|
Cranial Kinesis
Cranial kinesis is the term for significant movement of skull bones relative to each other in addition to movement at the joint between the upper and lower jaws. It is usually taken to mean relative movement between the upper jaw and the braincase. Most vertebrates have some form of a kinetic skull. Cranial kinesis, or lack thereof, is usually linked to feeding. Animals which must exert powerful bite forces, such as crocodiles, often have rigid skulls with little or no kinesis, which maximizes their strength. Animals which swallow large prey whole (snakes), which grip awkwardly shaped food items (parrots eating nuts), or, most often, which feed in the water via suction feeding often have very kinetic skulls, frequently with numerous mobile joints. In the case of mammals, which have akinetic skulls (except perhaps hares), the lack of kinesis is most likely to be related to the secondary palate, which prevents relative movement. This in turn is a consequence of the need to be able ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors and relatives, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads ( cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most only have one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have independently evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs at least twenty-five times via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, brain-pan, or brainbox, is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skullcap. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton. In comparative anatomy, neurocranium is sometimes used synonymously with endocranium or chondrocranium. Structure The neurocranium is divided into two portions: * the membranous part, consisting of flat bones, which surround the brain; and * the cartilaginous part, or chondrocranium, which forms bones of the base of the skull. In humans, the neurocranium is usually considered to include the following eight bones: * 1 ethmoid bone * 1 frontal bone * 1 occipital bone * 2 parietal bones * 1 sphenoid bone * 2 temporal bones The ossicles (three on each side) are usually not included as bones of the neurocranium. There may variably also be extra sutural bones present. Belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
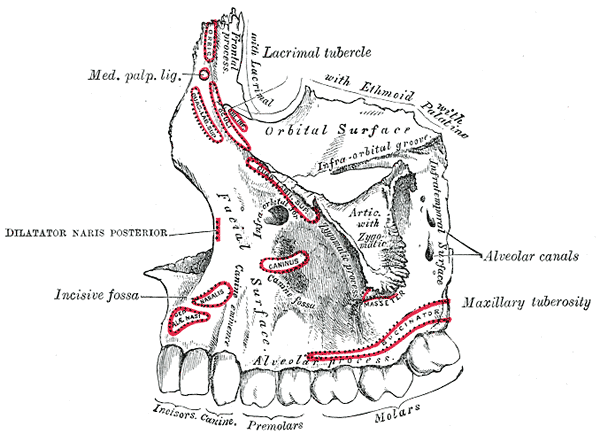
Parietal Bone
The parietal bones ( ) are two bones in the skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint known as a cranial suture, form the sides and roof of the neurocranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, and four angles. It is named from the Latin ''paries'' (''-ietis''), wall. Surfaces External The external surface [Fig. 1] is convex, smooth, and marked near the center by an eminence, the parietal eminence (''tuber parietale''), which indicates the point where ossification commenced. Crossing the middle of the bone in an arched direction are two curved lines, the superior and inferior temporal lines; the former gives attachment to the temporal fascia, and the latter indicates the upper limit of the muscular origin of the temporal muscle. Above these lines the bone is covered by a tough layer of fibrous tissue – the epicranial aponeurosis; below them it forms part of the temporal fossa, and affords attachment to the temporal mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecilian
Caecilians (; ) are a group of limbless, vermiform (worm-shaped) or serpentine (snake-shaped) amphibians with small or sometimes nonexistent eyes. They mostly live hidden in soil or in streambeds, and this cryptic lifestyle renders caecilians among the least familiar amphibians. Modern caecilians live in the tropics of South America, South and Central America, Africa, and southern Asia. Caecilians feed on small subterranean creatures, such as earthworms. The body is cylindrical and often darkly coloured, and the skull is bullet-shaped and strongly built. Caecilian heads have several unique adaptations, including fused cranial and jaw bones, a two-part system of jaw muscles, and a Chemoreceptor, chemosensory tentacle in front of the eye. The skin is slimy and bears ringlike markings or grooves and may contain scales. Modern caecilians are a clade, the Order (biology), order Gymnophiona (or Apoda ), one of the three living amphibian groups alongside Anura (frogs) and Urodela (sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammals has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lissamphibia
The Lissamphibia (from Greek λισσός (lissós, "smooth") + ἀμφίβια (amphíbia), meaning "smooth amphibians") is a group of tetrapods that includes all modern amphibians. Lissamphibians consist of three living groups: the Salientia (frogs and their extinct relatives), the Caudata (salamanders and their extinct relatives), and the Gymnophiona (the limbless caecilians and their extinct relatives). Salientians and caudatans are likely more closely related to each other than to caecilians. The name Batrachia is commonly used for the clade combining salientians and caudatans. A fourth group, the Allocaudata (also known as Albanerpetontidae) is also known, spanning 160 million years from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Pleistocene, but became extinct two million years ago. For several decades, this name has been used for a group that includes all living amphibians, but excludes all the main groups of Paleozoic tetrapods, such as Temnospondyli, Lepospondyli, Embolome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossopterygian
Sarcopterygii (; )—sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii ()—is a clade (traditionally a class or subclass) of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. These vertebrates are characterised by prominent muscular limb buds (lobes) within their fins, which are supported by articulated appendicular skeletons. This is in contrast to the other clade of bony fish, the Actinopterygii, which have only skin-covered bony spines supporting the fins. The tetrapods, a mostly terrestrial clade of vertebrates, are now recognized as having evolved from sarcopterygian ancestors and are most closely related to lungfishes. Their paired pectoral and pelvic fins evolved into limbs, and their foregut diverticulum eventually evolved into air-breathing lungs. Cladistically, this would make the tetrapods a subgroup within Sarcopterygii and thus sarcopterygians themselves. As a result, the phrase "lobe-finned fish" normally refers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccal Cavity
The buccal space (also termed the buccinator space) is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed fascial tissue spaces or tissue spaces). It is a potential space in the cheek, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the buccinator muscle and deep to the platysma muscle and the skin. The buccal space is part of the subcutaneous space, which is continuous from head to toe. Structure Boundaries The boundaries of each buccal space are: * the angle of the mouth anteriorly, * the masseter muscle posteriorly, * the zygomatic process of the maxilla and the zygomaticus muscles superiorly, * the depressor anguli oris muscle and the attachment of the deep fascia to the mandible inferiorly, * the buccinator muscle medially (the buccal space is superficial to the buccinator), * the platysma muscle, subcutaneous tissue and skin laterally (the space is deep to platysma). Communications * to the pterygomandibular space, infratemporal space, submasseter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class (biology), class of Osteichthyes, bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fish fin, fins made of webbings of skin supported by radially extended thin bony spine (zoology), spines called ''lepidotrichia'', as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister taxon, sister clade Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can easily change shape and wetted area, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation (anatomy), articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). The vast majority of actinopterygians are teleosts. By species count, they domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoid Arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are transient structures seen in the embryonic development of humans and other vertebrates, that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches support the gills and are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches. In the human embryo, the arches are first seen during the fourth week of development. They appear as a series of outpouchings of mesoderm on both sides of the developing pharynx. The vasculature of the pharyngeal arches are the aortic arches that arise from the aortic sac. Structure In humans and other vertebrates, the pharyngeal arches are derived from all three germ layers (the primary layers of cells that form during embryonic development). Neural crest cells enter these arches where they contribute to features of the skull and facial skeleton such as bone and cartilage. However, the existence of pharyngeal structures before neural crest cells evolved is indicated by the existenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
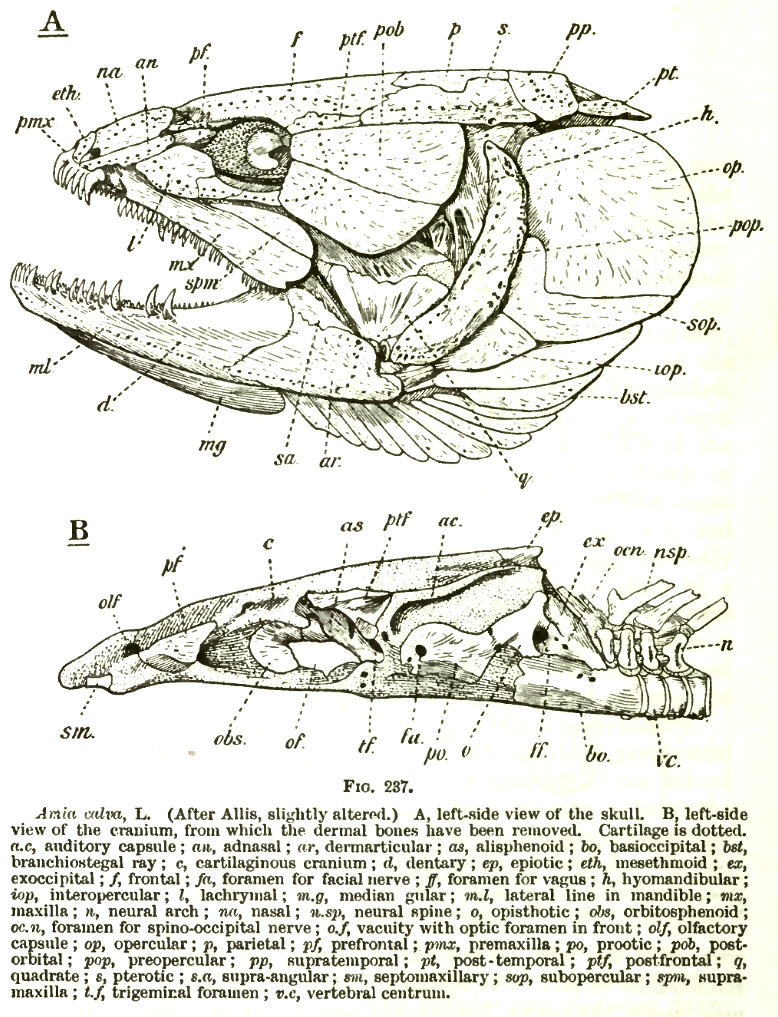
Hyomandibular
The hyomandibula, commonly referred to as hyomandibular one(, from , "upsilon-shaped" (υ), and Latin: mandibula, "jawbone"), is a set of bones that is found in the hyoid region in most fishes. It usually plays a role in suspending the jaws and/or operculum ( teleostomi only). It is commonly suggested that in tetrapods (land animals), the hyomandibula evolved into the columella (stapes). Evolutionary context In jawless fishes, a series of gills opened behind the mouth, and these gills became supported by cartilaginous elements. The first set of these elements surrounded the mouth to form the jaw. There is ample evidence For example: (1) both sets of bones are made from neural crest cells (rather than mesodermal tissue like most other bones); (2) both structures form the upper and lower bars that bend forward and are hinged in the middle; and (3) the musculature of the jaw seem homologous to the gill arches of jawless fishes. (Gilbert 2000) that vertebrate jaws are homol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharks
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the Division (taxonomy), division Selachii and are the sister group to the Batoidea, Batomorphi (Batoidea, rays and skate (fish), skates). Some sources extend the term "shark" as an informal category including Extinction, extinct members of Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) with a shark-like morphology, such as hybodonts. Shark-like chondrichthyans such as ''Cladoselache'' and ''Doliodus'' first appeared in the Devonian Period (419–359 million years), though some fossilized chondrichthyan-like scales are as old as the Ordovician, Late Ordovician (458–444 million years ago). The earliest confirmed modern sharks (Selachii) are known from the Early Jurassic around , with the oldest known member being ''Agaleus'', though records of true shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |