|
Connectedness
In mathematics, connectedness is used to refer to various properties meaning, in some sense, "all one piece". When a mathematical object has such a property, we say it is connected; otherwise it is disconnected. When a disconnected object can be split naturally into connected pieces, each piece is usually called a ''component'' (or ''connected component''). Connectedness in topology A topological space is said to be ''connected'' if it is not the union of two disjoint nonempty open sets. A set is open if it contains no point lying on its boundary; thus, in an informal, intuitive sense, the fact that a space can be partitioned into disjoint open sets suggests that the boundary between the two sets is not part of the space, and thus splits it into two separate pieces. Other notions of connectedness Fields of mathematics are typically concerned with special kinds of objects. Often such an object is said to be ''connected'' if, when it is considered as a topological space, it is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connected Space
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a connected space is a topological space that cannot be represented as the union of two or more disjoint non-empty open subsets. Connectedness is one of the principal topological properties that are used to distinguish topological spaces. A subset of a topological space X is a if it is a connected space when viewed as a subspace of X. Some related but stronger conditions are path connected, simply connected, and n-connected. Another related notion is ''locally connected'', which neither implies nor follows from connectedness. Formal definition A topological space X is said to be if it is the union of two disjoint non-empty open sets. Otherwise, X is said to be connected. A subset of a topological space is said to be connected if it is connected under its subspace topology. Some authors exclude the empty set (with its unique topology) as a connected space, but this article does not follow that practice. For a topologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path Connected
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a connected space is a topological space that cannot be represented as the union of two or more disjoint non-empty open subsets. Connectedness is one of the principal topological properties that are used to distinguish topological spaces. A subset of a topological space X is a if it is a connected space when viewed as a subspace of X. Some related but stronger conditions are path connected, simply connected, and n-connected. Another related notion is ''locally connected'', which neither implies nor follows from connectedness. Formal definition A topological space X is said to be if it is the union of two disjoint non-empty open sets. Otherwise, X is said to be connected. A subset of a topological space is said to be connected if it is connected under its subspace topology. Some authors exclude the empty set (with its unique topology) as a connected space, but this article does not follow that practice. For a topologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
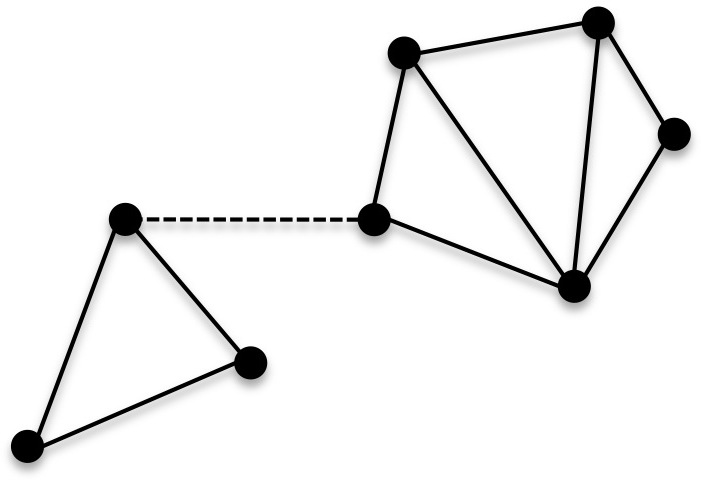
Connectivity (graph Theory)
In mathematics and computer science, connectivity is one of the basic concepts of graph theory: it asks for the minimum number of elements (nodes or edges) that need to be removed to separate the remaining nodes into two or more isolated subgraphs. It is closely related to the theory of network flow problems. The connectivity of a graph is an important measure of its resilience as a network. Connected vertices and graphs In an undirected graph , two '' vertices'' and are called connected if contains a path from to . Otherwise, they are called disconnected. If the two vertices are additionally connected by a path of length , i.e. by a single edge, the vertices are called adjacent. A graph is said to be connected if every pair of vertices in the graph is connected. This means that there is a path between every pair of vertices. An undirected graph that is not connected is called disconnected. An undirected graph ''G'' is therefore disconnected if there exist two vertices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connected Graph
In mathematics and computer science, connectivity is one of the basic concepts of graph theory: it asks for the minimum number of elements (nodes or edges) that need to be removed to separate the remaining nodes into two or more isolated subgraphs. It is closely related to the theory of network flow problems. The connectivity of a graph is an important measure of its resilience as a network. Connected vertices and graphs In an undirected graph , two '' vertices'' and are called connected if contains a path from to . Otherwise, they are called disconnected. If the two vertices are additionally connected by a path of length , i.e. by a single edge, the vertices are called adjacent. A graph is said to be connected if every pair of vertices in the graph is connected. This means that there is a path between every pair of vertices. An undirected graph that is not connected is called disconnected. An undirected graph ''G'' is therefore disconnected if there exist two vertices i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Space
In mathematics, a topological space is, roughly speaking, a geometrical space in which closeness is defined but cannot necessarily be measured by a numeric distance. More specifically, a topological space is a set whose elements are called points, along with an additional structure called a topology, which can be defined as a set of neighbourhoods for each point that satisfy some axioms formalizing the concept of closeness. There are several equivalent definitions of a topology, the most commonly used of which is the definition through open sets, which is easier than the others to manipulate. A topological space is the most general type of a mathematical space that allows for the definition of limits, continuity, and connectedness. Common types of topological spaces include Euclidean spaces, metric spaces and manifolds. Although very general, the concept of topological spaces is fundamental, and used in virtually every branch of modern mathematics. The study of topological spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordered Pair
In mathematics, an ordered pair (''a'', ''b'') is a pair of objects. The order in which the objects appear in the pair is significant: the ordered pair (''a'', ''b'') is different from the ordered pair (''b'', ''a'') unless ''a'' = ''b''. (In contrast, the unordered pair equals the unordered pair .) Ordered pairs are also called 2-tuples, or sequences (sometimes, lists in a computer science context) of length 2. Ordered pairs of scalars are sometimes called 2-dimensional vectors. (Technically, this is an abuse of terminology since an ordered pair need not be an element of a vector space.) The entries of an ordered pair can be other ordered pairs, enabling the recursive definition of ordered ''n''-tuples (ordered lists of ''n'' objects). For example, the ordered triple (''a'',''b'',''c'') can be defined as (''a'', (''b'',''c'')), i.e., as one pair nested in another. In the ordered pair (''a'', ''b''), the object ''a'' is called the ''first entry'', and the object ''b'' the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongly Connected Component
In the mathematical theory of directed graphs, a graph is said to be strongly connected if every vertex is reachable from every other vertex. The strongly connected components of an arbitrary directed graph form a partition into subgraphs that are themselves strongly connected. It is possible to test the strong connectivity of a graph, or to find its strongly connected components, in linear time (that is, Θ(''V'' + ''E'')). Definitions A directed graph is called strongly connected if there is a path in each direction between each pair of vertices of the graph. That is, a path exists from the first vertex in the pair to the second, and another path exists from the second vertex to the first. In a directed graph ''G'' that may not itself be strongly connected, a pair of vertices ''u'' and ''v'' are said to be strongly connected to each other if there is a path in each direction between them. The binary relation of being strongly connected is an equivalence relation, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directed Graph
In mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a directed graph (or digraph) is a graph that is made up of a set of vertices connected by directed edges, often called arcs. Definition In formal terms, a directed graph is an ordered pair where * ''V'' is a set whose elements are called '' vertices'', ''nodes'', or ''points''; * ''A'' is a set of ordered pairs of vertices, called ''arcs'', ''directed edges'' (sometimes simply ''edges'' with the corresponding set named ''E'' instead of ''A''), ''arrows'', or ''directed lines''. It differs from an ordinary or undirected graph, in that the latter is defined in terms of unordered pairs of vertices, which are usually called ''edges'', ''links'' or ''lines''. The aforementioned definition does not allow a directed graph to have multiple arrows with the same source and target nodes, but some authors consider a broader definition that allows directed graphs to have such multiple arcs (namely, they allow the arc set to be a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphism
In mathematics, particularly in category theory, a morphism is a structure-preserving map from one mathematical structure to another one of the same type. The notion of morphism recurs in much of contemporary mathematics. In set theory, morphisms are functions; in linear algebra, linear transformations; in group theory, group homomorphisms; in topology, continuous functions, and so on. In category theory, ''morphism'' is a broadly similar idea: the mathematical objects involved need not be sets, and the relationships between them may be something other than maps, although the morphisms between the objects of a given category have to behave similarly to maps in that they have to admit an associative operation similar to function composition. A morphism in category theory is an abstraction of a homomorphism. The study of morphisms and of the structures (called "objects") over which they are defined is central to category theory. Much of the terminology of morphisms, as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk (mathematics)
In geometry, a disk (also spelled disc). is the region in a plane bounded by a circle. A disk is said to be ''closed'' if it contains the circle that constitutes its boundary, and ''open'' if it does not. For a radius, r, an open disk is usually denoted as D_r and a closed disk is \overline. However in the field of topology the closed disk is usually denoted as D^2 while the open disk is \operatorname D^2. Formulas In Cartesian coordinates, the ''open disk'' of center (a, b) and radius ''R'' is given by the formula :D=\ while the ''closed disk'' of the same center and radius is given by :\overline=\. The area of a closed or open disk of radius ''R'' is π''R''2 (see area of a disk). Properties The disk has circular symmetry. The open disk and the closed disk are not topologically equivalent (that is, they are not homeomorphic), as they have different topological properties from each other. For instance, every closed disk is compact whereas every open disk is not compact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directed Path
In graph theory, a path in a graph is a finite or infinite sequence of edges which joins a sequence of vertices which, by most definitions, are all distinct (and since the vertices are distinct, so are the edges). A directed path (sometimes called dipathGraph Structure Theory: Proceedings of the AMS-IMS-SIAM Joint Summer Research Conference on Graph Minors, Held June 22 to July 5, 1991p.205/ref>) in a directed graph is a finite or infinite sequence of edges which joins a sequence of distinct vertices, but with the added restriction that the edges be all directed in the same direction. Paths are fundamental concepts of graph theory, described in the introductory sections of most graph theory texts. See e.g. Bondy and Murty (1976), Gibbons (1985), or Diestel (2005). Korte et al. (1990) cover more advanced algorithmic topics concerning paths in graphs. Definitions Walk, trail, and path * A walk is a finite or infinite sequence of edges which joins a sequence of vertices. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere () is a Geometry, geometrical object that is a solid geometry, three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre (geometry), centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. spherical Earth, The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in any direction, so mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_sine_curve.png)