|
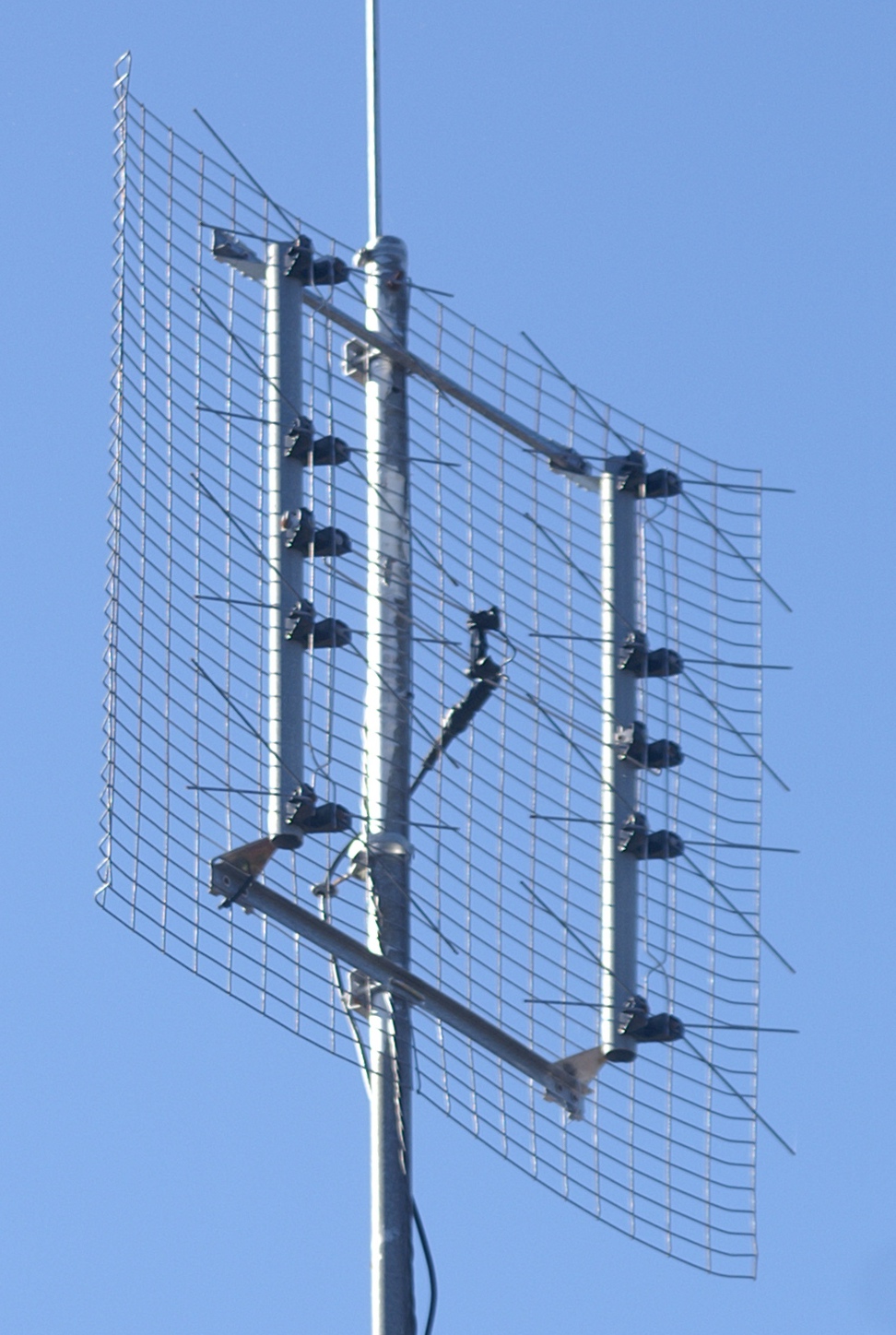
Corner Reflector Antenna
A corner reflector antenna is a type of directional antenna used at VHF and UHF frequencies. It was invented by John D. Kraus in 1938.Kraus, John D., US patent 2270314 Corner reflector antenna filed January 31, 1940; granted January 20, 1942. It consists of a dipole driven element mounted in front of two flat rectangular reflecting screens joined at an angle, usually 90°. Corner reflector antennas have moderate gain of 10–15 dB, high front-to-back ratio of 20–30 dB, and wide bandwidth. Corner reflector antennas are widely used for UHF television receiving antennas, point-to-point communication links and data links for wireless WANs, and amateur radio antennas on the 144, 420, and 1296 MHz bands. They radiate linearly polarized radio waves and can be mounted for either horizontal or vertical polarization. The corner reflector ''antenna'' should not be confused with a ''corner reflector'', a passive device used to reflect radio waves back toward the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corner Reflector TV Antenna
Corner may refer to: People *Corner (surname) *House of Cornaro, a noble Venetian family (''Corner'' in Venetian dialect) Places *Corner, Alabama, a community in the United States *Corner Inlet, Victoria, Australia *Corner River, a tributary of Harricana River, in Ontario, Canada *Corner Township, Custer County, Nebraska, a township in the United States Arts, entertainment, and media Music * The Corner (album), ''The Corner'' (album), an album by the Hieroglyphics * The Corner (song), "The Corner" (song), a 2005 song by Common * "Corner", a song by Allie Moss from her 2009 EP ''Passerby'' * "Corner", a song by Blue Stahli from their 2010 album ''Blue Stahli (album), Blue Stahli'' * "The Corner", a song by Dermot Kennedy from his 2019 album ''Without Fear (album), Without Fear'' * "The Corner", a song from Staind's 2008 album ''The Illusion of Progress'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media *Corner painters, a Danish artists association *The Corner (1916 film), ''The Corn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communications. The term "amateur" is used to specify "a duly authorised person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without pecuniary interest;" (either direct monetary or other similar reward) and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety (such as police and fire), or professional two-way radio services (such as maritime, aviation, taxis, etc.). The amateur radio service (''amateur service'' and '' amateur-satellite service'') is established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) through the Radio Regulations. National governments regulate technical and operational characteristics of transmissions and issue individual station licenses with a unique identifying call sign, which mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troposcatter
Tropospheric scatter, also known as troposcatter, is a method of communicating with microwave radio signals over considerable distances – often up to and further depending on frequency of operation, equipment type, terrain, and climate factors. This method of propagation uses the tropospheric scatter phenomenon, where radio waves at Ultra high frequency, UHF and Super high frequency, SHF Frequency, frequencies are randomly scattered as they pass through the upper layers of the troposphere. Radio signals are transmitted in a narrow beam aimed just above the horizon in the direction of the receiver station. As the signals pass through the troposphere, some of the energy is scattered back toward the Earth, allowing the receiver station to pick up the signal. Normally, signals in the microwave frequency range travel in straight lines, and so are limited to ''Line-of-sight propagation, line-of-sight'' applications, in which the receiver can be 'seen' by the transmitter. Communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopole Antenna
A monopole antenna is a class of radio antenna consisting of a straight rod-shaped conductor, often mounted perpendicularly over some type of conductive surface, called a ground plane. The driving signal from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output signal to the receiver is taken, between the lower end of the monopole and the ground plane. One side of the antenna feedline is attached to the lower end of the monopole, and the other side is attached to the ground plane, which is often the Earth. This contrasts with a dipole antenna which consists of two identical rod conductors, with the signal from the transmitter applied between the two halves of the antenna. The monopole is often used as a resonant antenna; the rod functions as an open resonator for radio waves, oscillating with standing waves of voltage and current along its length. Therefore the length of the antenna is determined by the wavelength of the radio waves it is used with. The most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabolic Antenna
A parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector, a curved surface with the cross-sectional shape of a parabola, to direct the radio waves. The most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or parabolic dish. The main advantage of a parabolic antenna is that it has high directivity. It functions similarly to a searchlight or flashlight reflector to direct radio waves in a narrow beam, or receive radio waves from one particular direction only. Parabolic antennas have some of the highest gains, meaning that they can produce the narrowest beamwidths, of any antenna type. In order to achieve narrow beamwidths, the parabolic reflector must be much larger than the wavelength of the radio waves used, so parabolic antennas are used in the high frequency part of the radio spectrum, at UHF and microwave ( SHF) frequencies, at which the wavelengths are small enough that conveniently-sized reflectors can be used. Parabolic antennas are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflective Array Antenna
In telecommunications and radar, a reflective array antenna is a class of directive antennas in which multiple driven elements are mounted in front of a flat surface designed to reflect the radio waves in a desired direction. They are a type of array antenna. They are often used in the VHF and UHF frequency bands. VHF examples are generally large and resemble a highway billboard, so they are sometimes called billboard antennas. Other names are bedspring array and bowtie array depending on the type of elements making up the antenna. The curtain array is a larger version used by shortwave radio broadcasting stations. Reflective array antennas usually have a number of identical driven elements, fed in phase, in front of a flat, electrically large reflecting surface to produce a unidirectional beam of radio waves, increasing antenna gain and reducing radiation in unwanted directions. The larger the number of elements used, the higher the gain; the narrower the beam is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Resistance
Radiation resistance, \ R_\mathsf\ or \ R_\mathsf\ , is proportional to the part of an antenna's feedpoint electrical resistance that is caused by power loss from the emission of radio waves from the antenna. Radiation resistance is an ''effective'' resistance, due to the power carried away from the antenna as radio waves. Unlike conventional resistance or " Ohmic resistance", radiation resistance is ''not'' due to the opposition to current (resistivity) of the imperfect conducting materials the antenna is made of. The radiation resistance (\ R_\mathsf\ ) is conventionally defined as the value of loss resistance that ''would'' dissipate the same amount of power as heat, as is dissipated by the radio waves emitted from the antenna, when fed at a minimum-voltage / maximum-current point ("voltage node"). From Joule's law, it is equal to the total power \ P_\mathsf\ radiated as radio waves by the antenna, divided by the square of the current \ I_\mathsf\ into the antenna termina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter ''lambda'' (λ). The term ''wavelength'' is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave: waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths. Wavelength depends on the medium (for example, vacuum, air, or water) that a wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corner Reflector Antenna Diagram
Corner may refer to: People *Corner (surname) *House of Cornaro, a noble Venetian family (''Corner'' in Venetian dialect) Places *Corner, Alabama, a community in the United States *Corner Inlet, Victoria, Australia *Corner River, a tributary of Harricana River, in Ontario, Canada *Corner Township, Custer County, Nebraska, a township in the United States Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''The Corner'' (album), an album by the Hieroglyphics * "The Corner" (song), a 2005 song by Common * "Corner", a song by Allie Moss from her 2009 EP ''Passerby'' * "Corner", a song by Blue Stahli from their 2010 album ''Blue Stahli'' * "The Corner", a song by Dermot Kennedy from his 2019 album ''Without Fear'' * "The Corner", a song from Staind's 2008 album ''The Illusion of Progress'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media *Corner painters, a Danish artists association * ''The Corner'' (1916 film), a 1916 film western * ''The Corner'' (2014 film), a 2014 Iranian drama film *''The Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corner Reflector
A corner reflector is a retroreflector consisting of three mutually perpendicular, intersecting flat surfaces, which reflects waves directly towards the source, but translated. The three intersecting surfaces often have square shapes. Radar corner reflectors made of metal are used to reflect radio waves from radar sets. Optical corner reflectors, called corner cubes or cube corners, made of three-sided glass prisms, are used in surveying and laser ranging. Principle The incoming ray is reflected three times, once by each surface, which results in a reversal of direction. To see this, the three corresponding normal vectors of the corner's perpendicular sides can be considered to form a basis (a rectangular coordinate system) (''x'', ''y'', ''z'') in which to represent the direction of an arbitrary incoming ray, . When the ray reflects from the first side, say ''x'', the ray's ''x'' component, ''a'', is reversed to −''a'' while the ''y'' and ''z'' components are unchange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarization'' (French: ''polarisation rectiligne'') was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866), pp.731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", , 2021 (open access); §9. See '' polarization'' and ''plane of polarization'' for more information. The orientation of a linearly polarized electromagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |