|
Class President
A class president, also known as a class representative, is usually the leader of a student body class, and presides over its class cabinet or organization within a student council. In a grade school, class presidents are generally elected by the class, a constituency composed of all students in a grade level. The practice of electing a class president is common in many countries around the world. While a class president is similar to a student government president in certain ways, the main difference between the two positions is that a class president usually only represents a specific grade within the school while the student government president represents the school's entire student body (for which reason they are sometimes called "student ''body'' president" or "''school'' president"). Studies have shown that co-ed schools are more likely to have male students as class presidents than female students. Duties and term The primary duties of the class president usually in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graduation
Graduation is the awarding of a diploma to a student by an educational institution. It may also refer to the ceremony that is associated with it. The date of the graduation ceremony is often called graduation day. The graduation ceremony is also sometimes called: commencement, congregation, convocation or invocation. History Ceremonies for graduating students date from the first universities in Europe in the twelfth century. At that time Latin was the language of scholars. A ''universitas'' was a guild of masters (such as MAs) with licence to teach. "Degree" and "graduate" come from ''gradus'', meaning "step". The first step was admission to a bachelor's degree. The second step was the masters step, giving the graduate admission to the ''universitas'' and license to teach. Typical dress for graduation is gown and hood, or hats adapted from the daily dress of university staff in the Middle Ages, which was in turn based on the attire worn by medieval clergy. The tradition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African-American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of Slavery in the United States, enslaved Africans who are from the United States. While some Black immigrants or their children may also come to identify as African-American, the majority of first generation immigrants do not, preferring to identify with their nation of origin. African Americans constitute the second largest racial group in the U.S. after White Americans, as well as the third largest ethnic group after Hispanic and Latino Americans. Most African Americans are descendants of enslaved people within the boundaries of the present United States. On average, African Americans are of West Africa, West/Central Africa, Central African with some European descent; some also have Native Americans in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of The United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of the United States, federal government and is the Powers of the president of the United States#Commander-in-chief, commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces. The power of the presidency has grown substantially since the first president, George Washington, took office in 1789. While presidential power has ebbed and flowed over time, the presidency has played an increasingly strong role in American political life since the beginning of the 20th century, with a notable expansion during the presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt. In contemporary times, the president is also looked upon as one of the world's most powerful political figures as the leader of the only remaining global superpower. As the leader of the nation with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allegory
As a literary device or artistic form, an allegory is a narrative or visual representation in which a character, place, or event can be interpreted to represent a hidden meaning with moral or political significance. Authors have used allegory throughout history in all forms of art to illustrate or convey complex ideas and concepts in ways that are comprehensible or striking to its viewers, readers, or listeners. Writers and speakers typically use allegories to convey (semi-)hidden or complex meanings through symbolic figures, actions, imagery, or events, which together create the moral, spiritual, or political meaning the author wishes to convey. Many allegories use personification of abstract concepts. Etymology First attested in English in 1382, the word ''allegory'' comes from Latin ''allegoria'', the latinisation of the Greek ἀλληγορία (''allegoría''), "veiled language, figurative", which in turn comes from both ἄλλος (''allos''), "another, differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popularity
In sociology, popularity is how much a person, idea, place, item or other concept is either liked or accorded status by other people. Liking can be due to reciprocal liking, interpersonal attraction, and similar factors. Social status can be due to dominance, superiority, and similar factors. For example, a kind person may be considered likable and therefore more popular than another person, and a wealthy person may be considered superior and therefore more popular than another person. There are two primary types of interpersonal popularity: perceived and sociometric. Perceived popularity is measured by asking people who the most popular or socially important people in their social group are. Sociometric popularity is measured by objectively measuring the number of connections a person has to others in the group. A person can have high perceived popularity without having high sociometric popularity, and ''vice versa''. According to psychologist Tessa Lansu at the Radboud U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underdog (competition)
An underdog is a person or group in a competition, usually in sports and creative works, who is largely expected to lose. The party, team, or individual expected to win is called the favorite or top dog. In the case where an underdog wins, the outcome is an upset. An "underdog bet" is a bet on the underdog or outsider for which the odds are generally higher. The first recorded uses of the term occurred in the second half of the 19th century; its first meaning was "the beaten dog in a fight". In British and American culture, underdogs are highly regarded. This harkens to core Judeo-Christian stories, such as that of David and Goliath, and also ancient British legends such as Robin Hood and King Arthur, and reflects the ideal behind the American dream, where someone who is poor and/or weak can use hard work to achieve victory. Underdogs are most valorized in sporting culture, both in real events, such as the Miracle on Ice, and in popular culture depictions of sports, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerd
A nerd is a person seen as overly intellectual, obsessive, introverted or lacking social skills. Such a person may spend inordinate amounts of time on unpopular, little known, or non-mainstream activities, which are generally either highly technical, abstract, or relating to topics of science fiction or fantasy, to the exclusion of more mainstream activities. Additionally, many so-called nerds are described as being shy, quirky, pedantic, and unattractive. Originally derogatory, the term "nerd" was a stereotype, but as with other pejoratives, it has been reclaimed and redefined by some as a term of pride and group identity. Etymology The first documented appearance of the word ''nerd'' is as the name of a creature in Dr. Seuss's book ''If I Ran the Zoo'' (1950), in which the narrator Gerald McGrew claims that he would collect "a Nerkle, a Nerd, and a Seersucker too" for his imaginary zoo.American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Third Edition, p. 1212, Houghton M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
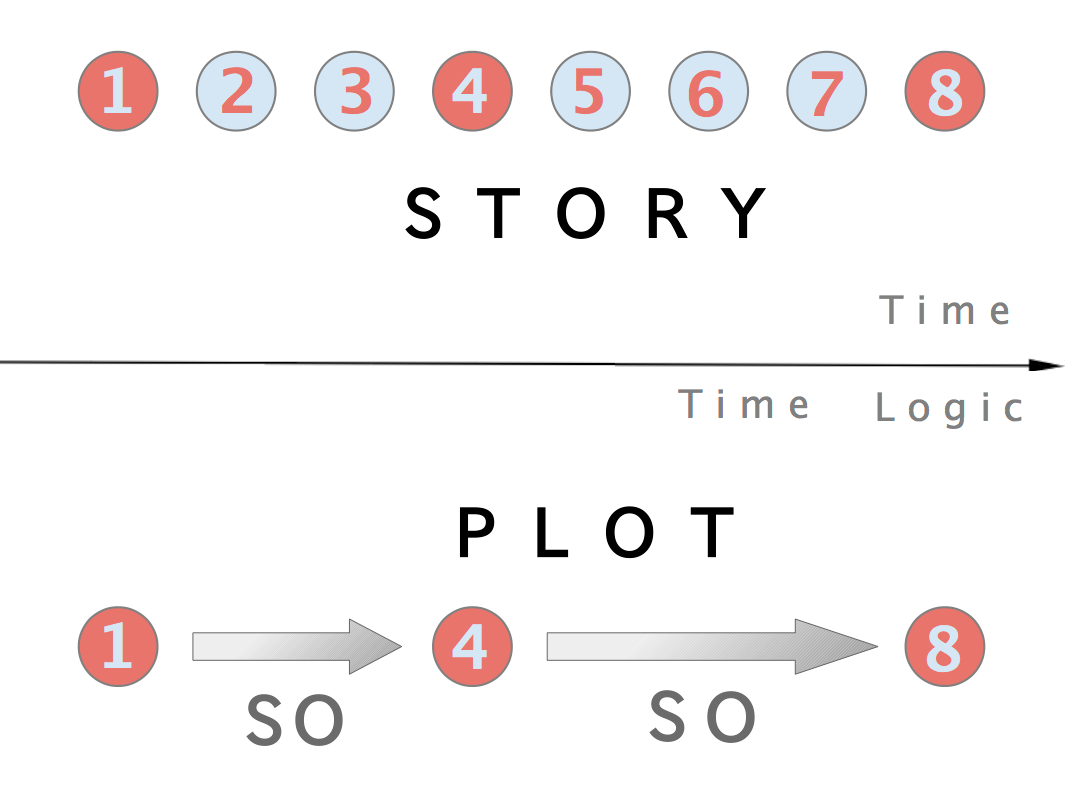
Plot (narrative)
In a literary work, film, or other narrative, the plot is the sequence of events in which each event affects the next one through the principle of cause-and-effect. The causal events of a plot can be thought of as a series of events linked by the connector "and so". Plots can vary from the simple—such as in a traditional ballad—to forming complex interwoven structures, with each part sometimes referred to as a subplot or ''imbroglio''. Plot is similar in meaning to the term ''storyline''. In the narrative sense, the term highlights important points which have consequences within the story, according to American science fiction writer Ansen Dibell. The term ''plot'' can also serve as a verb, referring to either the writer's crafting of a plot (devising and ordering story events), or else to a character's planning of future actions in the story. The term ''plot'', however, in common usage (for example, a "movie plot") can mean a narrative summary or story synopsis, rather t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HarperCollins
HarperCollins Publishers LLC is one of the Big Five English-language publishing companies, alongside Penguin Random House, Simon & Schuster, Hachette, and Macmillan. The company is headquartered in New York City and is a subsidiary of News Corp. The name is a combination of several publishing firm names: Harper & Row, an American publishing company acquired in 1987—whose own name was the result of an earlier merger of Harper & Brothers (founded in 1817) and Row, Peterson & Company—together with Scottish publishing company William Collins, Sons (founded in 1819), acquired in 1989. The worldwide CEO of HarperCollins is Brian Murray. HarperCollins has publishing groups in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, Brazil, India, and China. The company publishes many different imprints, both former independent publishing houses and new imprints. History Collins Harper Mergers and acquisitions Collins was bought by Rupert Murdoch's News ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typecasting (acting)
In film, television, and theatre, typecasting is the process by which a particular actor becomes strongly identified with a specific character, one or more particular roles, or characters having the same traits or coming from the same social or ethnic groups. There have been instances in which an actor has been so strongly identified with a role as to make it difficult for them to find work playing other characters. Character actors Actors are sometimes so strongly identified with a role as to make it difficult for them to find work playing other characters. It is especially common among leading actors in popular television series and films. ''Star Trek'' An example is the cast of the original ''Star Trek'' series. During ''Star Trek''s original run from 1966 to 1969, William Shatner was the highest-paid cast member at $5,000 per episode ($ today), with Leonard Nimoy and the other actors being paid much less. The press predicted that Nimoy would be a star after the series e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |