|
Cervical Plexus
The cervical plexus is a plexus of the anterior rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which arise from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral (m. scalenus, m. levator scapulae, m. splenius cervicis) from lateral side. There is anastomosis with accessory nerve, hypoglossal nerve and sympathetic trunk. It is located in the neck, deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Nerves formed from the cervical plexus innervate the back of the head, as well as some neck muscles. The branches of the cervical plexus emerge from the posterior triangle at the nerve point, a point which lies midway on the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid. Branches The cervical plexus has two types of branches: cutaneous and muscular. *Cutaneous (4 branches): **Lesser occipital nerve - innervates the skin and the scalp posterosuperior to the auricle (C2) **Great auricular nerve - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Nerves
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. Structure Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, formed from the combination of nerve fibers from its dorsal and ventral roots. The dorsal root is the afferent sensory root and carries sensory information to the brain. The ventral root is the efferent motor root and carries motor information from the brain. The spinal nerve emerges from the spinal column through an opening (intervertebral foramen) between adjacent vertebrae. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Auricular Nerve
The great auricular nerve is a cutaneous nerve of the head. It originates from the cervical plexus, with branches of spinal nerves C2 and C3. It provides sensory nerve supply to the skin over the parotid gland and the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and surfaces of the outer ear. Pain resulting from parotitis is caused by an impingement on the great auricular nerve. Structure The great auricular nerve is the largest of the ascending branches of the cervical plexus. It arises from the second and third cervical nerves. It winds around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and, after perforating the deep fascia, ascends upon that muscle beneath the platysma muscle to the parotid gland. Here, it divides into an anterior and a posterior branch. Branches * The anterior branch (ramus anterior; facial branch) is distributed to the skin of the face over the parotid gland. It communicates with the facial nerve inside the parotid gland. * The posterior branch ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
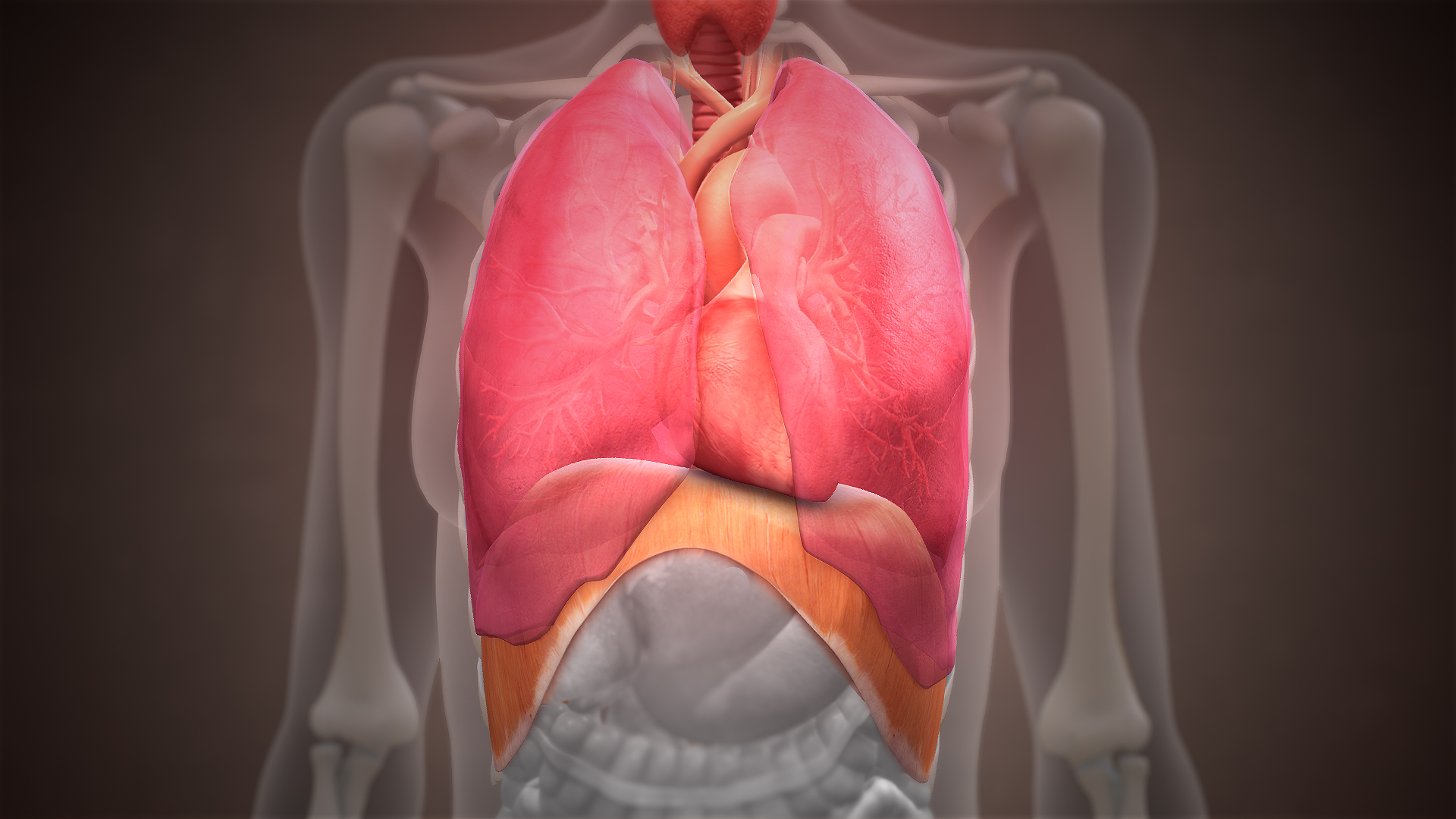
Pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of serous membrane (serous pericardium). It encloses the pericardial cavity, which contains pericardial fluid, and defines the middle mediastinum. It separates the heart from interference of other structures, protects it against infection and blunt trauma, and lubricates the heart's movements. The English name originates from the Ancient Greek prefix "''peri-''" (περί; "around") and the suffix "''-cardion''" (κάρδιον; "heart"). Anatomy The pericardium is a tough fibroelastic sac which covers the heart from all sides except at the cardiac root (where the great vessels join the heart) and the bottom (where only the serous pericardium exists to cover the upper surface of the central tendon of diaphragm). The fibrous pericardiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrenic
The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve which originates from the C3-C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm. In addition to motor fibers, the phrenic nerve contains sensory fibers, which receive input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal pleura, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibers. Although the nerve receives contributions from nerves roots of the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus, it is usually considered separate from either plexus. The name of the nerve comes from Ancient Greek ''phren'' 'diaphragm'. Structure The phrenic ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
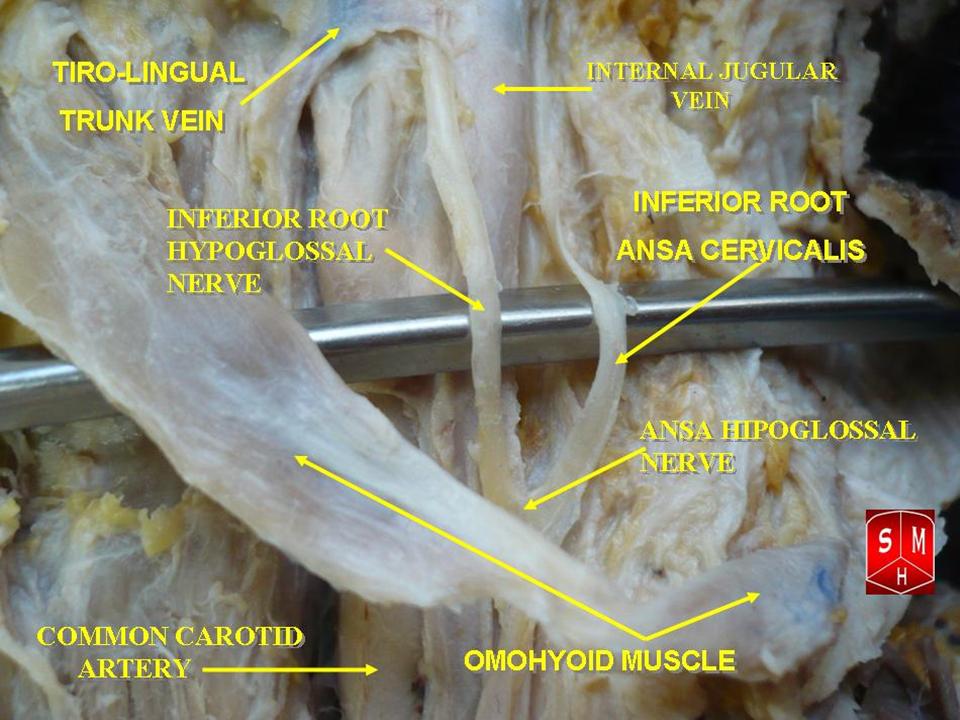
Omohyoid
The omohyoid muscle is a muscle that depresses the hyoid. It is located in the front of the neck, and consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. The omohyoid muscle is proximally attached to the scapula and distally attached to the hyoid bone, stabilising it. Its superior belly serves as the most lateral member of the infrahyoid muscles, located lateral to both the sternothyroid muscles and the thyrohyoid muscles.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 102 Structure The omohyoid muscle arises from the upper border of the scapula, inserting into the lower border of the body of the hyoid bone. It has two separate bellies, superior and inferior: * The ''inferior belly'' forms a flat, narrow fasciculus, which inclines forward and slightly upward across the lower part of the neck, being bound down to the clavicle by a fibrous expansion; it then passes behind the sternocleidomastoid, becomes tendinous and changes its dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternohyoid
The sternohyoid muscle is a thin, narrow muscle attaching the hyoid bone to the sternum. It is one of the paired strap muscles of the infrahyoid muscles. It is supplied by the ansa cervicalis. It depresses the hyoid bone. Structure The sternohyoid muscle is one of the paired strap muscles of the infrahyoid muscles. It arises from the posterior border of the medial end of the clavicle, the posterior sternoclavicular ligament, and the upper and posterior part of the manubrium of the sternum. Passing upward and medially, it is inserted by short tendinous fibers into the lower border of the body of the hyoid bone. It runs lateral to the trachea. Nerve supply The sternohyoid muscle is supplied by a branch of the ansa cervicalis. Variations The sternohyoid muscle may be doubled, have accessory slips (Cleidohyoideus) or be completely absent in some people. It sometimes presents a transverse tendinous inscription immediately above its origin. Function The sternohyoid muscle pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternothyroid
The sternothyroid muscle, or sternothyroideus, is an infrahyoid muscle in the neck. It acts to depress the hyoid bone. It is below the sternohyoid muscle. It is shorter and wider than the sternohyoid. Structure The sternothyroid arises from the posterior surface of the manubrium of the sternum, below the origin of the sternohyoid. It also arises from the edge of the cartilage of the first rib. It is inserted into the oblique line on the lamina of the thyroid cartilage. It is in close contact with its fellow at the lower part of the neck, but diverges somewhat as it ascends. It is occasionally traversed by a transverse or oblique tendinous inscription. Innervation The sternothyroid muscle is innervated by the ansa cervicalis. Variations Doubling; absence; accessory slips to the thyrohyoid, inferior pharyngeal constrictor, or to the carotid sheath. Function The sternothyroid muscle depresses the hyoid bone, along with the other infrahyoid muscle. Clinical significance The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyrohyoid
The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle on the neck. It originates from the lamina of the thyroid cartilage, and inserts into the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. It is supplied by the hypoglossal nerve, and a branch of the ventral rami of the cervical plexus, spinal nerve C1, which travels with the hypoglossal nerve. The thyrohyoid muscle depresses the hyoid bone and elevates the larynx. By controlling the position and shape of the larynx, it aids in making sound. Structure The thyrohyoid muscle is a quadrilateral muscle in shape. It appears like an upward continuation of the sternothyroid muscle. It belongs to the infrahyoid muscles group. It lies in the carotid triangle. It arises from the oblique line on the lamina of the thyroid cartilage. It is inserted into the lower border of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. Nerve supply The thyrohyoid muscle is supplied by the hypoglossal nerve (XII). It is the only infrahyoid muscle that is not supplied by the ansa cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansa Cervicalis
The ansa cervicalis (or ansa hypoglossi in older literature) is a loop of nerves that are part of the cervical plexus. It lies superficial to the internal jugular vein in the carotid triangle. Its name means "handle of the neck" in Latin. Branches from the ansa cervicalis innervate most of the infrahyoid muscles, including the sternothyroid muscle, sternohyoid muscle and the omohyoid muscle. Note that the thyrohyoid muscle, which is also an infrahyoid muscle and the geniohyoid muscle which is a suprahyoid muscle are innervated by cervical spinal nerve 1 via the hypoglossal nerve. Roots Two roots make up the ansa cervicalis, a superior root, and an inferior root. The superior root of the ansa cervicalis is formed from cervical spinal nerve 1 of the cervical plexus. These nerve fibers travel in the hypoglossal nerve before separating in the carotid triangle to form the superior root. The superior root goes around the occipital artery and then descends on the carotid sheath. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraclavicular Nerves
The supraclavicular nerves (descending branches) arise from the third and fourth cervical nerves. They emerge beneath the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus (sternocleidomastoid muscle), and descend in the posterior triangle of the neck beneath the platysma muscle and the deep cervical fascia. Together, they innervate skin over the shoulder. The supraclavicular nerve can be blocked during shoulder surgery. Branches The supraclavicular nerves arise from C3 and C4 spinal nerve roots. Near the clavicle, the supraclavicular nerves perforate the fascia and the platysma muscle to become cutaneous. They are arranged, according to their position, into three groups—anterior, middle, and posterior. Medial supraclavicular nerve The medial supraclavicular nerves or ''anterior supraclavicular nerves'' (nn. supraclaviculares anteriores; suprasternal nerves) cross obliquely over the external jugular vein and the clavicular and sternal heads of the sternocleidomastoideus, and supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Cervical Nerve
The transverse cervical nerve (superficial cervical or cutaneous cervical) arises from the second and third spinal nerves, turns around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus about its middle, and, passing obliquely forward beneath the external jugular vein to the anterior border of the muscle, it perforates the deep cervical fascia, and divides beneath the Platysma into ascending and descending branches, which are distributed to the antero-lateral parts of the neck The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In .... It provides cutaneous innervation to this area. During dissection, the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) is the landmark. The transverse cervical nerves will pass horizontally directly over the SCM from Erb's point. Additional images File:Gray784.png, Dermatome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |