|
Capacitor Types
Capacitors are manufactured in many styles, forms, dimensions, and from a large variety of materials. They all contain at least two electrical conductors, called ''plates'', separated by an insulating layer (''dielectric''). Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Capacitors, together with resistors and inductors, belong to the group of ''passive components'' in electronic equipment. Small capacitors are used in electronic devices to couple signals between stages of amplifiers, as components of electric filters and tuned circuits, or as parts of power supply systems to smooth rectified current. Larger capacitors are used for energy storage in such applications as strobe lights, as parts of some types of electric motors, or for power factor correction in AC power distribution systems. Standard capacitors have a fixed value of capacitance, but adjustable capacitors are frequently used in tuned circuits. Different types are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively). Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with an absence of net charge is referred to as neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum effects. Electric charge is a conserved property; the net charge of an isolated system, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge, cannot change. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms. If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase (matter)
In the physical sciences, a phase is a region of space (a thermodynamic system), throughout which all physical properties of a material are essentially uniform. Examples of physical properties include density, index of refraction, magnetization and chemical composition. A simple description is that a phase is a region of material that is chemically uniform, physically distinct, and (often) mechanically separable. In a system consisting of ice and water in a glass jar, the ice cubes are one phase, the water is a second phase, and the humid air is a third phase over the ice and water. The glass of the jar is another separate phase. (See ) The term ''phase'' is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but there can be several immiscible phases of the same state of matter. Also, the term ''phase'' is sometimes used to refer to a set of equilibrium states demarcated in terms of state variables such as pressure and temperature by a phase boundary on a phase diagram. Bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
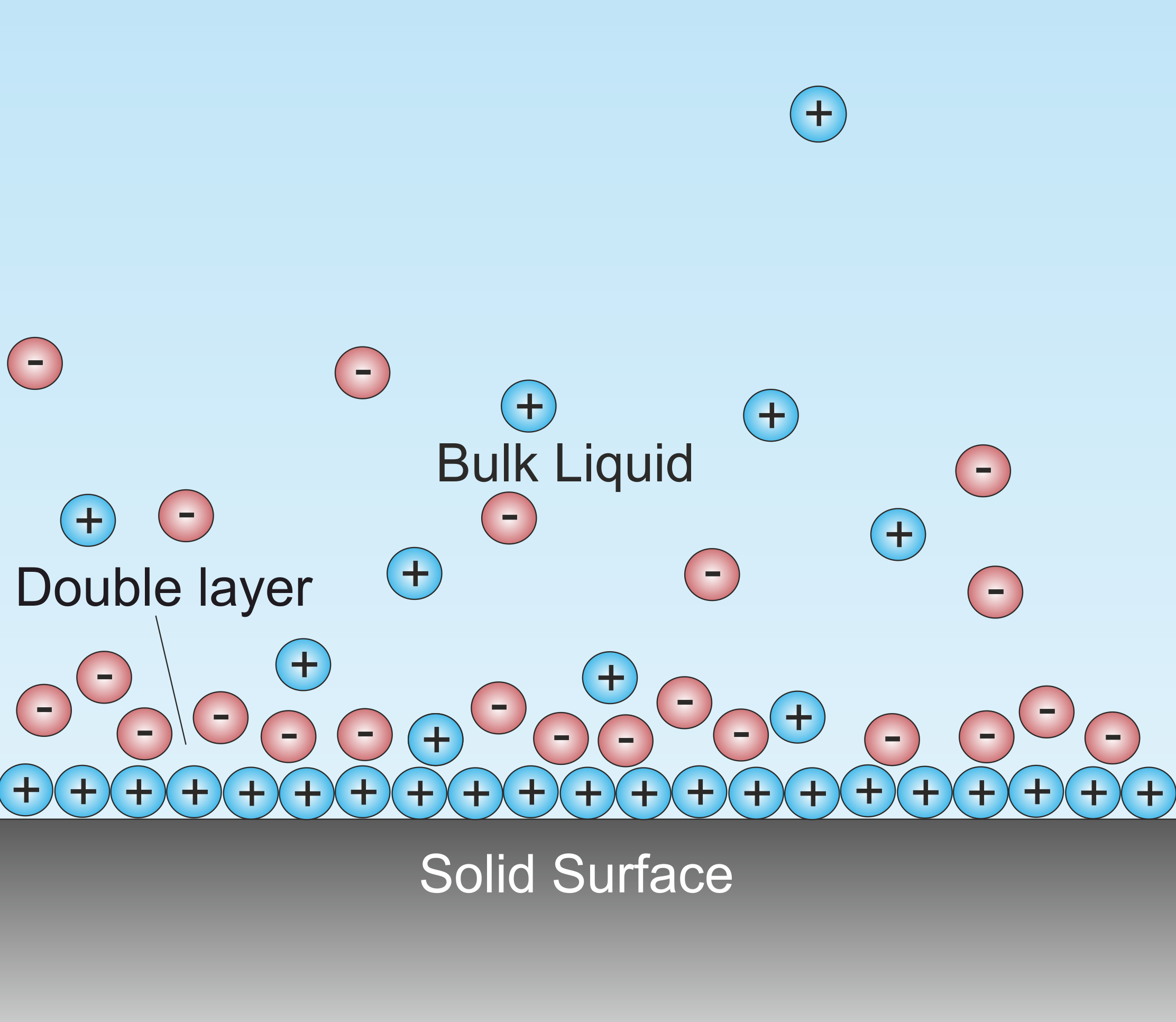
Double Layer (interfacial)
A double layer (DL, also called an electrical double layer, EDL) is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet, or a porous body. The DL refers to two parallel layers of charge surrounding the object. The first layer, the surface charge (either positive or negative), consists of ions adsorbed onto the object due to chemical interactions. The second layer is composed of ions attracted to the surface charge via the Coulomb force, electrically screening the first layer. This second layer is loosely associated with the object. It is made of free ions that move in the fluid under the influence of electric attraction and thermal motion rather than being firmly anchored. It is thus called the "diffuse layer". Interfacial DLs are most apparent in systems with a large surface area to volume ratio, such as a colloid or porous bodies with particles or pores (respectively) on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, the largest German association of research institutions, is named in his honor. In the fields of physiology and psychology, Helmholtz is known for his mathematics concerning the eye, theories of vision, ideas on the visual perception of space, color vision research, the sensation of tone, perceptions of sound, and empiricism in the physiology of perception. In physics, he is known for his theories on the conservation of energy, work in electrodynamics, chemical thermodynamics, and on a mechanical foundation of thermodynamics. As a philosopher, he is known for his philosophy of science, ideas on the relation between the laws of perception and the laws of nature, the science of aesthetics, and ideas on the civilizing power of science. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest (static electricity). Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, (), was thus the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law. Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, some electrostatic forces are relatively large. The force between an electron and a proton, which together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them. There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of plastic wrap to one's hand after it is removed from a package, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercapacitor
A supercapacitor (SC), also called an ultracapacitor, is a high-capacity capacitor, with a capacitance value much higher than other capacitors but with lower voltage limits. It bridges the gap between electrolytic capacitors and rechargeable batteries. It typically stores 10 to 100 times more energy per unit volume or mass than electrolytic capacitors, can accept and deliver charge much faster than batteries, and tolerates many more charge and discharge cycles than rechargeable batteries. Supercapacitors are used in applications requiring many rapid charge/discharge cycles, rather than long-term compact energy storage — in automobiles, buses, trains, cranes and elevators, where they are used for regenerative braking, short-term energy storage, or burst-mode power delivery. Smaller units are used as power backup for static random-access memory (SRAM). Unlike ordinary capacitors, supercapacitors do not use the conventional solid dielectric, but rather, they use electrosta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolytic Capacitors
An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel electrolyte covers the surface of this oxide layer, serving as the cathode or negative plate of the capacitor. Due to their very thin dielectric oxide layer and enlarged anode surface, electrolytic capacitors have a much higher capacitance-voltage (CV) product per unit volume than ceramic capacitors or film capacitors, and so can have large capacitance values. There are three families of electrolytic capacitor: aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors. The large capacitance of electrolytic capacitors makes them particularly suitable for passing or bypassing low-frequency signals, and for storing large amounts of energy. They are widely used for decoupling or noise filtering i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outcome of a particular chemical change, or vice versa. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase (typically an external electrical circuit, but not necessarily, as in electroless plating) between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). When a chemical reaction is driven by an electrical potential difference, as in electrolysis, or if a potential difference results from a chemical reaction as in an electric battery or fuel cell, it is called an ''electrochemical'' reaction. Unlike in other chemical reactions, in electrochemical reactions electrons are not transferred directly between atoms, ions, or molecules, but via the af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Double-layer (BMD Model) NT-int
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of positiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' ( epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in response to an applied electric field than a material with low permittivity, thereby storing more energy in the material. In electrostatics, the permittivity plays an important role in determining the capacitance of a capacitor. In the simplest case, the electric displacement field D resulting from an applied electric field E is :\mathbf = \varepsilon \mathbf. More generally, the permittivity is a thermodynamic function of state. It can depend on the frequency, magnitude, and direction of the applied field. The SI unit for permittivity is farad per meter (F/m). The permittivity is often represented by the relative permittivity ''ε''r which is the ratio of the absolute permittivity ''ε'' and the vacuum permittivity ''ε''0 :\kappa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric Breakdown
Electrical breakdown or dielectric breakdown is a process that occurs when an electrical insulating material, subjected to a high enough voltage, suddenly becomes an electrical conductor and electric current flows through it. All insulating materials undergo breakdown when the electric field caused by an applied voltage exceeds the material's dielectric strength. The voltage at which a given insulating object becomes conductive is called its breakdown voltage and in addition to its dielectric strength depends on its size and shape, and the location on the object at which the voltage is applied. Under sufficient electrical potential, electrical breakdown can occur within solids, liquids, or gases (and theoretically even in a vacuum). However, the specific breakdown mechanisms are different for each kind of dielectric medium. Electrical breakdown may be a momentary event (as in an electrostatic discharge), or may lead to a continuous electric arc if protective devices fail to int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |