|
De Havilland DH.60
The de Havilland DH.60 Moth is a 1920s British two-seat touring and training aircraft that was developed into a series of aircraft by the de Havilland Aircraft Company. Development The DH.60 was developed from the larger DH.51 biplane. The first flight of the ADC Cirrus powered prototype DH.60 Moth (registration ''G-EBKT'') was carried out by Geoffrey de Havilland at the works airfield at Stag Lane on 22 February 1925. The Moth was a two-seat biplane of wooden construction, it had a plywood covered fuselage and fabric covered surfaces, a standard tailplane with a single tailplane and fin. A useful feature of the design was its folding wings which allowed owners to hangar the aircraft in much smaller spaces. The then Secretary of State for Air Sir Samuel Hoare became interested in the aircraft and the Air Ministry subsidised five flying clubs and equipped them with Moths. The prototype was modified with a horn-balanced rudder, as used on the production aircraft, and wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Cup Race
The King's Cup air race is a British handicapped cross-country event, which has taken place annually since 1922. It is run by the Royal Aero Club Records Racing and Rally Association. The King's Cup is one of the most prestigious prizes of the British air racing season. The entrants are divided into classes, and each is evaluated and given a time handicap for the start of the race. They all take off at varying times according to their handicap, with the handicappers' aim being that they should all cross the finishing line at the same moment. The art of winning the race outright is therefore to beat the handicappers, rather than to make the fastest flight as such.Alex Henshaw, ''The Flight of the Mew Gull'', Murray, 1980. p.95 The aircraft are also divided into classes, with a winner for each class as well as the outright winner. History The King's Cup air race was established by King George V as an incentive to the development of light aircraft and engine design. Initially, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Klemm Swallow
The B.A Swallow was a British light aircraft of the 1930s. It was a license-built version by the British Klemm Aeroplane Company (which later became known as the British Aircraft Manufacturing Co.) of the German Klemm L.25. A total of 135 were built. Design and development The German aircraft manufacturer Klemm developed a successful low-powered light aeroplane, the Klemm L.25, which first flew in 1927,Smith and Kay 1972 of which over 600 were produced. Several were sold to British owners, where they proved popular, so the British dealer for the L.25, Major E.F Stephen, set up the "British Klemm Aeroplane Company" at London Air Park, Hanworth, Middlesex to produce a version of the L.25 under license. The prototype of the licensed version, known as the B.K. Swallow, first flew at Hanworth in November 1933.Jackson 1974 It was an all-wooden cantilever monoplane, with tandem cockpits accommodating two persons, and was powered by a 75 hp (56 kW) Salmson 9 or 85 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avro Avian
The Avro Avian was a series of British light aircraft designed and built by Avro in the 1920s and 1930s. While the various versions of the Avian were sound aircraft, they were comprehensively outsold by the de Havilland Moth and its descendants. Design and development The Avro 581 Avian prototype was designed and built to compete in the Lympne light aircraft trials at Lympne Aerodrome in September 1926. Its wooden fuselage was based on that of the Avro 576 autogyro, but it was fitted with conventional biplane wings and powered by a 70 hp (50 kW) Armstrong Siddeley Genet engine. It performed well at the trials, but was eliminated due to engine failure. In early 1927 it was re-engined with an ADC Cirrus engine as the Type 581A and sold to Bert Hinkler. Production aircraft were designated Type 594 and were built in a number of versions, mainly powered by Cirrus engines.Jackson 1990, pp. 249, 256. A version with a welded steel tube fuselage was produced in 1929 as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expressed as its lift-to-drag ratio. The lift a wing generates at a given speed and angle of attack can be one to two orders of magnitude greater than the total drag on the wing. A high lift-to-drag ratio requires a significantly smaller thrust to propel the wings through the air at sufficient lift. Lifting structures used in water include various foils, such as hydrofoils. Hydrodynamics is the governing science, rather than aerodynamics. Applications of underwater foils occur in hydroplanes, sailboats and submarines. Etymology and usage For many centuries, the word "wing", from the Old Norse ''vængr'', referred mainly to the foremost limbs of birds (in addition to the architectural aisle). But in recent centuries the word's meaning has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called 'rolling' or 'banking'. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal resolution. A much earlier aileron concept was patented in 1868 by British scientist Matthew Piers Watt Bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logo
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name it represents as in a wordmark. In the days of hot metal typesetting, a logotype was one word cast as a single piece of type (e.g. "The" in ATF Garamond), as opposed to a Typographic ligature, ligature, which is two or more letters joined, but not forming a word. By extension, the term was also used for a uniquely set and arranged typeface or colophon (publishing), colophon. At the level of mass communication and in common usage, a company's logo is today often synonymous with its trademark or brand.Wheeler, Alina. ''Designing Brand Identity'' © 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (page 4) Etymology Online Etymology Dictionary, Douglas Harper's Online Etymology Dictionary states that the term 'logo' used in 1937 "probably a shortening of logogram". History Numerous inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, usually near the front of an aircraft or spacecraft, from which a Pilot in command, pilot controls the aircraft. The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the controls that enable the pilot to fly the aircraft. In most airliners, a door separates the cockpit from the aircraft cabin. After the September 11 attacks, September 11, 2001 attacks, all major airlines Airport_security_repercussions_due_to_the_September_11_attacks#Improved_security_on_aircraft, fortified their cockpits against access by aircraft hijacking, hijackers. Etymology The word cockpit seems to have been cockpit (sailing), used as a nautical term in the 17th century, without reference to cock fighting. It referred to an area in the rear of a ship where the cockswain's station was located, the cockswain being the pilot of a smaller "boat" that could be dispatched from the ship to board another ship or to bring people ashore. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
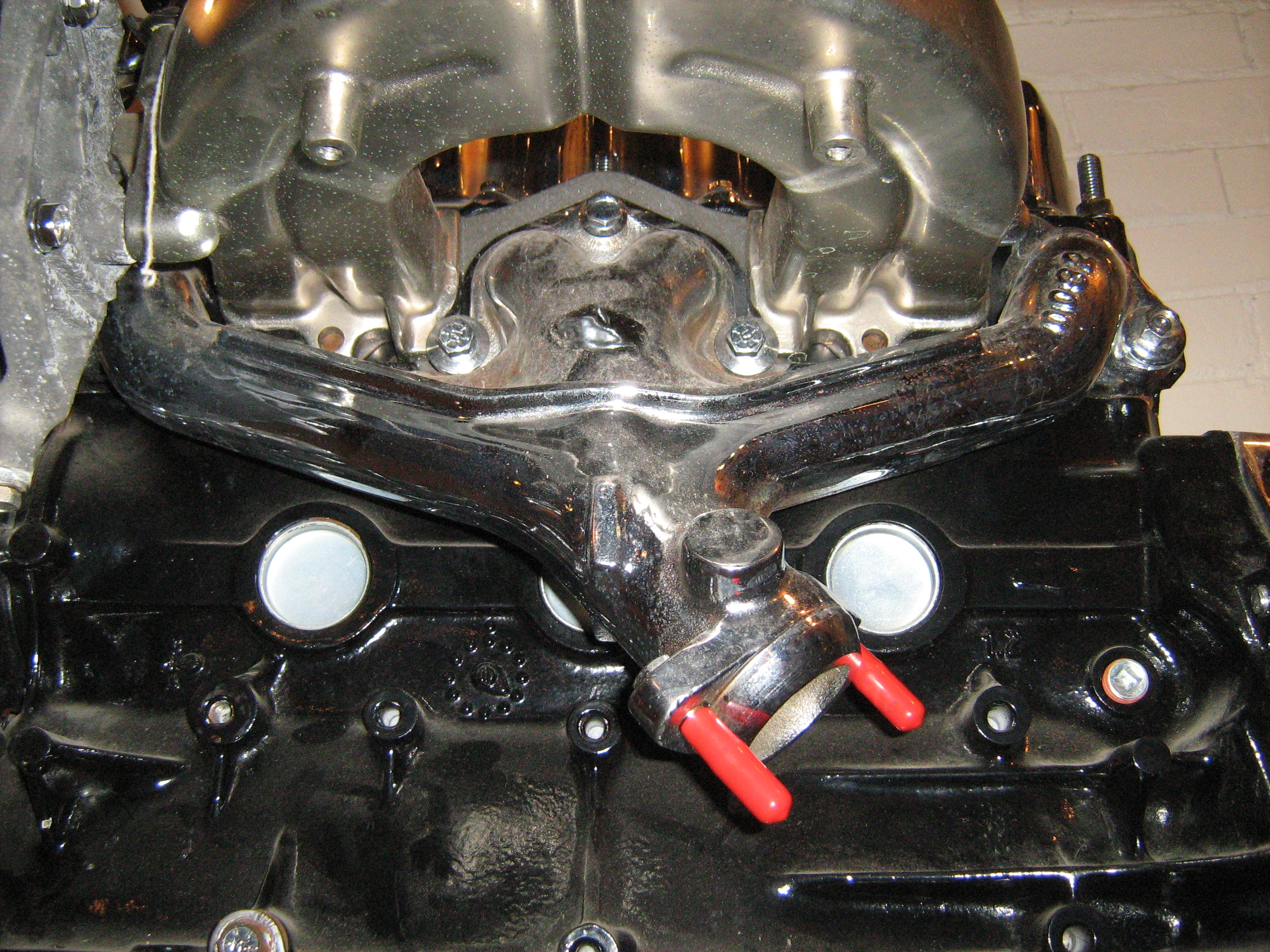
Exhaust System
An exhaust system is used to guide reaction exhaust gases away from a controlled combustion inside an engine or stove. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes. Depending on the overall system design, the exhaust gas may flow through one or more of: *Cylinder head and exhaust manifold *A turbocharger to increase engine power. *A catalytic converter to reduce air pollution. *A muffler (North America) / silencer (UK/India), to reduce noise. Design criteria An exhaust pipe must be carefully designed to carry toxic and/or noxious gases away from the users of the machine. Indoor generators and furnaces can quickly fill an enclosed space with poisonous exhaust gases such as hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, if they are not properly vented to the outdoors. Also, the gases from most types of machines are very hot; the pipe must be heat-resistant, and it must not pass through or near anything that can burn or can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft the single engine is mounted on a pylon attached to the fuselage, which in turn is used as a floating hull. The fuselage also serves to position the control and stabilization surfaces in specific relationships to lifting surfaces, which is required for aircraft stability and maneuverability. Types of structures Truss structure This type of structure is still in use in many lightweight aircraft using welded steel tube trusses. A box truss fuselage structure can also be built out of wood—often covered with plywood. Simple box structures may be rounded by the addition of supported lightweight stringers, allowing the fabric covering to form a more aerodynamic shape, or one more pleasing to the eye. Geodesic construction Geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabane Strut
In aeronautics, bracing comprises additional structural members which stiffen the functional airframe to give it rigidity and strength under load. Bracing may be applied both internally and externally, and may take the form of strut, which act in compression or tension as the need arises, and/or wires, which act only in tension. In general, bracing allows a stronger, lighter structure than one which is unbraced, but external bracing in particular adds drag which slows down the aircraft and raises considerably more design issues than internal bracing. Another disadvantage of bracing wires is that they require routine checking and adjustment, or rigging, even when located internally. During the early years of aviation, bracing was a universal feature of all forms of aeroplane, including the monoplanes and biplanes which were then equally common. Today, bracing in the form of lift struts is still used for some light commercial designs where a high wing and light weight are more impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)