|
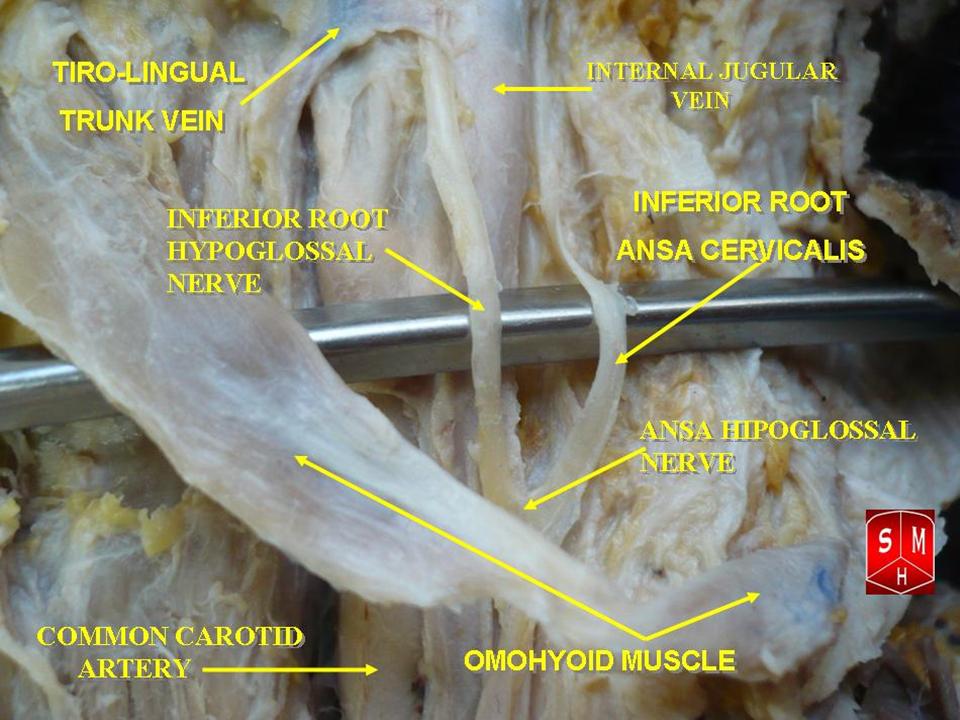
Omohyoid
The omohyoid muscle is a muscle in the neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. Its inferior belly is attached to the scapula; its superior belly is attached to the hyoid bone. Its intermediate tendon is anchored to the clavicle and first rib by a fascial sling. The omohyoid is innervated by the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus. It acts to depress the hyoid bone. Anatomy Structure The omohyoid muscle consists of muscle bellies that meet at an angle at the muscle's intermediate tendon. Inferior belly The inferior belly is narrow and flat band. It arises from the superior border of scapula (near the scapular notch). It sometimes also arises from the superior transverse scapular ligament. It is directed anteriorly and somewhat superiorly from its origin, extending across the inferior portion of the neck. It passes posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle to insert at the intermediate tendon. Superio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansa Cervicalis
The ansa cervicalis (or ansa hypoglossi in older literature) is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root (formed by branch of C1) and an inferior root (formed by union of branches of C2 and C3) - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated anterior to the carotid sheath. Branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate three of the four infrahyoid muscles: the sternothyroid, sternohyoid, and omohyoid muscles (note that the thyrohyoid muscle is the one infrahyoid muscle not innervated by the ansa cervicalis - it is instead innervated by cervical spinal nerve 1 via a separate thyrohyoid branch). Its name means "handle of the neck" in Latin. Anatomy The ansa cervicalis is typically embedded within the anterior wall of the carotid sheath anterior to the internal jugular vein. Superior root The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Root Of Ansa Cervicalis
The ansa cervicalis (or ansa hypoglossi in older literature) is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root (formed by branch of C1) and an inferior root (formed by union of branches of C2 and C3) - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated anterior to the carotid sheath. Branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate three of the four infrahyoid muscles: the sternothyroid, sternohyoid, and omohyoid muscles (note that the thyrohyoid muscle is the one infrahyoid muscle not innervated by the ansa cervicalis - it is instead innervated by cervical spinal nerve 1 via a separate thyrohyoid branch). Its name means "handle of the neck" in Latin. Anatomy The ansa cervicalis is typically embedded within the anterior wall of the carotid sheath anterior to the internal jugular vein. Superior root The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
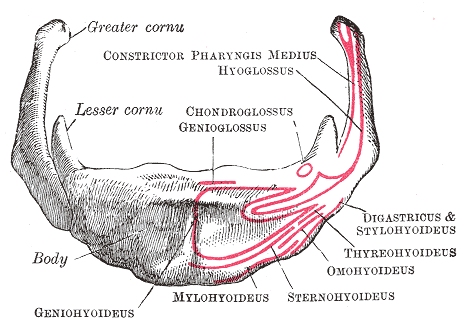
Hyoid
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrahyoid Muscles
The infrahyoid muscles, or strap muscles, are a group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck. The four infrahyoid muscles are the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid and omohyoid muscles. Excluding the sternothyroid, the infrahyoid muscles either originate from or insert on to the hyoid bone. The term ''infrahyoid'' refers to the region below the hyoid bone, while the term strap muscles refers to the long and flat muscle shapes which resembles a strap. The stylopharyngeus muscle is considered by many to be one of the strap muscles, but is not an infrahyoid muscle. Individual muscles The origin, insertion and innervation of the individual muscles: Nerve supply All of the infrahyoid muscles are innervated by the ansa cervicalis from the cervical plexus ( C1- C3) except the thyrohyoid muscle, which is innervated by fibers only from the first cervical spinal nerve travelling with the hypoglossal nerve. Function The infrahyoid muscles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Triangle Of The Neck
The posterior triangle (or lateral cervical region) is a region of the neck. Boundaries The posterior triangle has the following boundaries: Apex: Union of the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius muscles at the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone Anteriorly: Posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus Posteriorly: Anterior border of the trapezius Inferiorly: Middle one third of the clavicle Roof: Investing layer of the deep cervical fascia Floor: (From superior to inferior) 1) M. semispinalis capitis 2) M. splenius capitis 3) M. levator scapulae 4) M. scalenus posterior 5) M. scalenus medius Divisions The posterior triangle is crossed, about 2.5 cm above the clavicle, by the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle, which divides the space into two triangles: * an upper or occipital triangle * a lower or subclavian triangle (or supraclavicular triangle) Contents A) Nerves and plexuses: * Spinal accessory nerve (Cranial Nerve XI) * Branches of cervic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoid Bone
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Triangle
The inferior carotid triangle (or muscular triangle), is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid; above, by the superior belly of the omohyoid. It is covered by the integument, superficial fascia, platysma, and deep fascia, ramifying in which are some of the branches of the supraclavicular nerves. Beneath these superficial structures are the sternohyoid and sternothyroid, which, together with the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid, conceal the lower part of the common carotid artery. This vessel is enclosed within its sheath, together with the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve; the vein lies lateral to the artery on the right side of the neck, but overlaps it below on the left side; the nerve lies between the artery and vein, on a plane posterior to both. In front of the sheath are a few descending filaments from the ansa cervicalis; behind the sheath are the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Triangle
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck. Structure The triangle is inverted with its apex inferior to its base which is under the chin. Investing fascia covers the roof of the triangle while visceral fascia covers the floor. Anatomy Muscles: * Suprahyoid muscles - Digastric (Ant and post belly), mylohyoid, geniohyoid and stylohyoid. * Infrahyoid muscles - Omohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid, and thyrohyoid. Nerve supply 2 Bellies of digastric * Anterior: Mylohyoid nerve * Posterior: Facial nerve Stylohyoid: by the facial nerve, by a branch from that to the posterior belly of digastric. Mylohyoid: by its own nerve, a branch of the inferior alveolar (from the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve), which arises just before the parent nerve enters the mandibular foramen, pierces the sphenomandibular ligament, and runs forward on the inferior surface of the mylohyoid, supplying it and the anterior belly of the digastric. Geniohyoid: by a branch from the hypoglossal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Cervical Fascia
The deep cervical fascia (or fascia colli in older texts) lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap. The investing portion of the fascia is attached behind to the ligamentum nuchæ and to the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra. The ''alar fascia'' is a portion of the ''deep cervical fascia''. Divisions The deep cervical fascia is often divided into a superficial, middle, and deep layer. The superficial layer is also known as the investing layer of deep cervical fascia. It envelops the trapezius, sternocleidomastoid, and muscles of facial expression. It also contains the submandibular and parotid salivary gland as well as the muscles of mastication (the masseter, pterygoid, and temporalis muscles). The middle layer is also known as the pretracheal fas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Border Of The Scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrinsic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |