Carboxybenzyl on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Benzyl chloroformate, also known as benzyl chlorocarbonate or Z-chloride, is the
 This reaction was hailed as a "revolution" and essentially started the distinct field of synthetic peptide chemistry. It remained unsurpassed in utility for
This reaction was hailed as a "revolution" and essentially started the distinct field of synthetic peptide chemistry. It remained unsurpassed in utility for 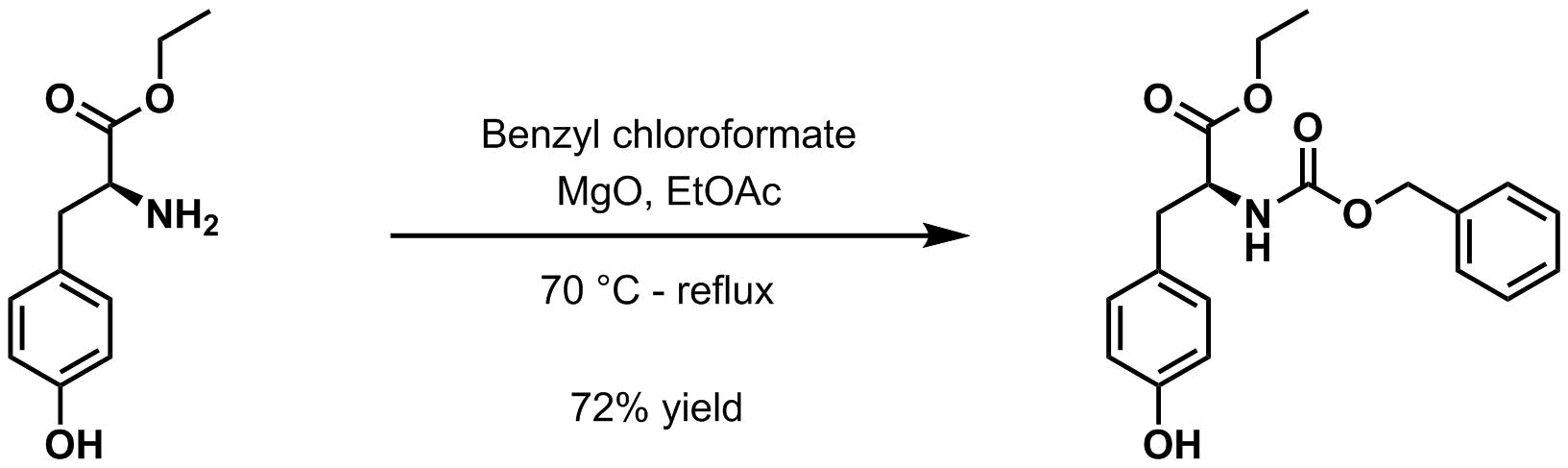 * Benzyl chloroformate,
* Benzyl chloroformate,  Alternatively, the Cbz group can be generated by the reaction of an
Alternatively, the Cbz group can be generated by the reaction of an
 Alternatively, HBr and strong Lewis acids have been used, provided that a trap is provided for the released benzyl carbocation.
When the protected amine is treated by either of the above methods (''i.e.'' by catalytic
Alternatively, HBr and strong Lewis acids have been used, provided that a trap is provided for the released benzyl carbocation.
When the protected amine is treated by either of the above methods (''i.e.'' by catalytic
benzyl
In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure . Benzyl features a benzene ring () attached to a methylene group () group.
Nomenclature
In IUPAC nomenclature, the prefix benzyl refers to a substi ...
ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
of chloroformic acid. It can be also described as the chloride of the benzyloxycarbonyl (Cbz or Z) group. In its pure form it is a water-sensitive oily colorless liquid, although impure samples usually appear yellow. It possesses a characteristic pungent odor and degrades in contact with water.
The compound was first prepared by Leonidas Zervas
Leonidas Zervas ( el, Λεωνίδας Ζέρβας, ; 21 May 1902 – 10 July 1980) was a Greek organic chemist who made seminal contributions in peptide chemical synthesis. Together with his mentor Max Bergmann they laid the foundations for t ...
in the early 1930s who used it for the introduction of the benzyloxycarbonyl protecting group, which became the basis of the Bergmann-Zervas carboxybenzyl method of peptide synthesis he developed with Max Bergmann
Max Bergmann (12 February 1886 – 7 November 1944) was a Jewish-German biochemist. Together with Leonidas Zervas, the discoverer of the group, they were the first to use the carboxybenzyl protecting group for the synthesis of oligopeptides.
...
. This was the first successful method of controlled peptide chemical synthesis and for twenty years it was the dominant procedure used worldwide until the 1950s. To this day, benzyl chloroformate is often used for amine group
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent ...
protection.
Preparation
The compound is prepared in the lab by treatingbenzyl alcohol
Benzyl alcohol is an aromatic alcohol with the formula C6H5CH2OH. The benzyl group is often abbreviated "Bn" (not to be confused with "Bz" which is used for benzoyl), thus benzyl alcohol is denoted as BnOH. Benzyl alcohol is a colorless liquid w ...
with phosgene
Phosgene is the organic chemical compound with the formula COCl2. It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. Phosgene is a valued and important industrial building block, espe ...
:
: PhCH2OH + COCl2 → PhCH2OC(O)Cl + HCl
Phosgene is used in excess to minimise the production of the carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ...
(PhCH2O)2C=O.
The use of phosgene gas in the lab preparation carries a very large health hazard, and has been implicated in the chronic pulmonary disease of pioneers in the usage of the compound such as Zervas.
Amine protection
Benzyl chloroformate is commonly used inorganic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
for the introduction of the benzyloxycarbonyl (formerly called carboxybenzyl) protecting group for amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
s. The protecting group is abbreviated Cbz or Z (in honor of discoverer Zervas), hence the alternative shorthand designation for benzyl chloroformate as Cbz-Cl or Z-Cl.
Benzyloxycarbonyl is a key protecting group for amines
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such ...
, suppressing the nucleophilic and basic properties of the N lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC ''Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. Lone ...
. This "reactivity masking" property, along with the ability to prevent racemization In chemistry, racemization is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into a racemic (optically inactive) form. This creates a 1:1 molar ratio of enantiomers and is referred too as a racemic mixture (i.e. con ...
of Z-protected amines, made the Z group the basis of the Begmann-Zervas synthesis of oligopeptides
An oligopeptide, often just called peptide ('' oligo-'', "a few"), consists of two to twenty amino acids and can include dipeptides, tripeptides, tetrapeptides, and pentapeptides. Some of the major classes of naturally occurring oligopeptides inc ...
(1932) where the following general reaction is performed to protect the ''N''-terminus of a serially growing oligopeptide chain:
:peptide synthesis
In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, compounds where multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds, also known as peptide bonds. Peptides are chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction of the carboxyl ...
until the early 1950s when mixed anhydride and active ester methodologies were developed.
Although the reaction is no longer commonly used for peptides, it is nonetheless very widespread for amine protection in other applications within organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
and total synthesis
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes ...
. Common procedures to achieve protection starting from benzyl chloroformate include:
* Benzyl chloroformate and a base, such as sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions ...
in water at 0 °C
* Benzyl chloroformate and magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide ( Mg O), or magnesia, is a white hygroscopic solid mineral that occurs naturally as periclase and is a source of magnesium (see also oxide). It has an empirical formula of MgO and consists of a lattice of Mg2+ ions and O2− ions ...
in ethyl acetate
Ethyl acetate ( systematically ethyl ethanoate, commonly abbreviated EtOAc, ETAC or EA) is the organic compound with the formula , simplified to . This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues ...
at 70 °C to reflux
*: * Benzyl chloroformate,
* Benzyl chloroformate, DIPEA
''N'',''N''-Diisopropylethylamine, or Hünig's base, is an organic compound and an amine. It is named after the German chemist Siegfried Hünig. It is used in organic chemistry as a base. It is commonly abbreviated as DIPEA, DIEA, or ''i''-Pr2N ...
, acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not clas ...
and scandium trifluoromethanesulfonate
Scandium trifluoromethanesulfonate, commonly called scandium triflate, is a chemical compound with formula Sc(SO3CF3)3, a salt consisting of scandium cations Sc3+ and triflate anions.
Scandium triflate is used as a reagent in organic chemistry ...
(Sc(OTf)3)
*: Alternatively, the Cbz group can be generated by the reaction of an
Alternatively, the Cbz group can be generated by the reaction of an isocyanate
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyan ...
with benzyl alcohol
Benzyl alcohol is an aromatic alcohol with the formula C6H5CH2OH. The benzyl group is often abbreviated "Bn" (not to be confused with "Bz" which is used for benzoyl), thus benzyl alcohol is denoted as BnOH. Benzyl alcohol is a colorless liquid w ...
(as in the Curtius rearrangement
The Curtius rearrangement (or Curtius reaction or Curtius degradation), first defined by Theodor Curtius in 1885, is the thermal decomposition of an acyl azide to an isocyanate with loss of nitrogen gas. The isocyanate then undergoes attack by a va ...
).
Deprotection
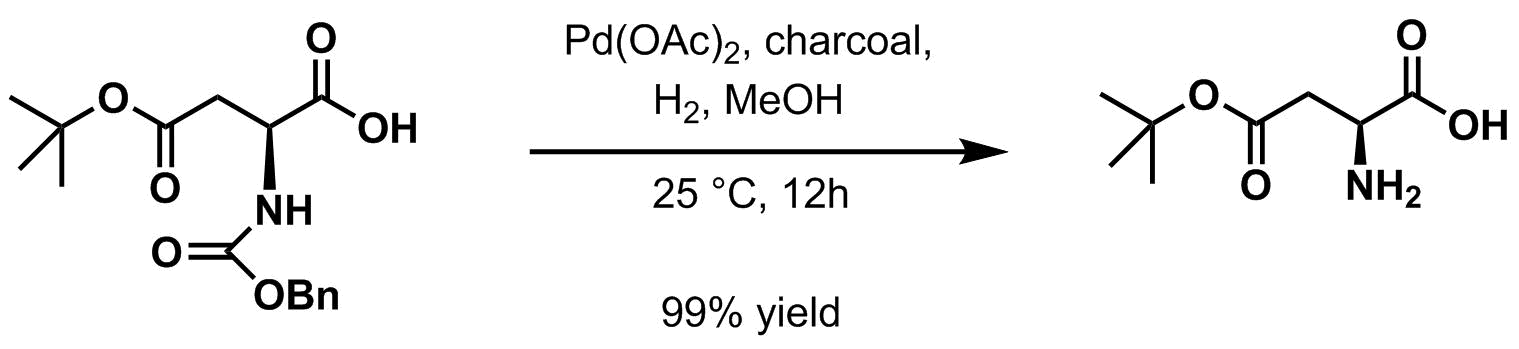
Hydrogenolysis
Hydrogenolysis is a chemical reaction whereby a carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom single bond is cleaved or undergoes lysis (breakdown) by hydrogen.Ralph Connor, Homer Adkins. Hydrogenolysis Of Oxygenated Organic Compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. ...
in the presence of a variety of palladium-based catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
s is the usual method for deprotection. Palladium on charcoal
Palladium on carbon, often referred to as Pd/C, is a form of palladium used as a catalyst. The metal is Catalyst support, supported on activated carbon to maximize its surface area and Activity (chemistry), activity.
Uses Hydrogenation
Palladium ...
is typical.
: Alternatively, HBr and strong Lewis acids have been used, provided that a trap is provided for the released benzyl carbocation.
When the protected amine is treated by either of the above methods (''i.e.'' by catalytic
Alternatively, HBr and strong Lewis acids have been used, provided that a trap is provided for the released benzyl carbocation.
When the protected amine is treated by either of the above methods (''i.e.'' by catalytic hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a Catalysis, catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or S ...
or acidic workup), it yields a terminal carbamic acid
Carbamic acid, which might also be called aminoformic acid or aminocarboxylic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula . It can be obtained by the reaction of ammonia and carbon dioxide at very low temperatures, which also yields an equ ...
which then readily decarboxylates to give the free amine.
2-Mercaptoethanol
2-Mercaptoethanol (also β-mercaptoethanol, BME, 2BME, 2-ME or β-met) is the chemical compound with the formula HOCH2CH2SH. ME or βME, as it is commonly abbreviated, is used to reduce disulfide bonds and can act as a biological antioxidant by sc ...
can also be used, in the presence of potassium phosphate
Potassium phosphate is a generic term for the salt (chemistry), salts of potassium and phosphate ions including:
* Monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4) (Molar mass approx: 136 g/mol)
* Dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4) (Molar mass approx: 174 g/mol)
* ...
in dimethylacetamide.
References
External links
* {{Organic reactions Chloroformates Benzyl esters Reagents for organic chemistry Foul-smelling chemicals