|
Dapansutrile
Dapansutrile (OLT1177) is an inhibitor of the NLRP3 (nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat and pyrin domain containing receptor 3) inflammasome. An inflammasome can be defined as an immune system Receptor (biochemistry), receptor that induces inflammation through the activation of caspase 1 and caspase 11 when it is triggered by damaged cells, microbial pathogens, and stress. NLRP3 is a canonical inflammasome. The NLRP3 inflammasome comprises NLRP3, the apoptosis spec-like protein (ASC) and the caspase-1 (Figure 1). The NLRP3 inflammasome forms by binding to pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and damage associated molecular patterns Damage-associated molecular pattern, (DAMPS) that activate caspase 1 which then signals for the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines Interleukin 1 beta, IL-1β and Interleukin-18 receptor, IL-18 resulting in pyroptosis Constant activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome is believed to play a direct or indirect role in acute arthritis, atherosclero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NLRP3
NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) (previously known as NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 ALP3and cryopyrin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NLRP3'' gene located on the long arm of chromosome 1. NLRP3 is expressed predominantly in macrophages and as a component of the inflammasome, detects products of damaged cells such as extracellular ATP and crystalline uric acid. Activated NLRP3 in turn triggers an immune response. Mutations in the NLRP3 gene are associated with a number of organ specific autoimmune diseases. Nomenclature NACHT, LRR, and PYD are respectively acronyms for: * NACHT – NAIP (neuronal apoptosis inhibitor protein), C2TA heterokaryon_incompatibility)_and_TP1_(telomerase-associated_protein_1) *_ MHC,_HET-E_(Podospora_anserina#Heterokaryon_incompatibility">heterokaryon_incompatibility)_and_TP1_(telomerase-associated_protein_1) *_Leucine-rich_repeat">LRR_–_"leucine-rich_repeat"__and_is_synonymous_with_NLR,_for_''_or_' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
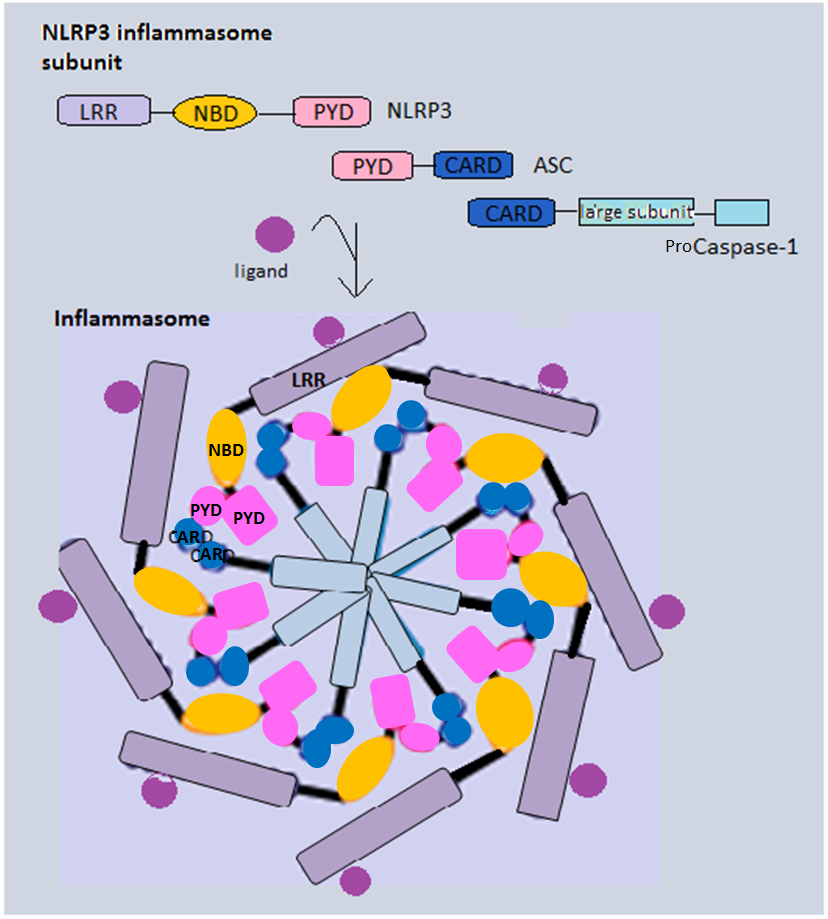
NLRP3 Protein Components And Inflammasome (1)
NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) (previously known as NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 ALP3and cryopyrin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NLRP3'' gene located on the long arm of chromosome 1. NLRP3 is expressed predominantly in macrophages and as a component of the inflammasome, detects products of damaged cells such as extracellular ATP and crystalline uric acid. Activated NLRP3 in turn triggers an immune response. Mutations in the NLRP3 gene are associated with a number of organ specific autoimmune diseases. Nomenclature NACHT, LRR, and PYD are respectively acronyms for: * NACHT – NAIP (neuronal apoptosis inhibitor protein), C2TA heterokaryon_incompatibility)_and_TP1_(telomerase-associated_protein_1) *_ MHC,_HET-E_(Podospora_anserina#Heterokaryon_incompatibility">heterokaryon_incompatibility)_and_TP1_(telomerase-associated_protein_1) *_Leucine-rich_repeat">LRR_–_"leucine-rich_repeat"__and_is_synonymous_with_NLR,_for_''_or_' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammasome
Inflammasomes are cytosolic multiprotein oligomers of the innate immune system responsible for the activation of inflammatory responses. Activation and assembly of the inflammasome promotes proteolytic cleavage, maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18), as well as cleavage of Gasdermin-D. The N-terminal fragment resulting from this cleavage induces a pro-inflammatory form of programmed cell death distinct from apoptosis, referred to as pyroptosis, and is responsible for secretion of the mature cytokines, presumably through the formation of pores in the plasma membrane. Inflammasome activation is initiated by different kinds of cytosolic pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that respond to either microbe-derived pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) generated by the host cell. Pattern recognition receptors involved in inflammasomes comprise NLRs (nucleoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols (that is, sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl () group of an alcohol), and the word is a blend of "''thio-''" with "alcohol". Many thiols have strong odors resembling that of garlic or rotten eggs. Thiols are used as odorants to assist in the detection of natural gas (which in pure form is odorless), and the "smell of natural gas" is due to the smell of the thiol used as the odorant. Thiols are sometimes referred to as mercaptans () or mercapto compounds, a term introduced in 1832 by William Christopher Zeise and is derived from the Latin ('capturing mercury')''Oxford American Dictionaries'' (Mac OS X Leopard). because the thiolate group () bonds very strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinner Reaction
The Pinner reaction refers to the acid catalysed reaction of a nitrile with an alcohol to form an imino ester salt (alkyl imidate salt); this is sometimes referred to as a Pinner salt. The reaction is named after Adolf Pinner, who first described it in 1877. Pinner salts are themselves reactive and undergo additional nucleophilic additions to give various useful products: * With an excess of alcohol to form an orthoester * With ammonia or an amine to form an amidine (di-nitriles may form imidines, for instance succinimidine from succinonitrile) * With water to form an ester * With hydrogen sulfide to form a thionoester Commonly the Pinner salt itself is not isolated, with the reaction being continued to give the desired functional group (orthoester etc.) in one go. It should be appreciated that the Pinner reaction refers specifically to an acid catalyzed process, but that similar results can often be achieved using base catalysis. The two approaches can be complementary, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Official Dapansutrile Mechanism Of Action (2)
An official is someone who holds an office (function or mandate, regardless whether it carries an actual working space with it) in an organization or government and participates in the exercise of authority, (either their own or that of their superior and/or employer, public or legally private). An elected official is a person who is an official by virtue of an election. Officials may also be appointed ''ex officio'' (by virtue of another office, often in a specified capacity, such as presiding, advisory, secretary). Some official positions may be inherited. A person who currently holds an office is referred to as an incumbent. Something "official" refers to something endowed with governmental or other authoritative recognition or mandate, as in official language, official gazette, or official scorer. Etymology The word ''official'' as a noun has been recorded since the Middle English period, first seen in 1314. It comes from the Old French ''official'' (12th century), from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in its own right, in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and production of methyl methacrylate (and from that PMMA) as well as bisphenol A.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in |
Alkylation
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents. Nucleophilic alkylating agents Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion ( carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new covalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Structure Of OTL1177
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt (sodium chloride) and refined sugar (sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as solids, liquids, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular-weight
The molecular mass (''m'') is the mass of a given molecule: it is measured in daltons (Da or u). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The related quantity relative molecular mass, as defined by IUPAC, is the ratio of the mass of a molecule to the unified atomic mass unit (also known as the dalton) and is unitless. The molecular mass and relative molecular mass are distinct from but related to the molar mass. The molar mass is defined as the mass of a given substance divided by the amount of a substance and is expressed in g/mol. That makes the molar mass an average of many particles or molecules, and the molecular mass the mass of one specific particle or molecule. The molar mass is usually the more appropriate figure when dealing with macroscopic (weigh-able) quantities of a substance. The definition of molecular weight is most authoritatively synonymous with relative molecular mass; ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |