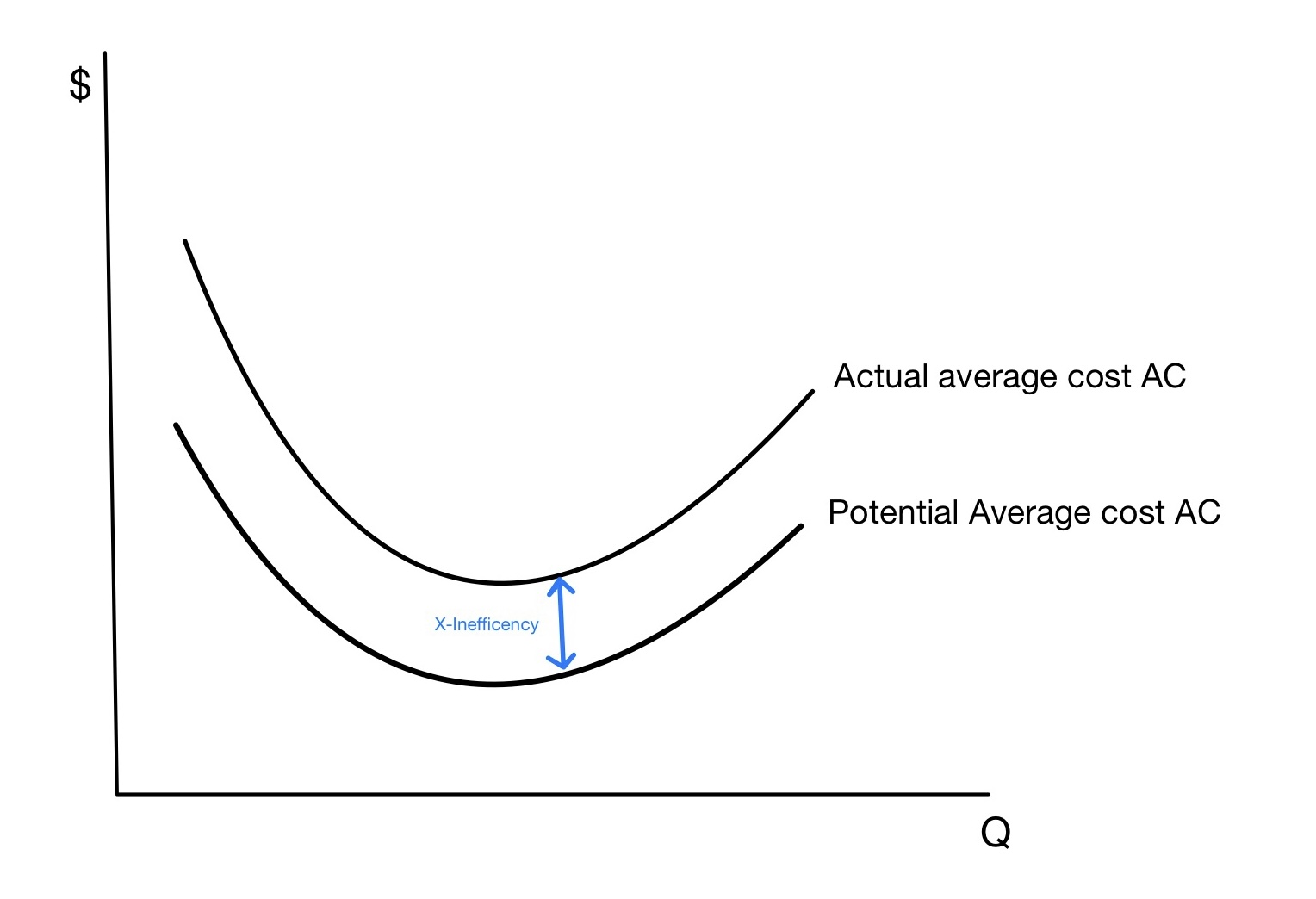
X-inefficiency
X-inefficiency is a concept used in economics to describe instances where firms go through internal inefficiency resulting in higher production costs than required for a given output. This inefficiency can result from various factors, such as outdated technology, inefficient production processes, poor management, and lack of competition, and it results in lower profits for the inefficient firm(s) and higher prices for consumers. The concept of X-inefficiency was introduced by Harvey Leibenstein. in 1966, Harvard University Professor Harvey Leibenstein first introduced the concept of X-inefficiency in his paper "Allocative Efficiency vs. X- Efficiency", which was published in '' American Economic Review''. X-Inefficiency refers to a firm's inability to fully utilize its resources, resulting in an output level that falls short of the maximum potential achievable given the resources and environment which is referred to as the efficiency frontier. More so, X-inefficiency focuses on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pareto Efficiency
In welfare economics, a Pareto improvement formalizes the idea of an outcome being "better in every possible way". A change is called a Pareto improvement if it leaves at least one person in society better off without leaving anyone else worse off than they were before. A situation is called Pareto efficient or Pareto optimal if all possible Pareto improvements have already been made; in other words, there are no longer any ways left to make one person better off without making some other person worse-off. In social choice theory, the same concept is sometimes called the unanimity principle, which says that if ''everyone'' in a society (strict inequality, non-strictly) prefers A to B, society as a whole also non-strictly prefers A to B. The Pareto frontier, Pareto front consists of all Pareto-efficient situations. In addition to the context of efficiency in ''allocation'', the concept of Pareto efficiency also arises in the context of productive efficiency, ''efficiency in prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heat Engine
A heat engine is a system that transfers thermal energy to do mechanical or electrical work. While originally conceived in the context of mechanical energy, the concept of the heat engine has been applied to various other kinds of energy, particularly electrical, since at least the late 19th century. The heat engine does this by bringing a working substance from a higher state temperature to a lower state temperature. A heat source generates thermal energy that brings the working substance to the higher temperature state. The working substance generates work in the working body of the engine while transferring heat to the colder sink until it reaches a lower temperature state. During this process some of the thermal energy is converted into work by exploiting the properties of the working substance. The working substance can be any system with a non-zero heat capacity, but it usually is a gas or liquid. During this process, some heat is normally lost to the surroundings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
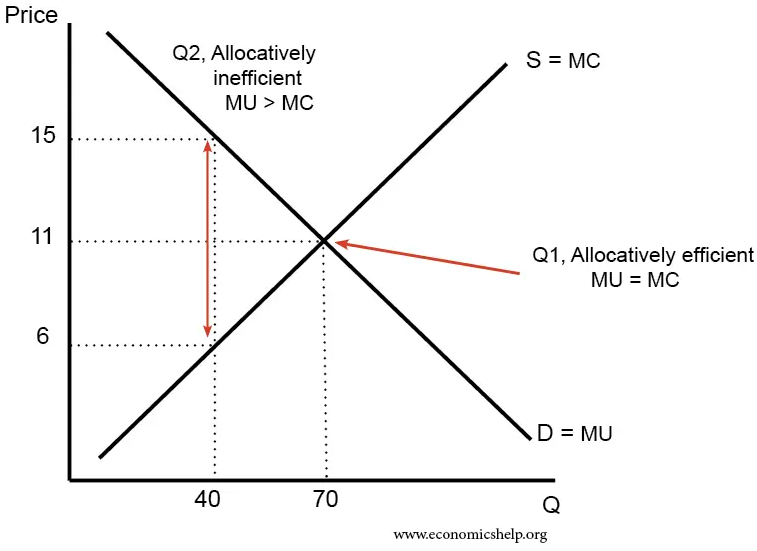
Allocative Efficiency
Allocative efficiency is a state of the economy in which production is aligned with the preferences of consumers and producers; in particular, the set of outputs is chosen so as to maximize the Economic surplus, social welfare of society. This is achieved if every produced good or service has a marginal benefit equal to or greater than the marginal cost of production. Description In economics, allocative efficiency entails production at the point on the production possibilities frontier that is optimal for society. In contract theory, allocative efficiency is achieved in a contract in which the skill demanded by the offering party and the skill of the agreeing party are the same. Resource allocation efficiency includes two aspects: # At the macro aspect, it is the allocation efficiency of social resources, which is achieved through the economic system arrangements of the entire society. # The micro aspect is the efficient use of resources, which can be understood as the produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Economic Inefficiency
In microeconomics, economic efficiency, depending on the context, is usually one of the following two related concepts: * Allocative efficiency, Allocative or Pareto efficiency: any changes made to assist one person would harm another. * Productive efficiency: no additional output of one good can be obtained without decreasing the output of another good, and Production (economics), production proceeds at the lowest possible average total cost. These definitions are not equivalent: a Market (economics), market or other economic system may be allocatively but not productively efficient, or productively but not allocatively efficient. There are also #Criteria, other definitions and measures. All characterizations of economic efficiency are encompassed by the more general engineering concept that a system is Efficiency, efficient or optimal when it maximizes desired outputs (such as utility) given available inputs. Standards of thought There are two main standards of thought on econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrical Efficiency
The efficiency of a system in electronics and electrical engineering is defined as useful power output divided by the total electrical power consumed (a vulgar fraction, fractional Expression (mathematics), expression), typically denoted by the Greek alphabet, Greek small letter eta (η – ήτα). : \mathrm=\frac If energy output and input are expressed in the same units, efficiency is a dimensionless number. Where it is not customary or convenient to represent input and output energy in the same units, efficiency-like quantities have units associated with them. For example, the heat rate (efficiency), heat rate of a fossil fuel power station, fossil fuel power plant may be expressed in British thermal unit, BTU per kilowatt-hour. Luminous efficacy of a light source expresses the amount of visible light for a certain amount of power transfer and has the units of lumen (unit), lumens per watt. Efficiency of typical electrical devices ''Efficiency'' should not be confused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Data Envelopment Analysis
Data envelopment analysis (DEA) is a nonparametric method in operations research and economics for the estimation of production frontiers.Charnes et al (1978) DEA has been applied in a large range of fields including international banking, economic sustainability, police department operations, and logistical applicationsCharnes et al (1995)Emrouznejad et al (2016)Thanassoulis (1995) Additionally, DEA has been used to assess the performance of natural language processing models, and it has found other applications within machine learning.Zhou et al (2022)Guerrero et al (2022) Description DEA is used to empirically measure productive efficiency of decision-making units (DMUs). Although DEA has a strong link to production theory in economics, the method is also used for benchmarking in operations management, whereby a set of measures is selected to benchmark the performance of manufacturing and service operations. In benchmarking, the efficient DMUs, as defined by DEA, may not nece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Productive Efficiency
In microeconomic theory, productive efficiency (or production efficiency) is a situation in which the economy or an economic system (e.g., bank, hospital, industry, country) operating within the constraints of current industrial technology cannot increase production of one good without sacrificing production of another good. In simple terms, the concept is illustrated on a production possibility frontier (PPF), where all points on the curve are points of productive efficiency. An equilibrium may be productively efficient without being allocatively efficient — i.e. it may result in a distribution of goods where social welfare is not maximized (bearing in mind that social welfare is a nebulous objective function subject to political controversy). Productive efficiency is an aspect of economic efficiency that focuses on how to maximize output of a chosen product portfolio, without concern for whether your product portfolio is making goods in the right proportion; in misgu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
External Cost
In economics, an externality is an indirect cost (external cost) or indirect benefit (external benefit) to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced components that are involved in either consumer or producer consumption. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. The cost of air pollution to society is not paid by either the producers or users of motorized transport. Water pollution from mills and factories are another example. All (water) consumers are made worse off by pollution but are not compensated by the market for this damage. The concept of externality was first developed by Alfred Marshall in the 1890s and achieved broader attention in the works of economist Arthur Pigou in the 1920s. The prototypical example of a negative externality is environmental pollution. Pigou argued that a tax, equal to the marginal damage or marginal external cost, (later called a "Pigouv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Keynesian
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the productive capacity of the economy. It is influenced by a host of factors that sometimes behave erratically and impact production, employment, and inflation. Keynesian economists generally argue that aggregate demand is volatile and unstable and that, consequently, a market economy often experiences inefficient macroeconomic outcomes, including recessions when demand is too low and inflation when demand is too high. Further, they argue that these economic fluctuations can be mitigated by economic policy responses coordinated between a government and their central bank. In particular, fiscal policy actions taken by the government and monetary policy action ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Specific Impulse
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated ) is a measure of how efficiently a reaction mass engine, such as a rocket engine, rocket using propellant or a jet engine using fuel, generates thrust. In general, this is a ratio of the ''Impulse (physics), impulse'', i.e. change in momentum, ''per mass'' of propellant. This is equivalent to "thrust per massflow". The resulting unit is equivalent to velocity. If the engine expels mass at a constant exhaust velocity v_e then the thrust will be \mathbf = v_e \frac . If we integrate over time to get the total change in momentum, and then divide by the mass, we see that the specific impulse is equal to the exhaust velocity v_e . In practice, the specific impulse is usually lower than the actual physical exhaust velocity inefficiencies in the rocket, and thus corresponds to an "effective" exhaust velocity. That is, the specific impulse I_ in units of velocity *is defined by* : \mathbf = I_ \frac , where \mathbf is the average thrust. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |