|
Scandium Trifluoromethanesulfonate
Scandium trifluoromethanesulfonate, commonly called scandium triflate, is a chemical compound with formula Sc(SO3CF3)3, a salt consisting of scandium cations Sc3+ and triflate anions. Scandium triflate is used as a reagent in organic chemistry as a Lewis acid. Compared to other Lewis acids, this reagent is stable towards water and can often be used in organic reactions as a true catalyst rather than one used in stoichiometric amounts. The compound is prepared by reaction of scandium oxide with trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. An example of the scientific use of scandium triflate is the Mukaiyama aldol addition reaction between benzaldehyde and the silyl enol ether of cyclohexanone with an 81% yield. : See also * Lanthanide trifluoromethanesulfonates Lanthanide triflates are triflate salts of the lanthanides. These salts have been investigated for application in organic synthesis as Lewis acid catalysts. These catalysts function similarly to aluminium chloride or ferric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mukaiyama Aldol Addition
The Mukaiyama aldol addition is an organic reaction and a type of aldol reaction between a silyl enol ether and an aldehyde or formate. The reaction was discovered by Teruaki Mukaiyama (1927–2018) in 1973. His choice of reactants allows for a crossed aldol reaction between an aldehyde and a ketone or a different aldehyde without self-condensation of the aldehyde. For this reason the reaction is used extensively in organic synthesis. General reaction scheme The Mukaiyama aldol addition is a Lewis acid mediated addition of enol silanes to carbonyl compounds. In this reaction compounds with various organic groups can be used (see educts). A basic version ( = H) without the presence of chiral catalysts is shown below. A racemic mix of enantiomers is built. If Z- or E-enol silanes are used in this reaction a mixture of four products occurs, yielding two racemates. Whether the ''anti''-diastereomer or the ''syn''-diastereomer is built depends largely on reaction conditions, sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandium Compounds
: Scandium compounds are compounds containing the element scandium. The chemistry of scandium is almost completely dominated by the trivalent ion, Sc3+, due to its electron configuration, r3d14s2. The radii of M3+ ions in the table below indicate that the chemical properties of scandium ions have more in common with yttrium ions than with aluminium ions. In part because of this similarity, scandium is often classified as a lanthanide-like element. +3 oxidation state Oxides and hydroxides The oxide and the hydroxide are amphoteric: : + 3 → (scandate ion) : + 3 + 3 → α- and γ-ScOOH are isostructural with their aluminium hydroxide oxide counterparts. Solutions of in water are acidic due to hydrolysis. Halides and pseudohalides The halides , where X= Cl, Br, or I, are very soluble in water, but is insoluble. In all four halides, the scandium is 6-coordinated. The halides are Lewis acids; for example, dissolves in a solution containing excess fluorid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanide Trifluoromethanesulfonates
Lanthanide triflates are triflate salts of the lanthanides. These salts have been investigated for application in organic synthesis as Lewis acid catalysts. These catalysts function similarly to aluminium chloride or ferric chloride, but are stable in water. Commonly written as Ln(OTf)3·(H2O)9 the nine waters are bound to the lanthanide and the triflates are counteranions, so more accurately lanthanide triflate nonahydrate is written as n(H2O)9OTf)3. Synthesis Lanthanide triflates are synthesized from lanthanide oxide and aqueous triflic acid: ::Ln2O3 + 6HOTf + 18H2O → 2 n(H2O)9OTf)3 + 3H2O Anhydrous lanthanide triflates can be produced by dehydrating their hydrated counterparts by heating between 180 and 200 °C under reduced pressure: : n(H2O)9OTf)3 → Ln(OTf)3 + 9H2O Example reactions Friedel-Crafts reactions Lanthanide triflates are proposed for Friedel-Crafts acylations and alkylations, which are usually carried out with AlCl3 as the catalyst in an organic solvent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Journal Of Organic Chemistry
The ''European Journal of Organic Chemistry'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering organic chemistry. It is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of Chemistry Europe. The journal, along with the ''European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry'', was established in 1998 as the result of a merger of '' Chemische Berichte/Recueil,'' ''Bulletin de la Société Chimique de France,'' ''Bulletin des Sociétés Chimiques Belges,'' ''Gazzetta Chimica Italiana,'' ''Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas'', ''Anales de Química,'' ''Chimika Chronika,'' ''Revista Portuguesa de Química, and'' ''ACH-Models in Chemistry.'' According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 3.261. See also *List of chemistry journals *''European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry The ''European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering inorganic, organometallic, bioinorganic, and solid-state chemistry. It is published by W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yield (chemistry)
In chemistry, yield, also referred to as reaction yield, is a measure of the quantity of Mole (unit), moles of a Product (chemistry), product formed in relation to the reactant consumed, obtained in a chemical reaction, usually expressed as a percentage. Yield is one of the primary factors that scientists must consider in organic synthesis, organic and inorganic chemical synthesis processes. In chemical reaction engineering, "yield", "Conversion (chemistry), conversion" and "selectivity" are terms used to describe ratios of how much of a reactant was consumed (conversion), how much desired product was formed (yield) in relation to the undesired product (selectivity), represented as X, Y, and S. Definitions In chemical reaction engineering, "yield", "Conversion (chemistry), conversion" and "selectivity" are terms used to describe ratios of how much of a reactant has reacted—conversion, how much of a desired product was formed—yield, and how much desired product was formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has an odor reminiscent of acetone. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Billions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon. Production Cyclohexanone is produced by the oxidation of cyclohexane in air, typically using cobalt catalysts: :C6H12 + O2 → (CH2)5CO + H2O This process forms cyclohexanol as a by-product, and this mixture, called "KA Oil" for ketone-alcohol oil, is the main feedstock for the production of adipic acid. The oxidation involves radicals and the hydroperoxide C6H11O2H as an intermediate. In some cases, purified cyclohexanol, obtained by hydration of cyclohexene, is the precursor. Alternatively, cyclohexanone can be produced by the partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
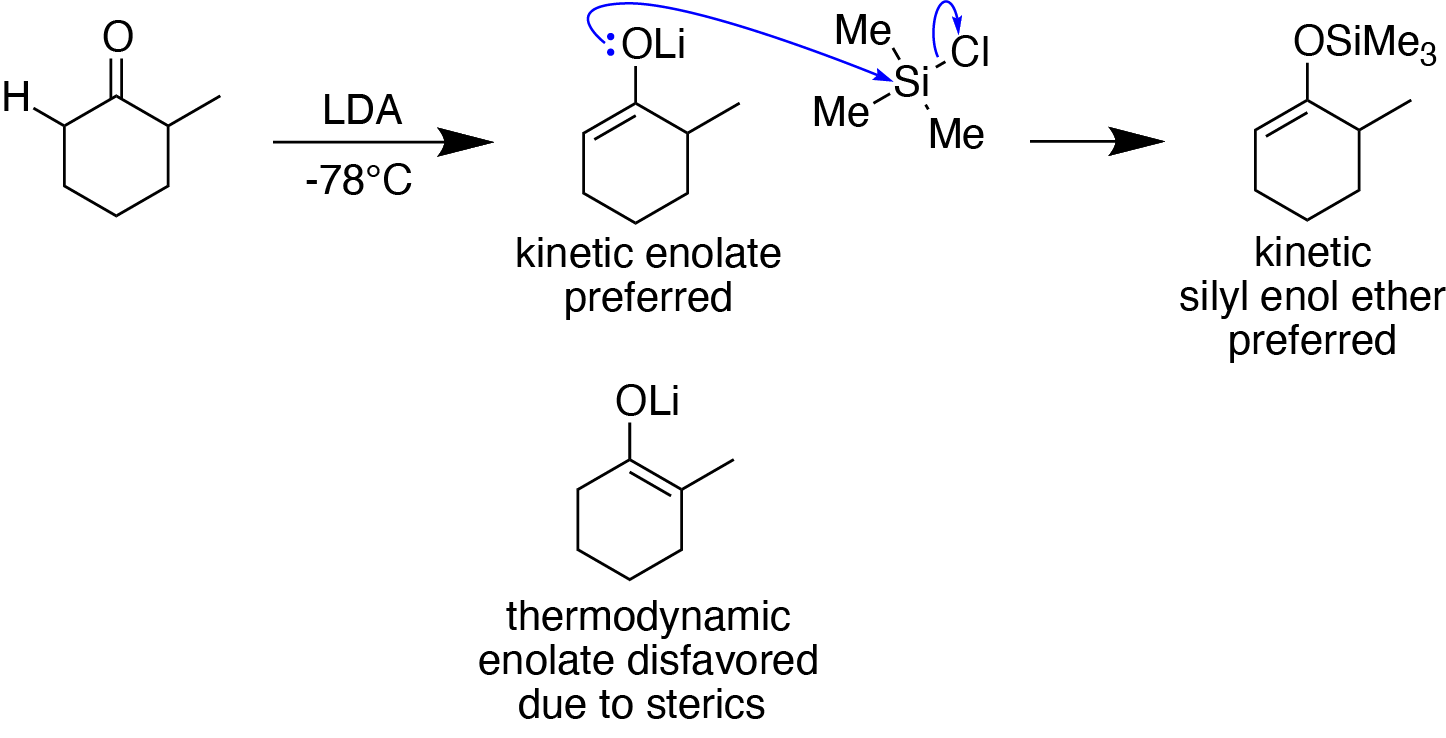
Silyl Enol Ether
Silyl enol ethers in organic chemistry are a class of organic compounds that share a common functional group composed of an enolate bonded through its oxygen end to an organosilicon group. They are important intermediates in organic synthesis. Synthesis Silyl enol ethers are generally prepared by reacting an enolizable Carbonyl group, carbonyl compound with a silyl electrophile and a Base (chemistry), base, or just reacting an enolate with a silyl electrophile.Clayden, J., Greeves, N., & Warren, S. (2012). Silyl enol ethers. In ''Organic chemistry'' (Second ed., pp. 466-467). Oxford University Press. Since silyl electrophiles are HSAB theory, hard and silicon-oxygen bonds are very strong, the oxygen (of the carbonyl compound or enolate) acts as the nucleophile to form a Si-O single bond. The most commonly used silyl electrophile is trimethylsilyl chloride. To increase the rate of reaction, trimethylsilyl triflate may also be used in the place of trimethylsilyl chloride as a more el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is the simplest aromatic aldehyde and one of the most industrially useful. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-like odor. The primary component of bitter almond oil, benzaldehyde can be extracted from a number of other natural sources. Synthetic benzaldehyde is the flavoring agent in imitation almond extract, which is used to flavor cakes and other baked goods. History Benzaldehyde was first extracted in 1803 by the French pharmacist Martrès. His experiments focused on elucidating the nature of amygdalin, the poisonous material found in bitter almonds, the fruit of ''Prunus dulcis''. Further work on the oil by Pierre Robiquet and Antoine Boutron-Charlard, two French chemists, produced benzaldehyde. In 1832, Friedrich Wöhler and Justus von Liebig first synthesized benzaldehyde. Production As of 1999, 7000 tonnes of synthetic and 100 tonnes of natural b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoromethanesulfonic Acid
Triflic acid, the short name for trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, TFMS, TFSA, HOTf or TfOH, is a sulfonic acid with the chemical formula CF3SO3H. It is one of the strongest known acids. Triflic acid is mainly used in research as a catalyst for esterification. It is a hygroscopic, colorless, slightly viscous liquid and is soluble in polar solvents. Synthesis Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid is produced industrially by electrochemical fluorination (ECF) of methanesulfonic acid: : CH3SO3H + 4 HF ->CF3SO2F + H2O + 3 H2 The resulting CF3SO2F is hydrolyzed, and the resulting triflate salt is reprotonated. Alternatively, trifluoromethanesulfonic acid arises by oxidation of trifluoromethyl sulfenyl chloride: :CF3SCl + 2 Cl2 + 3 H2O -> CF3SO3H + 5 HCl Triflic acid is purified by distillation from triflic anhydride. Historical Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid was first synthesized in 1954 by Robert Haszeldine and Kidd by the following reaction: : Reactions As an acid In the laboratory, trifl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called ''alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called ''acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered salts. Examples of zwitterions are amino acids, many metabolites, peptid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |