|
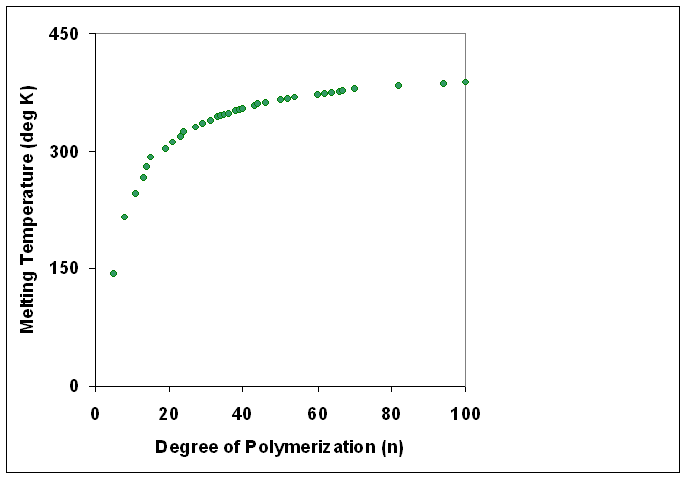
Degree Of Polymerisation
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is the number of monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule. For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and the ''number-average'' degree of polymerization is given by DP_n\equiv X_n=\frac, where Mn is the number-average molecular weight and M0 is the molecular weight of the monomer unit. For most industrial purposes, degrees of polymerization in the thousands or tens of thousands are desired. This number does not reflect the variation in molecule size of the polymer that typically occurs, it only represents the mean number of monomeric units. Some authors, however, define DP as the number of repeat units, where for copolymers the repeat unit may not be identical to the monomeric unit.Fried J.R. "Polymer Science and Technology" (Pearson Prentice-Hall, 2nd edn 2003), p.27 For example, in nylon-6,6, the repeat unit contains the two monomeric units —NH(CH2)6NH— and —OC(CH2)4CO—, so that a chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Unit
In polymer chemistry, a structural unit is a building block of a polymer chain. It is the result of a monomer which has been polymerized into a long chain. There may be more than one structural unit in the repeat unit. When different monomers are polymerized, a copolymer is formed. It is a routine way of developing new properties for new materials. Example Consider the example of polyethylene terephthalate (PET or "polyester"). The monomers which could be used to create this polymer are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid: HO-CH2-CH2-OH and HOOC-C6H4-COOH In the polymer, there are two structural units, which are -O-CH2-CH2-O- and -CO-C6H4-CO- The repeat unit is -CH2-CH2-O-CO-C6H4-CO-O- Functionality of structural units The functionality of a monomeric structural unit is defined as the number of covalent bonds which it forms with other reactants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain-growth Polymerization
Chain-growth polymerization (American English, AE) or chain-growth polymerisation (British English, BE) is a polymerization technique where Unsaturated compound, unsaturated monomer molecules add onto the active site on a growing polymer chain one at a time. There are a limited number of these active sites at any moment during the polymerization which gives this method its key characteristics. Introduction In 1953, Paul Flory first classified polymerization as "step-growth polymerization" and "chain-growth polymerization". IUPAC recommends to further simplify "chain-growth polymerization" to "chain polymerization". It is a kind of polymerization where an active center (free radical or ion) is formed, and a plurality of monomers can be polymerized together in a short period of time to form a macromolecule having a large molecular weight. In addition to the regenerated active sites of each monomer unit, polymer growth will only occur at one (or possibly more) endpoint. Many comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh scattering ( ), named after the 19th-century British physicist Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt), is the predominantly elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. For light frequencies well below the resonance frequency of the scattering particle (normal dispersion regime), the amount of scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. Rayleigh scattering results from the electric polarizability of the particles. The oscillating electric field of a light wave acts on the charges within a particle, causing them to move at the same frequency. The particle, therefore, becomes a small radiating dipole whose radiation we see as scattered light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules; it can occur when light travels through transparent solids and liquids, but is most prominently seen in gases. Rayleigh scattering of sunlight in Earth's atmosphere causes d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmotic Pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure solvent by osmosis. Potential osmotic pressure is the maximum osmotic pressure that could develop in a solution if it were separated from its pure solvent by a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis occurs when two solutions containing different concentrations of solute are separated by a selectively permeable membrane. Solvent molecules pass preferentially through the membrane from the low-concentration solution to the solution with higher solute concentration. The transfer of solvent molecules will continue until equilibrium is attained. Theory and measurement Jacobus van 't Hoff found a quantitative relationship between osmotic pressure and solute concentration, expressed in the following equation: :\Pi = icRT where \Pi is osmotic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighted Mean
The weighted arithmetic mean is similar to an ordinary arithmetic mean (the most common type of average), except that instead of each of the data points contributing equally to the final average, some data points contribute more than others. The notion of weighted mean plays a role in descriptive statistics and also occurs in a more general form in several other areas of mathematics. If all the weights are equal, then the weighted mean is the same as the arithmetic mean. While weighted means generally behave in a similar fashion to arithmetic means, they do have a few counterintuitive properties, as captured for instance in Simpson's paradox. Examples Basic example Given two school with 20 students, one with 30 test grades in each class as follows: :Morning class = :Afternoon class = The mean for the morning class is 80 and the mean of the afternoon class is 90. The unweighted mean of the two means is 85. However, this does not account for the difference in number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Flory
Paul John Flory (June 19, 1910 – September 9, 1985) was an American chemist and Nobel laureate who was known for his work in the field of polymers, or macromolecules. He was a leading pioneer in understanding the behavior of polymers in solution, and won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1974 "for his fundamental achievements, both theoretical and experimental, in the physical chemistry of macromolecules". Biography Personal life Flory was born in Sterling, Illinois, on June 19, 1910. He was raised by Ezra Flory and Nee Martha Brumbaugh. His father worked as a clergyman-educator, and his mother was a school teacher. He first gained his interest in science from Carl W Holl, who was a professor in chemistry. Holl was employed in Indiana at Manchester College as a chemistry professor. In 1936, he married Emily Catherine Tabor. He and Emily had three children together; Susan Springer, Melinda Groom and Paul John Flory jr. They also had five grandchildren. All of his children purs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree Of Polymerization
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is the number of monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule. For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and the ''number-average'' degree of polymerization is given by DP_n\equiv X_n=\frac, where Mn is the number-average molecular weight and M0 is the molecular weight of the monomer unit. For most industrial purposes, degrees of polymerization in the thousands or tens of thousands are desired. This number does not reflect the variation in molecule size of the polymer that typically occurs, it only represents the mean number of monomeric units. Some authors, however, define DP as the number of repeat units, where for copolymers the repeat unit may not be identical to the monomeric unit.Fried J.R. "Polymer Science and Technology" (Pearson Prentice-Hall, 2nd edn 2003), p.27 For example, in nylon-6,6, the repeat unit contains the two monomeric units —NH(CH2)6NH— and —OC(CH2)4CO—, so that a chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Transfer
Chain transfer is a polymerization Chemical reaction, reaction by which the activity of a growing polymer chain is transferred to another molecule. :P• + XR' → PX + R'• Chain transfer reactions reduce the average molecular weight of the final polymer. Chain transfer can be either introduced deliberately into a polymerization (by use of a ''chain transfer agent'') or it may be an unavoidable side-reaction with various components of the polymerization. Chain transfer reactions occur in most forms of addition polymerization including radical polymerization, ring-opening polymerization, coordination polymerization, and cationic polymerization, as well as anionic polymerization. Types Chain transfer reactions are usually categorized by the nature of the molecule that reacts with the growing chain. * Transfer to chain transfer agent. Chain transfer agents have at least one weak chemical bond, which therefore facilitates the chain transfer reaction. Common chain transfer age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Termination
Chain termination is any chemical reaction that ceases the formation of reactive intermediates in a chain propagation step in the course of a polymerization, effectively bringing it to a halt. Mechanisms of termination In polymer chemistry, there are several mechanisms by which a polymerization reaction can terminate depending on the mechanism and circumstances of the reaction. A method of termination that applies to all polymer reactions is the depletion of monomer. In chain growth polymerization, two growing chains can collide head to head causing the growth of both of the chains to stop. In the case of radical or anionic polymerization, chain transfer can occur where the radical at the end of the growing chain can be transferred from the chain to an individual monomer unit causing a new chain to start growing and the previous chain to stop growing. With step-growth polymerization, the reaction can be terminated by adding a monofunctional species containing the same funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Chain Length
In polymer chemistry the kinetic chain length of a polymer, ''ν'', is the average number of units called monomers added to a growing chain during chain-growth polymerization. During this process, a polymer chain is formed when monomers are bonded together to form long chains known as polymers. Kinetic chain length is defined as the average number of monomers that react with an active center such as a radical from initiation to termination.Rudin, Alfred ''The Elements of Polymer Science and Engineering'' (Academic Press 1982) pp.209-211 This definition is a special case of the concept of ''chain length'' in chemical kinetics. For any chemical chain reaction, the chain length is defined as the average number of times that the closed cycle of chain propagation steps is repeated. It is equal to the rate of the overall reaction divided by the rate of the initiation step in which the chain carriers are formed.Keith J. Laidler, ''Chemical Kinetics'' (3rd ed., Harper and Row 1987) pp.289 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carothers' Equation
In step-growth polymerization, the Carothers equation (or Carothers' equation) gives the degree of polymerization, , for a given fractional monomer conversion, . There are several versions of this equation, proposed by Wallace Carothers, who invented nylon in 1935. Linear polymers: two monomers in equimolar quantities The simplest case refers to the formation of a strictly linear polymer by the reaction (usually by condensation) of two monomers in equimolar quantities. An example is the synthesis of nylon-6,6 whose formula is from one mole of hexamethylenediamine, , and one mole of adipic acid, . For this case :\bar_n=\frac In this equation * is the number-average value of the degree of polymerization, equal to the average number of monomer units in a polymer molecule. For the example of nylon-6,6 \bar_n = 2n ( diamine units and diacid units). *p=\tfrac is the extent of reaction (or conversion to polymer), defined by ** is the number of molecules present initially as monomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macromolecule
A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biophysical processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. The most common macromolecules in biochemistry are biopolymers (nucleic acids, proteins, and carbohydrates) and large non-polymeric molecules such as lipids, nanogels and macrocycles. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes are also examples of macromolecules. Definition The term ''macromolecule'' (''macro-'' + ''molecule'') was coined by Nobel laureate Hermann Staudinger in the 1920s, although his first relevant publication on this field only mentions ''high molecular compounds'' (in excess of 1,000 atoms). At that time the term ''polymer'', as introduced by Berzelius in 1832, had a different meaning from that of today: it simply was another form of isomerism for example with benzene and acetylene and had litt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

