Oligodendrocyte on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Oligodendrocytes (), or oligodendroglia, are a type of
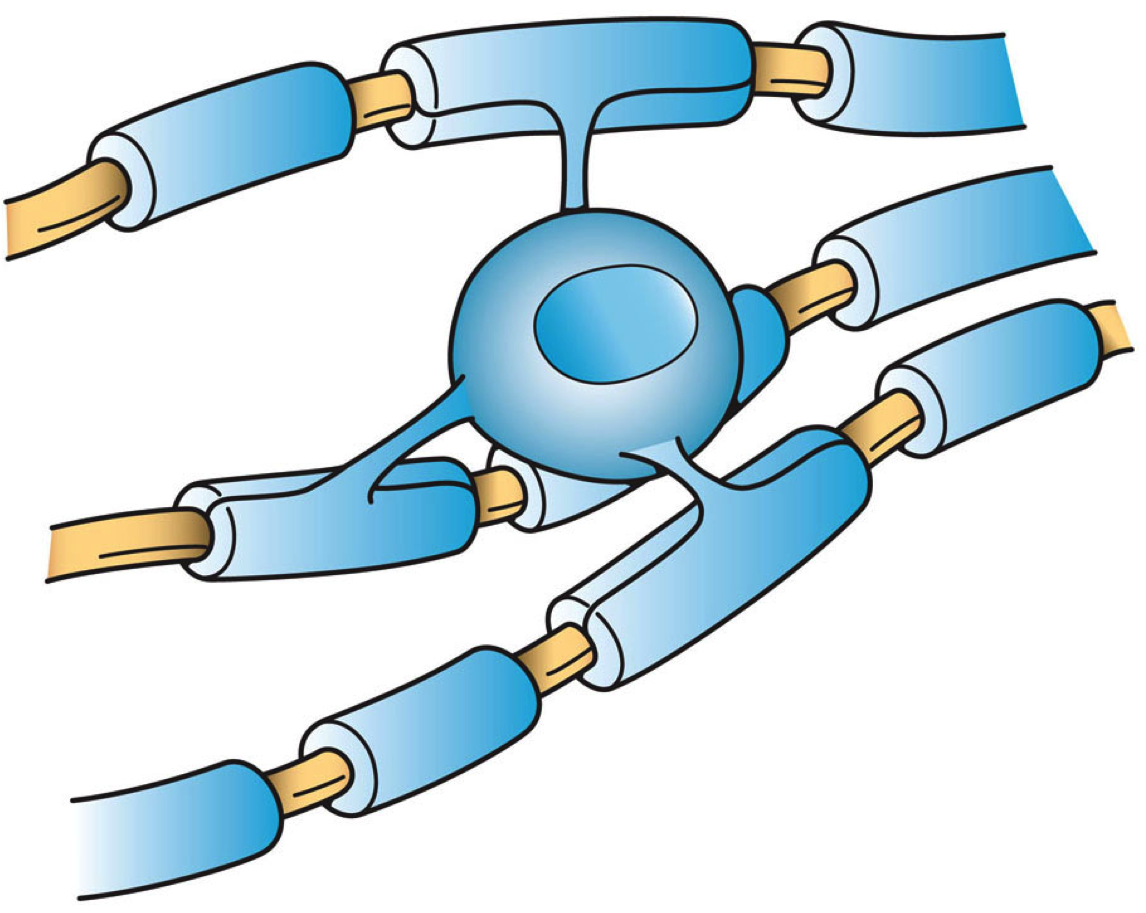 Mammalian
Mammalian
NIF Search – Oligodendrocyte
via the Neuroscience Information Framework {{Authority control Glial cells Biology of bipolar disorder
neuroglia
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form myel ...
whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
s in the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
of jawed vertebrates, equivalent to the function performed by Schwann cell
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells, olfactory en ...
s in the peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brai ...
. Oligodendrocytes do this by creating the myelin sheath. A single oligodendrocyte can extend its processes to 50 axons, wrapping approximately 1 μm of myelin sheath around each axon; Schwann cells, on the other hand, can wrap around only one axon. Each oligodendrocyte forms one segment of myelin for several adjacent axons.
Oligodendrocytes are found only in the central nervous system, which comprises the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
. These cells were originally thought to have been produced in the ventral neural tube; however, research now shows oligodendrocytes originate from the ventral ventricular zone of the embryonic spinal cord and possibly have some concentrations in the forebrain. They are the last cell type to be generated in the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
(CNS). Oligodendrocytes were discovered by Pío del Río Hortega.
Classification
Oligodendrocytes are a type of glial cell. They arise during development from oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs), which can be identified by their expression of a number ofantigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
, including the ganglioside
A ganglioside is a molecule composed of a glycosphingolipid (ceramide and oligosaccharide) with one or more sialic acids (e.g. ''N''-acetylneuraminic acid, NANA) linked on the sugar chain. NeuNAc, an acetylated derivative of the carbohydrate ...
GD3, the NG2 chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, and the platelet-derived growth factor-alpha receptor subunit (PDGF-alphaR). Mature oligodendrocytes are broadly classified into either myelinating or non-myelinating satellite oligodendrocytes. Precursors and both mature types are typically identified by their expression of the transcription factor OLIG2.
Development
Most oligodendrocytes develop duringembryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
and early postnatal life from restricted periventricular germinal regions. Oligodendrocyte formation in the adult brain is associated with glial-restricted progenitor cells, known as oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs). SVZ cells migrate away from germinal zones to populate both developing white and gray matter, where they differentiate and mature into myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can ...
-forming oligodendrocytes. However, it is not clear whether all oligodendrocyte progenitors undergo this sequence of events.
Between midgestation and term birth in human cerebral white matter, three successive stages of the classic human oligodendrocyte lineage are found: OPCs, immature oligodendrocytes (non-myelinating), and mature oligodendrocytes (myelinating). It has been suggested that some undergo apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
and others fail to differentiate into mature oligodendrocytes but persist as adult OPCs. Remarkably, oligodendrocyte population originated in the subventricular zone can be dramatically expanded by administering epidermal growth factor
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a protein that stimulates cell growth and differentiation by binding to its receptor, EGFR. Human EGF is 6-k Da and has 53 amino acid residues and three intramolecular disulfide bonds.
EGF was originally de ...
(EGF).
Function
Myelination
 Mammalian
Mammalian nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes ...
s depend crucially on myelin sheaths, which reduce ion leakage and decrease the capacitance of the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
, for rapid signal conduction. Myelin also increases impulse speed, as saltatory propagation of action potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells ...
s occurs at the nodes of Ranvier in between Schwann cells (of the PNS) and oligodendrocytes (of the CNS). Furthermore, impulse speed of myelinated axons increases linearly with the axon diameter, whereas the impulse speed of unmyelinated cells increases only with the square root of the diameter. The insulation must be proportional to the diameter of the fibre inside. The optimal ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
of axon diameter divided by the total fiber diameter (which includes the myelin) is 0.6.
Myelination is only prevalent in a few brain regions at birth and continues into adulthood. The entire process is not complete until about 25–30 years of age. Myelination is an important component of intelligence, and white matter quantity may be positively correlated with IQ test results in children. Rats that were raised in an enriched environment, which is known to increase cognitive flexibility, had more myelination in their corpus callosi.
Metabolic support
Oligodendrocytes interact closely with nerve cells and provide trophic support by the production of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), or insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). They may also directly provide metabolites to neurons, as described by thelactate shuttle hypothesis
The lactate shuttle hypothesis describes the movement of lactate intracellularly (within a cell) and intercellularly (between cells). The hypothesis is based on the observation that lactate is formed and utilized continuously in diverse cells und ...
.
It is hypothesized that satellite oligodendrocytes (or perineuronal oligodendrocytes) are functionally distinct from other oligodendrocytes. They are not attached to neurons via myelin sheaths and, therefore, do not contribute to insulation. They remain opposed to neurons and regulate the extracellular fluid. Satellite oligodendrocytes are considered to be a part of the grey matter whereas myelinating oligodendrocytes are a part of the white matter. They may support neuronal metabolism. Satellite oligodendrocytes may be recruited to produce new myelin after a demyelinating injury.
Clinical significance
Diseases that result in injury to oligodendrocytes include demyelinating diseases such asmultiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This ...
and various leukodystrophies. Trauma to the body, e.g. spinal cord injury, can also cause demyelination. The immature oligodendrocytes, which increase in number during mid-gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pr ...
, are more vulnerable to hypoxic injury and are involved in periventricular leukomalacia
Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) is a form of white-matter brain injury, characterized by the necrosis (more often coagulation) of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It can affect newborns and (less commonly) fetuses; premature infant ...
. This largely congenital condition of damage to the newly forming brain can therefore lead to cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sens ...
. In cerebral palsy, spinal cord injury, stroke and possibly multiple sclerosis, oligodendrocytes are thought to be damaged by excessive release of the neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neu ...
, glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
.Káradóttir et al., 2007 Damage has also been shown to be mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
The ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA rece ...
s. Oligodendrocyte dysfunction may also be implicated in the pathophysiology
Pathophysiology ( physiopathology) – a convergence of pathology with physiology – is the study of the disordered physiological processes that cause, result from, or are otherwise associated with a disease or injury. Pathology is ...
of schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social w ...
and bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevat ...
.
Oligodendrocytes are also susceptible to infection by the JC virus
''Human polyomavirus 2'', commonly referred to as the JC virus or John Cunningham virus, is a type of human polyomavirus (formerly known as papovavirus). It was identified by electron microscopy in 1965 by ZuRhein and Chou, and by Silverman an ...
, which causes progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a rare and often fatal viral disease characterized by progressive damage (''-pathy'') or inflammation of the white matter (''leuko-'') of the brain (''-encephalo-'') at multiple locations (''mu ...
(PML), a condition that specifically affects white matter, typically in immunocompromised patients. Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s of oligodendrocytes are called oligodendrogliomas. The chemotherapy agent Fluorouracil (5-FU) causes damage to the oligodendrocytes in mice, leading to both acute central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
(CNS) damage and progressively worsening delayed degeneration of the CNS.
See also
*White matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribu ...
* Schwann cells
* 2',3'-Cyclic-nucleotide 3'-phosphodiesterase (CNPase)
*List of human cell types derived from the germ layers
This is a list of cells in humans derived from the three embryonic germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Cells derived from ectoderm
Surface ectoderm Skin
* Trichocyte
* Keratinocyte
Anterior pituitary
* Gonadotrope
* Corti ...
References
;Bibliography *Raine, C.S. (1991). Oligodendrocytes and central nervous system myelin. In Textbook of Neuropathology, second edition, R.L. Davis and D.M. Robertson, eds. (Baltimore, Maryland: Williams and Wilkins), pp. 115–141. * * * * *External links
* The Department of Neuroscience atWikiversity
Wikiversity is a Wikimedia Foundation project that supports learning communities, their learning materials, and resulting activities. It differs from Wikipedia in that it offers tutorials and other materials for the fostering of learning, rather ...
NIF Search – Oligodendrocyte
via the Neuroscience Information Framework {{Authority control Glial cells Biology of bipolar disorder