|
Color Opponency
The opponent process is a color theory that states that the human visual system interprets information about color by processing signals from photoreceptor cells in an antagonistic manner. The opponent-process theory suggests that there are three opponent channels, each comprising an opposing color pair: red versus green, blue versus yellow, and black versus white (luminance). The theory was first proposed in 1892 by the German physiologist Ewald Hering. Color theory Complementary colors When staring at a bright color for a while (e.g. red), then looking away at a white field, an afterimage is perceived, such that the original color will evoke its complementary colors, complementary color (green, in the case of red input). When complementary colors are combined or mixed, they "cancel each other out" and become neutral (white or gray). That is, complementary colors are never perceived as a mixture; there is no "greenish red" or "yellowish blue", despite Impossible color#Colors ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
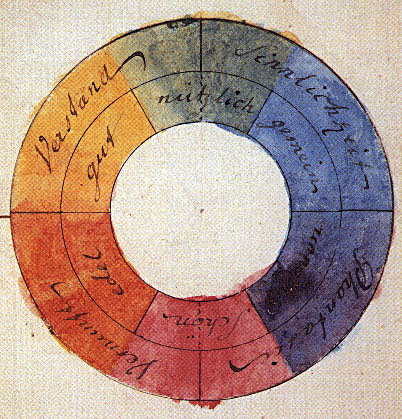
Color Theory
Color theory, or more specifically traditional color theory, is a historical body of knowledge describing the behavior of colors, namely in color mixing, color contrast effects, color harmony, color schemes and color symbolism. Modern color theory is generally referred to as color science. While there is no clear distinction in scope, traditional color theory tends to be more subjective and have artistic applications, while color science tends to be more objective and have functional applications, such as in chemistry, astronomy or color reproduction. Color theory dates back at least as far as Aristotle's treatise ''On Colors'' and Bharata_(sage), Bharata's Natya_Shastra, Nāṭya Shāstra. A formalization of "color theory" began in the 18th century, initially within a partisan controversy over Isaac Newton's theory of color (''Opticks'', 1704) and the nature of primary colors. By the end of the 19th century, a schism had formed between traditional color theory and color science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |