|
Demyelinating
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Rather, myelin sheaths the nerve in segments: in general, each axon is encased with multiple long myelinated sections with short gaps in between called nodes of Ranvier. Myelin is formed in the central nervous system (CNS; brain, spinal cord and optic nerve) by glial cells called oligodendrocytes and in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) by glial cells called Schwann cells. In the CNS, axons carry electrical signals from one nerve cell body to another. In the PNS, axons carry signals to muscles and glands or from sensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demyelinating Disorder
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn, the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency in sensation, movement, cognition, or other functions depending on which nerves are involved. Demyelinating diseases can be caused by genetics, infectious agents, autoimmune reactions, and other unknown factors. Proposed causes for demyelination include genetics and environmental factors such as being triggered by a viral infection or chemical exposure. Organophosphate poisoning by commercial insecticides such as sheep dip, weed killers, and flea treatment preparations for pets, can also result in nerve demyelination. Chronic neuroleptic exposure may cause demyelination. Vitamin B12 deficiency may also result in dysmyelination. Demyelinating diseases are traditionally classified in two kinds: demyelinating myelinoclastic diseases and dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
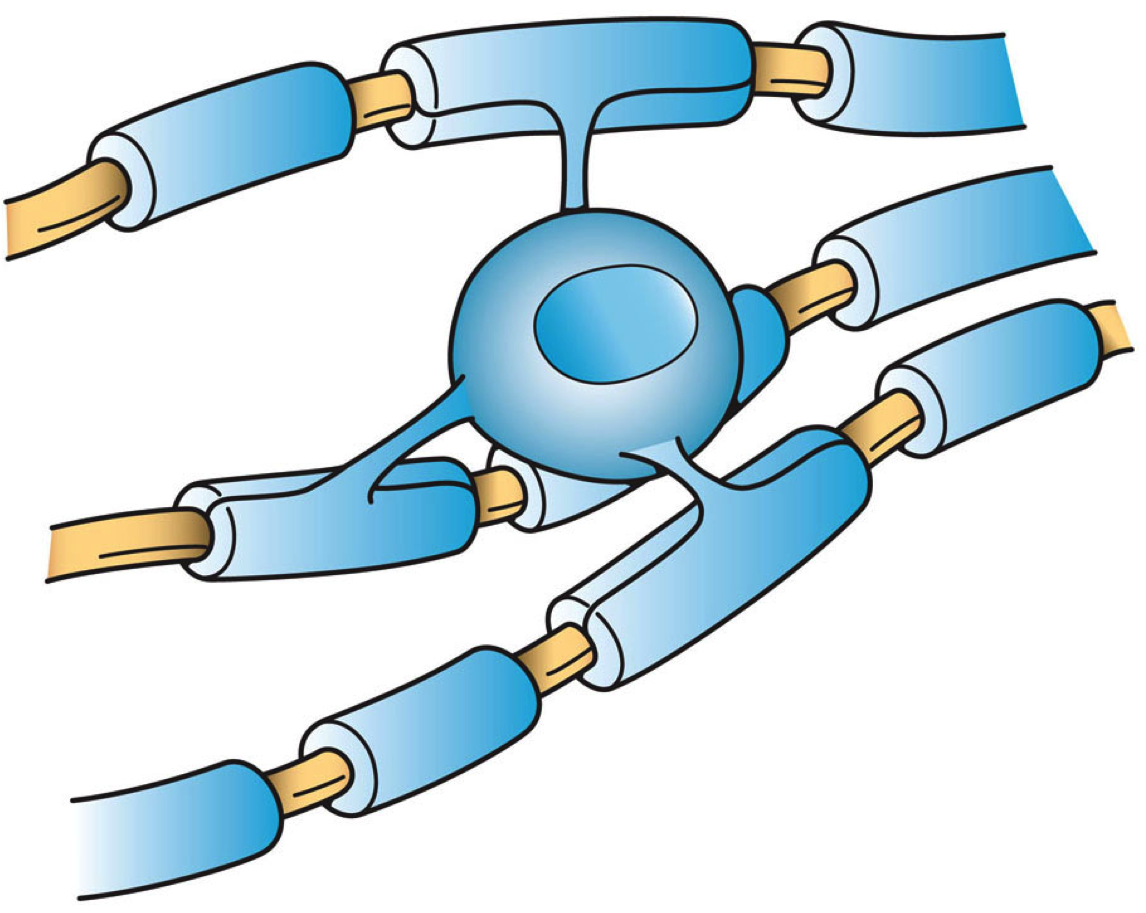
Axons
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the Soma (biology), nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the peripheral nervous system, periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the Peripheral nervous system, peripheral and Central nervous system, central neurons. Nerve fibers are Axon#Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligodendrocyte
Oligodendrocytes (), or oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axons in the central nervous system of jawed vertebrates, equivalent to the function performed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. Oligodendrocytes do this by creating the myelin sheath. A single oligodendrocyte can extend its processes to 50 axons, wrapping approximately 1 μm of myelin sheath around each axon; Schwann cells, on the other hand, can wrap around only one axon. Each oligodendrocyte forms one segment of myelin for several adjacent axons. Oligodendrocytes are found only in the central nervous system, which comprises the brain and spinal cord. These cells were originally thought to have been produced in the ventral neural tube; however, research now shows oligodendrocytes originate from the ventral ventricular zone of the embryonic spinal cord and possibly have some concentrations in the forebrain. They are the last cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins. The peripheral nervous system can be divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, the cranial nerves are part of the PNS with the exception of the optic nerve (cranial nerve II), along with the retina. The second cranial nerve is not a true peripheral nerve but a tract of the diencephalon. Cranial nerve ganglia, as with all ganglia, are part of the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Acquisition
Speech acquisition focuses on the development of vocal, acoustic and oral language by a child. This includes motor planning and execution, pronunciation, phonological and articulation patterns (as opposed to content and grammar which is language). Spoken speech consists of an organized set of sounds or phonemes that are used to convey meaning while language is an arbitrary association of symbols used according to prescribed rules to convey meaning. While grammatical and syntactic learning can be seen as a part of language acquisition, speech acquisition includes the development of speech perception and speech production over the first years of a child's lifetime. There are several models to explain the norms of speech sound or phoneme acquisition in children. Development of speech perception Sensory learning concerning acoustic speech signals already starts during pregnancy. Hepper and Shahidullah (1992) described the progression of fetal response to different pure tone frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramaticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells
Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs), also known as oligodendrocyte precursor cells, NG2-glia, O2A cells, or polydendrocytes, are a subtype of glia in the central nervous system named for their essential role as precursors to oligodendrocytes. They are typically identified by coexpression of PDGFRA and NG2. OPCs play a critical role in developmental and adult myelinogenesis by giving rise to oligodendrocytes, which then ensheath axons and provide electrical insulation in the form of a myelin sheath, enabling faster action potential propagation and high fidelity transmission without a need for an increase in axonal diameter. The loss or lack of OPCs, and consequent lack of differentiated oligodendrocytes, is associated with a loss of myelination and subsequent impairment of neurological functions. In addition, OPCs express receptors for various neurotransmitters and undergo membrane depolarization when they receive synaptic inputs from neurons. Structure OPCs are glial cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelinogenesis
Myelinogenesis is the formation and development of myelin sheaths in the nervous system, typically initiated in late prenatal neurodevelopment and continuing throughout postnatal development. Myelinogenesis continues throughout the lifespan to support learning and memory via neural circuit plasticity as well as remyelination following injury. Successful myelination of axons increases action potential speed by enabling saltatory conduction, which is essential for timely signal conduction between spatially separate brain regions, as well as provides metabolic support to neurons. Stages Myelin is formed by oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. Therefore, the first stage of myelinogenesis is often defined as the differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells or Schwann cell progenitors into their mature counterparts, followed by myelin formation around axons. The oligodendrocyte lineage can be further classified into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Neuropathies
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or organ function depending on which nerves are affected; in other words, neuropathy affecting motor, sensory, or autonomic nerves result in different symptoms. More than one type of nerve may be affected simultaneously. Peripheral neuropathy may be acute (with sudden onset, rapid progress) or chronic (symptoms begin subtly and progress slowly), and may be reversible or permanent. Common causes include systemic diseases (such as diabetes or leprosy), hyperglycemia-induced glycation, vitamin deficiency, medication (e.g., chemotherapy, or commonly prescribed antibiotics including metronidazole and the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)), traumatic injury, ischemia, radiation therapy, excessiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukodystrophies
Leukodystrophies are a group of usually inherited disorders characterized by degeneration of the white matter in the brain. The word ''leukodystrophy'' comes from the Greek roots ''leuko'', "white", ''dys'', "abnormal" and ''troph'', "growth". The leukodystrophies are caused by imperfect growth or development of the myelin sheath, the fatty insulating covering around nerve fibers. Leukodystrophies may be classified as hypomyelinating or demyelinating diseases, depending on whether the damage is present before birth or occurs after. Other demyelinating diseases are usually not congenital and have a toxic or autoimmune cause. When damage occurs to white matter, immune responses can lead to inflammation in the central nervous system (CNS), along with loss of myelin. The degeneration of white matter can be seen in an MRI scan and used to diagnose leukodystrophy. Leukodystrophy is characterized by specific symptoms including decreased motor function, muscle rigidity, and eventual dege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |