|
Defleshing
In archaeology and anthropology, the term excarnation (also known as defleshing) refers to the practice of removing the flesh and organs of the dead before burial. Excarnation may be achieved through natural means, such as leaving a dead body exposed to the elements or for animals to scavenge; or by butchering the corpse by hand. Following excarnation, some societies retrieved the bones for burial. Excarnation has been practiced throughout the world for hundreds of thousands of years. The earliest archaeological evidence of excarnation is from the Awash River Valley in Ethiopia, 160,000 years ago. Examples of excarnation include 'sky burials' in parts of Asia, the Zoroastrian 'Tower of Silence', and Native American ' tree burials'. Excarnation is practiced for a variety of spiritual and practical reasons, including the Tibetian spiritual belief that excarnation is the most generous form of burial and the Comanche practical concern that in the winter the ground is too hard for an u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Sapiens Idaltu
Herto Man refers to the 154,000 - 160,000-year-old human remains (''Homo sapiens'') discovered in 1997 from the Upper Herto member of the Bouri Formation in the Afar Triangle, Ethiopia. The discovery of Herto Man was especially significant at the time, as it fell within a long gap in the fossil record between 300 and 100 thousand years ago, and at its description in 2003, it represented the oldest dated ''H. sapiens'' remains. In the original description paper, these 12 (at minimum) individuals were described as falling just outside the umbrella of "anatomically modern human". Thus, Herto Man was classified into a new subspecies as "''H. s. idaltu''" ( aa, Idaltu "elder"). It supposedly represented a transitional morph between the more archaic "'' H. (s.?) rhodesiensis'' and ''H. s. sapiens'' (that is, a stage in a chronospecies). Subsequent researchers have rejected this classification. The validity of such subspecies is difficult to justify because of the vague definitions of "sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Sky Burial
Sky burial (, "bird-scattered") is a funeral practice in which a human corpse is placed on a mountaintop to decompose while exposed to the elements or to be eaten by scavenging animals, especially carrion birds. It is a specific type of the general practice of excarnation. It is practiced in the Chinese provinces and autonomous regions of Tibet, Qinghai, Sichuan, and Inner Mongolia, as well as in Mongolia, Bhutan, and parts of India such as Sikkim and Zanskar. The locations of preparation and sky burial are understood in the Vajrayana Buddhist traditions as charnel grounds. Comparable practices are part of Zoroastrian burial rites where deceased are exposed to the elements and scavenger birds on stone structures called Dakhma. Few such places remain operational today due to religious marginalisation, urbanisation and the decimation of vulture populations. The majority of Tibetan people and many Mongols adhere to Vajrayana Buddhism, which teaches the transmigration of spirit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouri Formation
The Bouri Formation is a sequence of sedimentary deposits that is the source of australopithecine and Homo (that is, hominin) fossils, artifacts, and bones of large mammals with cut marks from butchery with tools by early hominins. It is located in the Middle Awash Valley, in Ethiopia, East Africa, and is a part of the Afar Depression that has provided rich human fossil sites such as Gona and Hadar. The Bouri Formation stretches down much of the length and breadth of the Bouri "peninsula", which projects across the dry bed of the Afar Depression. The Formation is sufficiently eroded to expose three geological members or layers: the Hatayae, the Dakanihylo, and the Herto. Human remains with signs of having been prepared for burial have been found in the Upper Herto layers. Geology The Bouri "peninsula" is a geological fault-raised horst that diverts the Awash River, forming a partial dam and creating Lake Yardi; and it contains the Bouri Formation. The peninsula is about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sky Burial
Sky burial (, "bird-scattered") is a funeral practice in which a human corpse is placed on a mountaintop to decompose while exposed to the elements or to be eaten by scavenging animals, especially carrion birds. It is a specific type of the general practice of excarnation. It is practiced in the Chinese provinces and autonomous regions of Tibet, Qinghai, Sichuan, and Inner Mongolia, as well as in Mongolia, Bhutan, and parts of India such as Sikkim and Zanskar. The locations of preparation and sky burial are understood in the Vajrayana Buddhist traditions as charnel grounds. Comparable practices are part of Zoroastrian burial rites where deceased are exposed to the elements and scavenger birds on stone structures called Dakhma. Few such places remain operational today due to religious marginalisation, urbanisation and the decimation of vulture populations. The majority of Tibetan people and many Mongols adhere to Vajrayana Buddhism, which teaches the transmigration of spiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremation
Cremation is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a Cadaver, dead body through Combustion, burning. Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India and Nepal, cremation on an Pyre, open-air pyre is an ancient tradition. Starting in the 19th century, cremation was introduced or reintroduced into other parts of the world. In modern times, cremation is commonly carried out with a Crematorium, closed furnace (cremator), at a crematorium. Cremation leaves behind an average of 2.4 kg (5.3 lbs) of remains known as "ashes" or "cremains". This is not all ash but includes unburnt fragments of bone mineral, which are commonly ground into powder. They do not constitute a health risk and may be buried, interred in a memorial site, retained by relatives or scattered in various ways. History Ancient Cremation dates from at least 17,000 years ago in the archaeological record, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
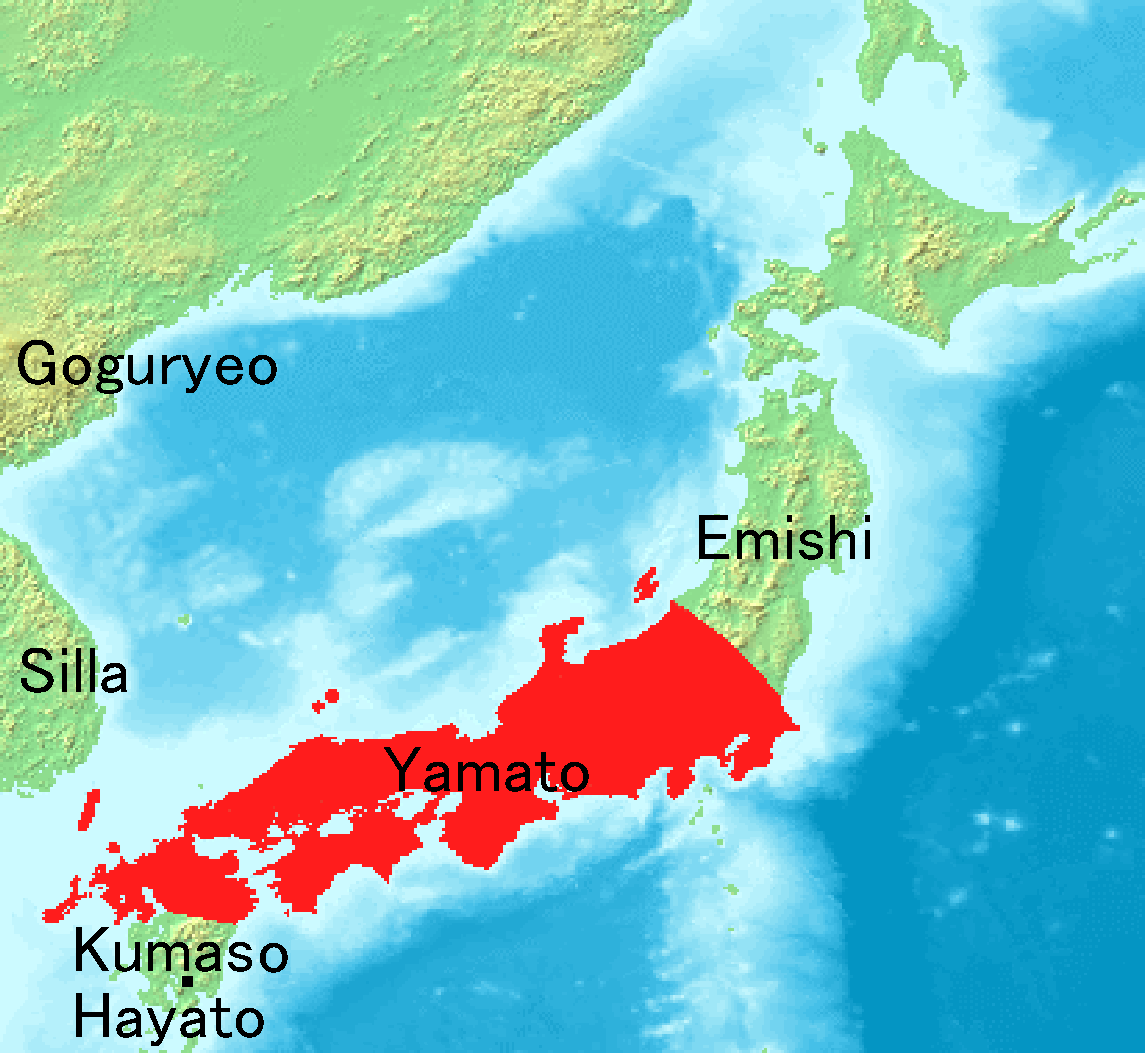
Yamato Period
The is the period of Japanese history when the Imperial court ruled from modern-day Nara Prefecture, then known as Yamato Province. While conventionally assigned to the period 250–710, including both the Kofun period (–538) and the Asuka period (538–710), the actual start of Yamato rule is disputed. The Yamato court's supremacy was challenged during the Kofun period by other polities centered in various parts of Japan. What is certain is that Yamato clans had major advantages over their neighbouring clans in the 6th century. This period is divided by the relocation of the capital to Asuka, in modern Nara Prefecture. However, the Kofun period is an archaeological period while the Asuka period is a historical period. Therefore, many think of this as an old division and this concept of period division is no longer applicable. At the era of Prince Shōtoku in the early 7th century, a new constitution was prescribed for Japan based on the Chinese model. After the fall of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bumburet
Bumburet (Kalasha: ', ur, وادی پمپوریت) is the largest valley of Kalasha Desh in Lower Chitral District, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa the province of Pakistan. The Bumburet valley joins the Rumbur valley at , and then joins the Kunar Valley at the village of Ayun (, , some south (downstream) of Chitral. To the west the valley rises to a pass connecting to Afghanistan's Nuristan Province at about . The valley is inhabited by the Kalash people The Kalasha (Kalasha: کالؕاشؕا, romanised: ''Kaḷaṣa)'', or Kalash, are an Indo-Aryan indigenous people residing in the Chitral District of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. The Kalash population in Pakistan numbers only in ..., and has become a tourist destination. However, their population is rapidly declining. As of 2019, only 37 households existed in the valley that still followed traditional practices.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Muhammad_Atif22/publication/283190904_Exports_and_Economic_Growth_Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalash People
The Kalasha (Kalasha: کالؕاشؕا, romanised: ''Kaḷaṣa)'', or Kalash, are an Indo-Aryan indigenous people residing in the Chitral District of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. The Kalash population in Pakistan numbers only in a few thousands, making them one of the smallest ethnic minorities in Pakistan. They are considered unique among the people of Pakistan.The kalaṣa of kalaṣüm They are also considered to be Pakistan's smallest , and tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration with its suburbs Oegstgeest, Leiderdorp, Voorschoten and Zoeterwoude with 206,647 inhabitants. The Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) further includes Katwijk in the agglomeration which makes the total population of the Leiden urban agglomeration 270,879, and in the larger Leiden urban area also Teylingen, Noordwijk, and Noordwijkerhout are included with in total 348,868 inhabitants. Leiden is located on the Oude Rijn, at a distance of some from The Hague to its south and some from Amsterdam to its north. The recreational area of the Kaag Lakes (Kagerplassen) lies just to the northeast of Leiden. A university city since 1575, Leiden has been one of Europe's most prominent scientific centres for more than four centuries. Leide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bali Aga
The Bali Aga, Baliaga or Bali Mula are the indigenous people of Bali, predominantly located in the eastern part of the island, in Karangasem. They can also be found in north-western and central regions. Bali Aga people that are referred to as ''Bali Pergunungan'' (Mountain Balinese) are those that are located at Trunyan village. For the Trunyan Bali Aga people, the term ''Bali Aga'' (Mountain Balinese) is regarded as an insult with an additional meaning of "the mountain people that are fools"; therefore, they prefer the term ''Bali Mula'' (''lit'' Original Balinese) instead. Origin The original inhabitants of Bali are said to have come from Bedulu village long before the Hindu-Javanese immigration wave. The legend is, there lived the last king of the Pejeng (an old Balinese kingdom), Sri Aji Asura Bumibanten, who had supernatural powers. He could cut off his head without feeling pain and put it back on again. One day, though, his head accidentally fell into a river and was swept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)