|
Carboxybenzyl
Benzyl chloroformate, also known as benzyl chlorocarbonate or Z-chloride, is the benzyl ester of chloroformic acid. It can be also described as the chloride of the benzyloxycarbonyl (Cbz or Z) group. In its pure form it is a water-sensitive oily colorless liquid, although impure samples usually appear yellow. It possesses a characteristic pungent odor and degrades in contact with water. The compound was first prepared by Leonidas Zervas in the early 1930s who used it for the introduction of the benzyloxycarbonyl protecting group, which became the basis of the Bergmann-Zervas carboxybenzyl method of peptide synthesis he developed with Max Bergmann. This was the first successful method of controlled peptide chemical synthesis and for twenty years it was the dominant procedure used worldwide until the 1950s. To this day, benzyl chloroformate is often used for amine group protection. Preparation The compound is prepared in the lab by treating benzyl alcohol with phosgene: : PhCH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Synthesis
In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, compounds where multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds, also known as peptide bonds. Peptides are chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction of the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another. Protecting group strategies are usually necessary to prevent undesirable side reactions with the various amino acid side chains. Chemical peptide synthesis most commonly starts at the carboxyl end of the peptide (C-terminus), and proceeds toward the amino-terminus (N-terminus). Protein biosynthesis (long peptides) in living organisms occurs in the opposite direction. The chemical synthesis of peptides can be carried out using classical solution-phase techniques, although these have been replaced in most research and development settings by solid-phase methods (see below). Solution-phase synthesis retains its usefulness in large-scale production of peptides for industrial purposes howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtius Rearrangement
The Curtius rearrangement (or Curtius reaction or Curtius degradation), first defined by Theodor Curtius in 1885, is the thermal decomposition of an acyl azide to an isocyanate with loss of nitrogen gas. The isocyanate then undergoes attack by a variety of nucleophiles such as water, alcohols and amines, to yield a primary amine, carbamate or urea derivative respectively. Several reviews have been published. Preparation of acyl azide The acyl azide is usually made from the reaction of acid chlorides or anydrides with sodium azide or trimethylsilyl azide. Acyl azides are also obtained from treating acylhydrazines with nitrous acid. Alternatively, the acyl azide can be formed by the direct reaction of a carboxylic acid with diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA). Reaction mechanism It was believed that the Curtius rearrangement was a two-step processes, with the loss of nitrogen gas forming an acyl nitrene, followed by migration of the R-group to give the isocyanate. However, recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonidas Zervas
Leonidas Zervas ( el, Λεωνίδας Ζέρβας, ; 21 May 1902 – 10 July 1980) was a Greek organic chemist who made seminal contributions in peptide chemical synthesis. Together with his mentor Max Bergmann they laid the foundations for the field in 1932 with their major discovery, the Bergmann-Zervas carboxybenzoxy oligopeptide synthesis which remained unsurpassed in utility for the next two decades. The carboxybenzyl protecting group he discovered is often abbreviated Z in his honour. Throughout his life Zervas also served in many important posts, including President of the Academy of Athens or briefly Minister of Industry of Greece. He received numerous awards and honours during his life and posthumously, such as Foreign Member of the USSR Academy of Sciences or the first Max Bergmann golden medal. Biography Early life and career abroad Zervas was born in 1902 in the rural town of Megalopolis in Arcadia, southern Greece. He was the first of 7 children of lawyer and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
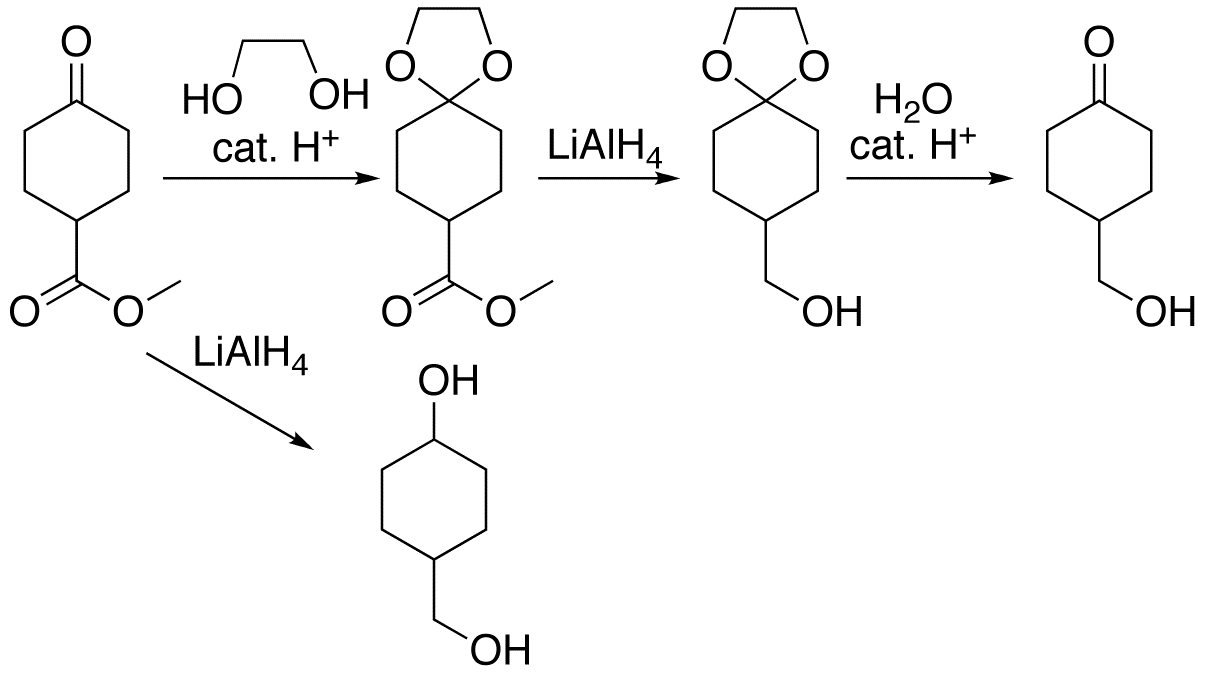
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Bergmann
Max Bergmann (12 February 1886 – 7 November 1944) was a Jewish-German biochemist. Together with Leonidas Zervas, the discoverer of the group, they were the first to use the carboxybenzyl protecting group for the synthesis of oligopeptides. Life and work Bergmann was born in Fürth, Bavaria, Germany on February 12, 1886, the seventh child of coal wholesalers Salomon and Rosalie Bergmann. Bergmann started studying Biology at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, but lectures by Adolf von Baeyer captured his interest and eventually persuaded him to switch to Organic Chemistry. He continued his chemical studies at the Friedrich Wilhelm University of Berlin, where he was taught by Emil Fischer. After receiving his PhD under the supervision of Ignaz Bloch de.html"_;"title=":de:Ignaz_Bloch.html"_;"title="nowiki/>:de:Ignaz_Bloch">de">:de:Ignaz_Bloch.html"_;"title="nowiki/>:de:Ignaz_Bloch">de/small>_in_1911_for_his_thesis_on_Polysulfide#Organic_polysulfides.html" ;"title= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Synthesis
In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, compounds where multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds, also known as peptide bonds. Peptides are chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction of the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another. Protecting group strategies are usually necessary to prevent undesirable side reactions with the various amino acid side chains. Chemical peptide synthesis most commonly starts at the carboxyl end of the peptide (C-terminus), and proceeds toward the amino-terminus (N-terminus). Protein biosynthesis (long peptides) in living organisms occurs in the opposite direction. The chemical synthesis of peptides can be carried out using classical solution-phase techniques, although these have been replaced in most research and development settings by solid-phase methods (see below). Solution-phase synthesis retains its usefulness in large-scale production of peptides for industrial purposes howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants growing in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process. Hydrates Sodium carbonate is obtained as three hydrates and as the anhydrous salt: * sodium carbonate decahydrate ( natron), Na2CO3·10H2O, which readily effloresces to form the monohydrate. * sodium carbonate heptahydrate (not known in mineral form), Na2CO3·7H2O. * sodium carbonate monohydrate ( thermonatrite), Na2CO3·H2O. Also known as crystal carbonate. * anhydrous sodium carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium oxide ( Mg O), or magnesia, is a white hygroscopic solid mineral that occurs naturally as periclase and is a source of magnesium (see also oxide). It has an empirical formula of MgO and consists of a lattice of Mg2+ ions and O2− ions held together by ionic bonding. Magnesium hydroxide forms in the presence of water (MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2), but it can be reversed by heating it to remove moisture. Magnesium oxide was historically known as magnesia alba (literally, the white mineral from Magnesia), to differentiate it from ''magnesia negra'', a black mineral containing what is now known as manganese. Related oxides While "magnesium oxide" normally refers to MgO, the compound magnesium peroxide MgO2 is also known. According to evolutionary crystal structure prediction, MgO2 is thermodynamically stable at pressures above 116 GPa (gigapascals), and a semiconducting suboxide Mg3O2 is thermodynamically stable above 500 GPa. Because of its stability, MgO is used as a model s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Acetate
Ethyl acetate ( systematically ethyl ethanoate, commonly abbreviated EtOAc, ETAC or EA) is the organic compound with the formula , simplified to . This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and in the decaffeination process of tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent. Production and synthesis Ethyl acetate was first synthesized by the Count de Lauraguais in 1759 by distilling a mixture of ethanol and acetic acid. In 2004, an estimated 1.3 million tonnes were produced worldwide. The combined annual production in 1985 of Japan, North America, and Europe was about 400,000 tonnes. The global ethyl acetate market was valued at $3.3 billion in 2018. Ethyl acetate is synthesized in industry mainly via the classic Fischer esterification reaction of ethanol and acetic acid. This mixture converts to the ester in ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torr
The torr (symbol: Torr) is a unit of pressure based on an absolute scale, defined as exactly of a standard atmosphere (). Thus one torr is exactly (≈ ). Historically, one torr was intended to be the same as one " millimeter of mercury", but subsequent redefinitions of the two units made them slightly different (by less than ). The torr is not part of the International System of Units (SI). It is often combined with the metric prefix milli to name one millitorr (mTorr) or 0.001 Torr. The unit was named after Evangelista Torricelli, an Italian physicist and mathematician who discovered the principle of the barometer in 1644. Nomenclature and common errors The unit name ''torr'' is written in lower case, while its symbol ("Torr") is always written with upper-case initial; including in combinations with prefixes and other unit symbols, as in "mTorr" (millitorr) or "Torr⋅L/s" (torr-litres per second). The symbol (uppercase) should be used with prefix symbols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIPEA
''N'',''N''-Diisopropylethylamine, or Hünig's base, is an organic compound and an amine. It is named after the German chemist Siegfried Hünig. It is used in organic chemistry as a base. It is commonly abbreviated as DIPEA, DIEA, or ''i''-Pr2NEt. Structure DIPEA consists of a central nitrogen atom that is bonded to an ethyl group and two isopropyl groups. A lone pair of electrons resides on the nitrogen atom, which can react with electrophiles. However, as the two isopropyl groups and the ethyl group occupy much of the space surrounding the N atom, only small electrophiles such as protons can react with the nitrogen lone pair. Occurrence and preparation DIPEA is commercially available. It is traditionally prepared by the alkylation of diisopropylamine with diethyl sulfate. Pure DIPEA exists as a colorless liquid, although commercial samples can be slightly yellow. If necessary, the compound can be purified by distillation from potassium hydroxide or calcium hydride. Us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |