|
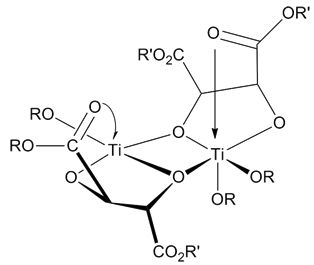
Concerted Mechanism
In chemistry, a concerted reaction is a chemical reaction in which all bond breaking and bond making occurs in a single step. Reactive intermediates or other unstable high energy intermediates are not involved. Concerted reaction rates tend not to depend on solvent polarity Polarity may refer to: Science *Electrical polarity, direction of electrical current *Polarity (mutual inductance), the relationship between components such as transformer windings * Polarity (projective geometry), in mathematics, a duality of ord ... ruling out large buildup of charge in the transition state. The reaction is said to progress through a concerted mechanism as all bonds are formed and broken ''in concert''. Pericyclic reactions, the S2 reaction, and some rearrangements - such as the Claisen rearrangement - are concerted reactions. The rate of the SN2 reaction is second order overall due to the reaction being bimolecular (i.e. there are two molecular species involved in the rate-de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
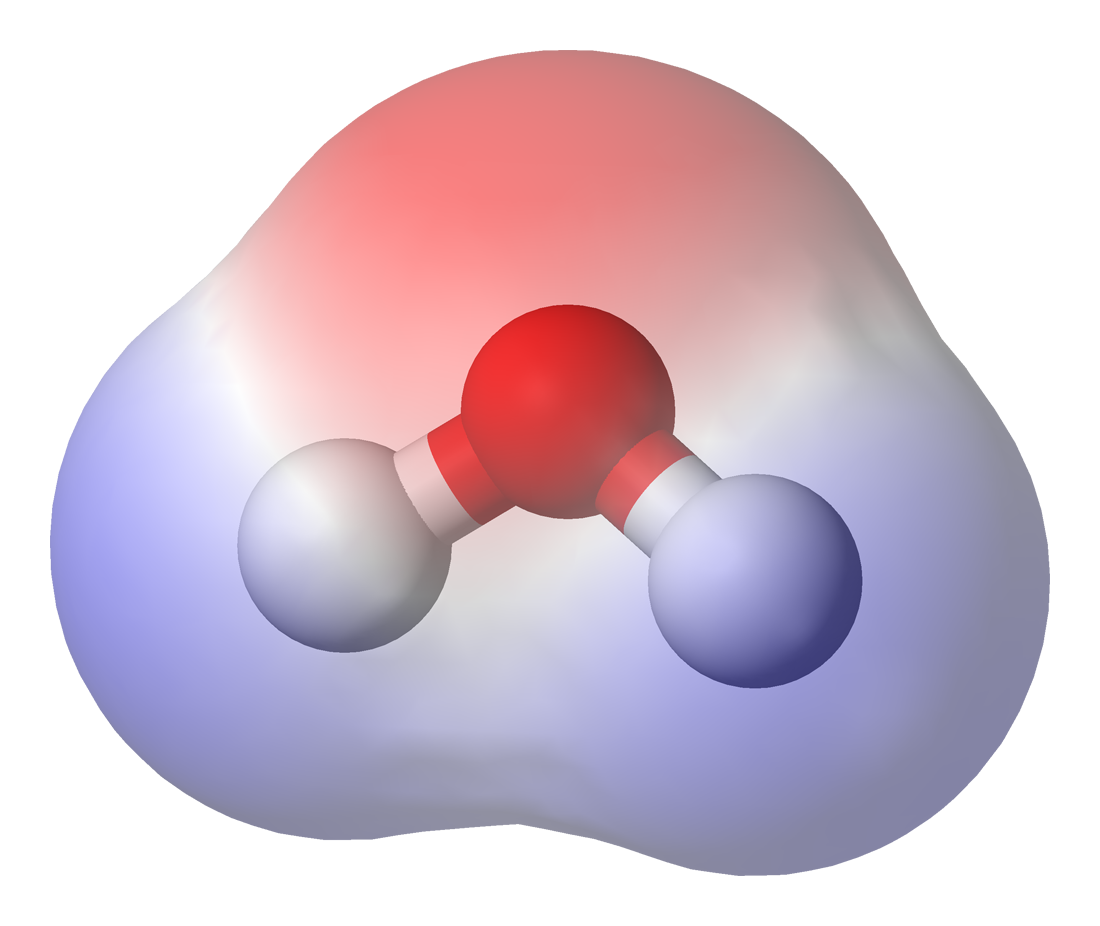
Chemical Polarity
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimolecular
In chemistry, molecularity is the number of molecules that come together to react in an elementary (single-step) reactionAtkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical Chemistry. Oxford University Press, 2014 and is equal to the sum of stoichiometric coefficients of reactants in the elementary reaction with effective collision ( sufficient energy) and correct orientation. Depending on how many molecules come together, a reaction can be unimolecular, bimolecular or even trimolecular. The kinetic order of any elementary reaction or reaction step is ''equal'' to its molecularity, and the rate equation of an elementary reaction can therefore be determined by inspection, from the molecularity. The kinetic order of a complex (multistep) reaction, however, is not necessarily equal to the number of molecules involved. The concept of molecularity is only useful to describe elementary reactions or steps. Unimolecular reactions In a unimolecular reaction, a single molecule rearranges atoms, forming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claisen Rearrangement
The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon–carbon bond-forming chemical reaction discovered by Rainer Ludwig Claisen. The heating of an allyl vinyl ether will initiate a ,3sigmatropic rearrangement to give a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl, driven by exergonically favored carbonyl CO bond formation (ΔΔHf = -327kcalmol−1). Mechanism The Claisen rearrangement is an exothermic, concerted (bond cleavage and recombination) pericyclic reaction. Woodward–Hoffmann rules show a suprafacial, stereospecific reaction pathway. The kinetics are of the first order and the whole transformation proceeds through a highly ordered cyclic transition state and is intramolecular. Crossover experiments eliminate the possibility of the rearrangement occurring via an intermolecular reaction mechanism and are consistent with an intramolecular process. There are substantial solvent effects observed in the Claisen rearrangement, where polar solvents tend to accelerate the reaction to a greater e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rearrangement Reaction
In organic chemistry, a rearrangement reaction is a broad class of organic reactions where the carbon skeleton of a molecule is rearranged to give a structural isomer of the original molecule. Often a substituent moves from one atom to another atom in the same molecule, hence these reactions are usually intramolecular. In the example below, the substituent R moves from carbon atom 1 to carbon atom 2: :\underset\ce\ce\underset\ce\ce Intermolecular rearrangements also take place. A rearrangement is not well represented by simple and discrete electron transfers (represented by curved arrows in organic chemistry texts). The actual mechanism of alkyl groups moving, as in Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement, probably involves transfer of the moving alkyl group fluidly along a bond, not ionic bond-breaking and forming. In pericyclic reactions, explanation by orbital interactions give a better picture than simple discrete electron transfers. It is, nevertheless, possible to draw the curv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericyclic
In organic chemistry, a pericyclic reaction is the type of organic reaction wherein the transition state of the molecule has a cyclic geometry, the reaction progresses in a concerted fashion, and the bond orbitals involved in the reaction overlap in a continuous cycle at the transition state. Pericyclic reactions stand in contrast to ''linear reactions'', encompassing most organic transformations and proceeding through an acyclic transition state, on the one hand and '' coarctate reactions'', which proceed through a doubly cyclic, concerted transition state on the other hand. Pericyclic reactions are usually rearrangement or addition reactions. The major classes of pericyclic reactions are given in the table below (the three most important classes are shown in bold). Ene reactions and cheletropic reactions are often classed as group transfer reactions and cycloadditions/cycloeliminations, respectively, while dyotropic reactions and group transfer reactions (if ene reactions are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition State
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked with the double dagger ‡ symbol. As an example, the transition state shown below occurs during the SN2 reaction of bromoethane with a hydroxide anion: The activated complex of a reaction can refer to either the transition state or to other states along the reaction coordinate between reactants and products, especially those close to the transition state.Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, ''Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed., W.H. Freeman 2006), p.809 According to the transition state theory, once the reactants have passed through the transition state configuration, they always continue to form products. History of concept The concept of a transition state has been important in many theories of the rates at which chemical reactions occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Charge
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of positiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. The quantity of solute that can dissolve in a specific volume of solvent varies with temperature. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents ( citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas industries, including in chemical syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a Chemical reaction, reaction with other Chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Rate
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit time. Reaction rates can vary dramatically. For example, the oxidative rusting of iron under Earth's atmosphere is a slow reaction that can take many years, but the combustion of cellulose in a fire is a reaction that takes place in fractions of a second. For most reactions, the rate decreases as the reaction proceeds. A reaction's rate can be determined by measuring the changes in concentration over time. Chemical kinetics is the part of physical chemistry that concerns how rates of chemical reactions are measured and predicted, and how reaction-rate data can be used to deduce probable reaction mechanisms. The concepts of chemical kinetics are applied in many disciplines, such as chemical engineering, enzymology and environmental engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |