|
Contractile Ring
In molecular biology, an actomyosin contractile ring is a prominent structure during cytokinesis.Cheffings TH, Burroughs NJ, Balasubramanian MK. (2016). Actomyosin Ring Formation and Tension Generation in Eukaryotic Cytokinesis. Curr Biol. 26(15):719-737. It forms perpendicular to the axis of the spindle apparatus towards the end of telophase, in which sister chromatids are identically separated at the opposite sides of the spindle forming nuclei (Figure 1). The actomyosin ring follows an orderly sequence of events: identification of the active division site, formation of the ring, constriction of the ring, and disassembly of the ring. It is composed of actin and myosin II bundles, thus the term actomyosin. The actomyosin ring operates in contractile motion, although the mechanism on how or what triggers the constriction is still an evolving topic. Other cytoskeletal proteins are also involved in maintaining the stability of the ring and driving its constriction. Apart from cytokine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle With Images
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery with only a few monks or nuns * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Groups of people * Cell, a group of people in a cell group, a form of Christian church organization * Cell, a unit of a clandestine cell system, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Cellular organizational structure, such as in business management Science, mathematics, and technology Computing and telecommunications * Cell (EDA), a term used in an electronic circuit design schematics * Cell (microprocessor), a microprocessor architecture developed by Sony, Toshiba, and IBM * Memory cell (computing), the basic unit of (volatile or non-volatile) computer memory * Cell, a unit in a database table or spreadsheet, formed by the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleavage Furrow
In cell biology, the cleavage furrow is the indentation of the cell's surface that begins the progression of cleavage, by which animal and some algal cells undergo cytokinesis, the final splitting of the membrane, in the process of cell division. The same proteins responsible for muscle contraction, actin and myosin, begin the process of forming the cleavage furrow, creating an actomyosin ring. Other cytoskeletal proteins and actin binding proteins are involved in the procedure. Mechanism Plant cells do not perform cytokinesis through this exact method but the two procedures are not totally different. Animal cells form an actin-myosin contractile ring within the equatorial region of the cell membrane that constricts to form the cleavage furrow. In plant cells, Golgi vesicle secretions form a cell plate or septum on the equatorial plane of the cell wall by the action of microtubules of the phragmoplast. The cleavage furrow in animal cells and the phragmoplast in plant cells ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. Cell walls are absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, but are present in some other ones like fungi, algae and plants, and in most prokaryotes (except mollicute bacteria). A major function is to act as pressure vessels, preventing over-expansion of the cell when water enters. The composition of cell walls varies between taxonomic group and species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin. Often, other polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae possess cell walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides such as carrageenan and agar that are absent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Plate
image:Phragmoplast.png, 300px, Phragmoplast and cell plate formation in a plant cell during cytokinesis. Left side: Phragmoplast forms and cell plate starts to assemble in the center of the cell. Towards the right: Phragmoplast enlarges in a donut-shape towards the outside of the cell, leaving behind mature cell plate in the center. The cell plate will transform into the new cell wall once cytokinesis is complete. Cytokinesis in embryophyte, terrestrial plants occurs by cell plate formation. This process entails the delivery of Golgi-derived and endosomal vesicles carrying [ ell wall and cell membrane components to the plane of cell division and the subsequent fusion of these vesicles within this plate. After formation of an early tubulo-vesicular network at the center of the cell, the initially labile cell plate consolidates into a tubular network and eventually a fenestrated sheet. The cell plate grows outward from the center of the cell to the parental plasma membrane with whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplasts
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules Adenosine triphosphate, ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by Chloroplast membrane, its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division. In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.Turk E, Wills AA, Kwon T, Sedzinski J, Wallingford JB, Stearns "Zeta-Tubulin Is a Member of a Conserved Tubulin Module and Is a Component of the Centriolar Basal Foot in Multiciliated Cells"Current Biology (2015) 25:2177-2183. Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus in a similar range compared to actin (with a mass of ~42 kDa). In contrast, tubulin polymers (microtubules) te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FtsZ
FtsZ is a protein encoded by the ''ftsZ'' gene that assembles into a ring at the future site of bacterial cell division (also called the Z ring). FtsZ is a prokaryotic homologue of the eukaryotic protein tubulin. The initials FtsZ mean "Filamenting temperature-sensitive mutant Z." The hypothesis was that cell division mutants of '' E. coli'' would grow as filaments due to the inability of the daughter cells to separate from one another. FtsZ is found in almost all bacteria, many archaea, all chloroplasts and some mitochondria, where it is essential for cell division. FtsZ assembles the cytoskeletal scaffold of the Z ring that, along with additional proteins, constricts to divide the cell in two. History In the 1960s scientists screened for temperature sensitive mutations that blocked cell division at 42 °C. The mutant cells divided normally at 30°, but failed to divide at 42°. Continued growth without division produced long filamentous cells (Filamenting temperature s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
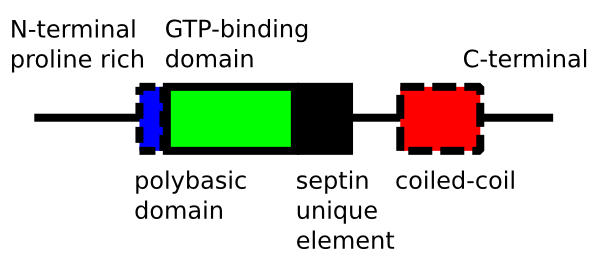
Septin
Septins are a group of guanosine triphosphate, GTP-molecular binding, binding proteins gene expression, expressed in all eukaryote, eukaryotic cells except plants. Different septins form protein complexes with each other. These complexes can further assemble into filaments, rings and gauzes. Assembled as such, septins function in cells by localizing other proteins, either by providing a scaffold to which proteins can attach, or by forming a barrier preventing the diffusion of molecules from one compartment of the cell to another, or in the cell cortex as a barrier to the diffusion of membrane-bound proteins. Septins have been implicated in the localization of cellular processes at the site of cell division, and at the cell membrane at sites where specialized structures like cilium, cilia or flagella are attached to the cell body. In yeast cells, they compartmentalize parts of the cell and build scaffolding to provide structural support during cell division at the septum (cell biol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)