|
Deverbal
Deverbal nouns are nouns that are derived from verbs or verb phrases. The formation of deverbal nouns is a type of nominalization (noun formation). Examples of deverbal nouns in English include ''organization'' (derived from the verb ''organize''), the noun ''construct'' (from the verb ''construct'' ), ''discovery'' (from the verb ''discover''), and ''opening'' (in the sense of 'aperture') from the verb ''open''. Distinction between deverbal nouns, verbal nouns, and gerunds in English In English, the ''deverbal noun'' stands in contrast with the ''verbal noun'' and the ''gerund''. A verbal noun has the same verb+''ing'' form as a participle or gerund. Syntactically, unlike a gerund, a verbal noun functions purely as a noun; it cannot take adverbs or objects. Semantically, like a gerund, a verbal noun directly names the action described by the verb, as in ''Brown's deft painting of his daughter is wonderful'', which describes the way that Brown paints, ''the building of the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deverbal Adjective
An attributive verb is a verb that modifies (expresses an attribute of) a noun in the manner of an attributive adjective, rather than express an independent idea as a predicate. In English (and in most European languages), verb forms that can be used attributively are typically non-finite forms — participles and infinitives — as well as certain verb-derived words that function as ordinary adjectives. All words of these types may be called verbal adjectives, although those of the latter type (those that behave grammatically like ordinary adjectives, with no verb-like features) may be distinguished as deverbal adjectives. An example of a verbal adjective with verb-like features is the word ''wearing'' in the sentence ''The man wearing a hat is my father'' (it behaves as a verb in taking an object, ''a hat'', although the resulting phrase ''wearing a hat'' functions like an attributive adjective in modifying ''man''). An example of a deverbal adjective is the word ''interesting'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okurigana
are kana suffixes following kanji stems in Japanese written words. They serve two purposes: to inflect adjectives and verbs, and to force a particular kanji to have a specific meaning and be read a certain way. For example, the plain verb form (''miru'', "see") inflects to past tense (''mita'', "saw"), where is the kanji stem, and る and た are okurigana, written in hiragana script. With very few exceptions, okurigana are only used for kun'yomi (native Japanese readings), not for on'yomi (Chinese readings), as Chinese morphemes do not inflect in Japanese, and their pronunciation is inferred from context, since many are used as parts of compound words (kango). The technique in which native scripts are used to inflect adjectives or verbs was first used by Korean scribes in the form of gugyeol, and later spread to Japan. When used to inflect an adjective or verb, okurigana can indicate aspect (perfective versus imperfective), affirmative or negative meaning, or grammatical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
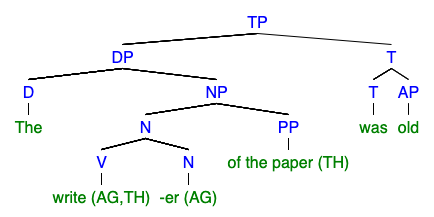
Nominalization
In linguistics, nominalization or nominalisation is the use of a word that is not a noun (e.g., a verb, an adjective or an adverb) as a noun, or as the head of a noun phrase. This change in functional category can occur through morphological transformation, but it does not always. Nominalization can refer, for instance, to the process of producing a noun from another part of speech by adding a derivational affix (e.g., the noun ''legalization'' from the verb ''legalize''), but it can also refer to the complex noun that is formed as a result. Nominalization is also known as "nouning". Some languages simply allow verbs to be used as nouns without inflectional difference (conversion or zero derivation), while others require some form of morphological transformation. English has cases of both. Nominalization is a natural part of language, but some instances are more noticeable than others. Writing advice sometimes focuses on avoiding overuse of nominalization. In various lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-ing
''-ing'' is a suffix used to make one of the inflected forms of English verbs. This verb form is used as a present participle, as a gerund, and sometimes as an independent noun or adjective. The suffix is also found in certain words like ''morning'' and ''ceiling'', and in names such as ''Browning''. Etymology and pronunciation The Modern English ''-ing'' ending, which is used to form both gerunds and present participles of verbs (i.e. in noun and adjective uses), derives from two different historical suffixes. The gerund (noun) use comes from Middle English , which is from Old English , (suffixes forming nouns from verbs). These in turn are from Proto-Germanic ''*-inga-'', ''*-unga-'', ''*-ingō'', ''*-ungō'', which derives from Proto-Indo-European . This use of English ''-ing'' is thus cognate with the suffix of Dutch, West Frisian, the North Germanic languages, and with German . The ''-ing'' of Modern English in its participial (adjectival) use comes from Middle Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verbal Noun
A verbal noun or gerundial noun is a verb form that functions as a noun. An example of a verbal noun in English is 'sacking' as in the sentence "The sacking of the city was an epochal event" (''sacking'' is a noun formed from the verb ''sack''). Verbal nouns are morphologically related to non-finite verb forms, but they are not themselves non-finite verbs. Non-finite verb forms are forms such as gerunds, infinitives and participles in English. Some grammarians use the term "verbal noun" to cover verbal noun, gerund, and nominal infinitive. Some may use the term "gerund" to cover both verbal noun and gerund. "Verbal noun" has often been treated as a synonym for "gerund". This article includes only gerundial nouns within the scope of "verbal nouns", excluding gerunds, nominal infinitives, and nouns formed from verbs through derivational processes. Outside of English, the term "verbal noun" may be used for 1) the citation form of verbs such as the masdar in Arabic and the verbal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerund
In linguistics, a gerund ( abbreviated ) is any of various nonfinite verb forms in various languages; most often, but not exclusively, one that functions as a noun. In English, it has the properties of both verb and noun, such as being modifiable by an adverb and being able to take a direct object. The term "''-ing'' form" is often used in English to refer to the gerund specifically. Traditional grammar makes a distinction within ''-ing'' forms between present participles and gerunds, a distinction that is not observed in such modern grammars as ''A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language'' and '' The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language''. Traditional use The Latin gerund, in a restricted set of syntactic contexts, denotes the sense of the verb in isolation after certain prepositions, and in certain uses of the genitive, dative, and ablative cases. It is very rarely combined with dependent sentence elements such as object. To express such concepts, the constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Nelson Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Grand Canyon, utopia'', etc. * Actions: ''swimming, exercises, diffusions, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Qualities: ''colors, lengths, deafness, weights, roundness, symmetry, warp speed,'' etc. * Mental or physical states of existence: ''jealousy, sleep, heat, joy, stomachache, confusion, mind meld,'' etc. Lexical categories ( parts of speech) are defined in terms of the ways in which their members combine with other kinds of expressions. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abat
Abat is a community in the former Shalë municipality, Shkodër County, northern Albania Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares .... At the 2015 local government reform it became part of the municipality Shkodër. References Populated places in Shkodër Villages in Shkodër County {{Shkodër-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiragana
is a Japanese syllabary, part of the Japanese writing system, along with ''katakana'' as well as ''kanji''. It is a phonetic lettering system. The word ''hiragana'' literally means "flowing" or "simple" kana ("simple" originally as contrasted with kanji). Hiragana and katakana are both kana systems. With few exceptions, each mora in the Japanese language is represented by one character (or one digraph) in each system. This may be either a vowel such as ''"a"'' (hiragana あ); a consonant followed by a vowel such as ''"ka"'' (か); or ''"n"'' ( ん), a nasal sonorant which, depending on the context, sounds either like English ''m'', ''n'' or ''ng'' () when syllable-final or like the nasal vowels of French language, French, Portuguese language, Portuguese or Polish language, Polish. Because the characters of the kana do not represent single consonants (except in the case of ん "n"), the kana are referred to as syllabic symbols and not alphabetic letters. Hiragana is used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumfix
A circumfix (abbreviated ) (also confix or ambifix) is an affix which has two parts, one placed at the start of a word, and the other at the end. Circumfixes contrast with prefixes, attached to the beginnings of words; suffixes, attached at the end; and infixes, inserted in the middle. Circumfixes are common in Malay and Georgian. Examples are used to mark off circumfixes. Germanic languages The circumfix is probably most widely known from the German past participle, which is ''ge-'-t'' (ge- prefix + -t suffix) for regular verbs. The verb ''spiel-en'', for example, has the participle ''ge-spiel-t''. Dutch has a similar system (''spel-en'' → ''ge-speel-d'' in this case). In Dutch, the circumfix ''ge-'-te'' (ge- prefix + -te suffix) can be used to form certain collective nouns (''berg'' (mountain) → ''ge-berg-te'' (mountain range)). East Asian languages In Japanese, some linguists consider ''o--ni naru'' (o- honorific prefix + ni particle + verb naru) and ''o--suru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy''. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed. Prefixes, like other affixes, can be either inflectional, creating a new form of the word with the same basic meaning and same lexical category (but playing a different role in the sentence), or derivational, creating a new word with a new semantic meaning and sometimes also a different lexical category. Prefixes, like all other affixes, are usually bound morphemes. In English, there are no inflectional prefixes; English uses suffixes instead for that purpose. The word ''prefix'' is itself made up of the stem ''fix'' (meaning "attach", in this case), and the prefix ''pre-'' (meaning "before"), both o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |