|
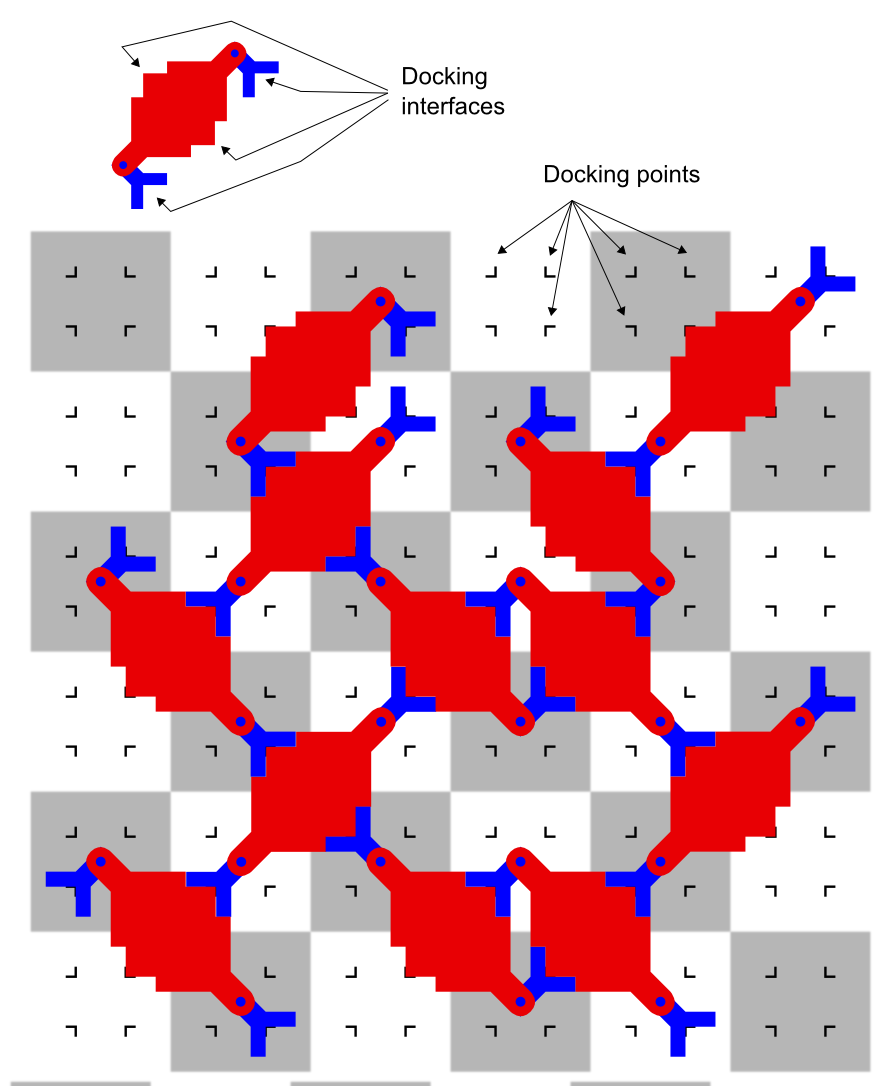
Claytronics
Claytronics is an abstract future concept that combines nanoscale robotics and computer science to create individual nanometer-scale computers called claytronic atoms, or ''catoms'', which can interact with each other to form tangible 3D objects that a user can interact with. This idea is more broadly referred to as programmable matter. Claytronics has the potential to greatly affect many areas of daily life, such as telecommunication, human-computer interfaces, and entertainment. Current research Current research is exploring the potential of modular reconfigurable robotics and the complex software necessary to control the “shape changing” robots. “Locally Distributed Predicates or LDP is a distributed, high-level language for programming modular reconfigurable robot systems (MRRs)”. There are many challenges associated with programming and controlling a large number of discrete modular systems due to the degrees of freedom that correspond with each module. For exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Matter
Programmable matter is matter which has the ability to change its physical properties (shape, density, moduli, conductivity, optical properties, etc.) in a programmable fashion, based upon user input or autonomous sensing. Programmable matter is thus linked to the concept of a material which inherently has the ability to perform information processing. History Programmable matter is a term originally coined in 1991 by Toffoli and Margolus to refer to an ensemble of fine-grained computing elements arranged in space. Their paper describes a computing substrate that is composed of fine-grained compute nodes distributed throughout space which communicate using only nearest neighbor interactions. In this context, programmable matter refers to compute models similar to cellular automata and lattice gas automata. The CAM-8 architecture is an example hardware realization of this model. This function is also known as "digital referenced areas" (DRA) in some forms of self-replicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-reconfiguring Modular Robot
Modular self-reconfiguring robotic systems or self-reconfigurable modular robots are autonomous kinematic machines with variable morphology. Beyond conventional actuation, sensing and control typically found in fixed-morphology robots, self-reconfiguring robots are also able to deliberately change their own shape by rearranging the connectivity of their parts, in order to adapt to new circumstances, perform new tasks, or recover from damage. For example, a robot made of such components could assume a worm-like shape to move through a narrow pipe, reassemble into something with spider-like legs to cross uneven terrain, then form a third arbitrary object (like a ball or wheel that can spin itself) to move quickly over a fairly flat terrain; it can also be used for making "fixed" objects, such as walls, shelters, or buildings. In some cases this involves each module having 2 or more connectors for connecting several together. They can contain electronics, sensors, computer processo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensemble Axiom
The ensemble axiom is an engineering concept which states that if an engineer designs parts to cooperate with each other in an ensemble, he or she can simplify the parts and the ensemble will operate better. This term is used within a research area called self-reconfiguring modular robotics, and specifically within claytronics, where it is stated as: A catom includes only enough functionality to contribute to the functionality desired in the claytronic ensemble.Claytronics Research Building synthetic reality from technological concept to engineered project References * The Robot is the Tether A tether is a cord, fixture, or flexible attachment that characteristically anchors something movable to something fixed; it also maybe used to connect two movable objects, such as an item being towed by its tow. Applications for tethers include ...: Active, Adaptive Power Routing for Modular Robots With Unary Inter-robot Connectors by Jason Campbell, Padmanabhan Pillai and Seth Copen Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconventional Computing
Unconventional computing is computing by any of a wide range of new or unusual methods. It is also known as alternative computing. The term ''unconventional computation'' was coined by Cristian S. Calude and John Casti and used at the First International Conference on Unconventional Models of Computation in 1998. Background The general theory of computation allows for a variety of models. Computing technology first developed using mechanical systems and then evolved into the use of electronic devices. Other fields of modern physics provide additional avenues for development. Computational model Computational models use computer programs to simulate and study complex systems using an algorithmic or mechanistic approach. They are commonly used to study complex nonlinear systems for which simple analytical solutions are not readily available. Experimentation with the model is done by adjusting parameters in the computer and studying the differences in the outcome. Operation th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. One of its predecessors was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools; it became the Carnegie Institute of Technology in 1912 and began granting four-year degrees in the same year. In 1967, the Carnegie Institute of Technology merged with the Mellon Institute of Industrial Research, founded in 1913 by Andrew Mellon and Richard B. Mellon and formerly a part of the University of Pittsburgh. Carnegie Mellon University has operated as a single institution since the merger. The university consists of seven colleges and independent schools: The College of Engineering, College of Fine Arts, Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences, Mellon College of Science, Tepper School of Business, Heinz College of Information Systems and Public Policy, and the School of Computer Science. The university has its main campus located 5 miles (8 km) from D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Research Lablets
The Intel Research Labs were a research division of Intel. The organization was known for most of its life as Intel Research, but towards the end of its life the name Intel Research was re-defined to refer to all research performed in Intel, including work done outside the labs. At its peak, there were six Intel Research Labs. The four university labs were each hosted by a partner university, while the two on-site labs were embedded inside normal Intel sites. Intel Research Berkeley was hosted by UC Berkeley, Intel Research Seattle by the University of Washington, Intel Research Pittsburgh by Carnegie Mellon University, and Intel Research Cambridge by the University of Cambridge in the United Kingdom. In addition, the People and Practices Research Lab (PaPR) performed ethnographic research at Intel's Hillsboro, Oregon campus, and one at Intel's Santa Clara, California headquarters. The Intel PaPR was composed of sociologists and anthropologists whose job it was to understan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Fog
Utility fog (also referred to as foglets) is a hypothetical collection of tiny nanobots that can replicate a physical structure.LEGOs (TM) to the Stars The Assembler, Volume 4, Number 3 Third Quarter, 1996, Tihamer Toth-Fejel As such, it is a form of self-reconfiguring modular robotics. Conception The term was coined by John Storrs Hall in 1989 Hall thought of it as a nanotechnological replacement for car |
Smartdust
Smartdust is a system of many tiny microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) such as sensors, robots, or other devices, that can detect, for example, light, temperature, vibration, magnetism, or chemicals. They are usually operated on a computer network wirelessly and are distributed over some area to perform tasks, usually sensing through radio-frequency identification. Without an antenna of much greater size the range of tiny smart dust communication devices is measured in a few millimeters and they may be vulnerable to electromagnetic disablement and destruction by microwave exposure. Design and engineering The concepts for Smart Dust emerged from a workshop at RAND in 1992 and a series of DARPA ISAT studies in the mid-1990s due to the potential military applications of the technology. The work was strongly influenced by work at UCLA and the University of Michigan during that period, as well as science fiction authors Stanislaw Lem (in novels ''The Invincible'' in 1964 and '' Peace o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoscopic Scale
The nanoscopic scale (or nanoscale) usually refers to structures with a length scale applicable to nanotechnology, usually cited as 1–100 nanometers (nm). A nanometer is a billionth of a meter. The nanoscopic scale is (roughly speaking) a lower bound to the mesoscopic scale for most solids. For technical purposes, the nanoscopic scale is the size at which fluctuations in the averaged properties (due to the motion and behavior of individual particles) begin to have a significant effect (often a few percent) on the behavior of a system, and must be taken into account in its analysis. The nanoscopic scale is sometimes marked as the point where the properties of a material change; above this point, the properties of a material are caused by 'bulk' or 'volume' effects, namely which atoms are present, how they are bonded, and in what ratios. Below this point, the properties of a material change, and while the type of atoms present and their relative orientations are still importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can perform automated deductions (referred to as automated reasoning) and use mathematical and logical tests to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making). Using human characteristics as descriptors of machines in metaphorical ways was already practiced by Alan Turing with terms such as "memory", "search" and "stimulus". In contrast, a heuristic is an approach to problem solving that may not be fully specified or may not guarantee correct or optimal results, especially in problem domains where there is no well-defined correct or optimal result. As an effective method, an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptable Robotics
Adaptable robotics are generally based in robot developer kits. This technology is distinguished from static automation due to its capacity to adapt to changing environmental conditions and material features while retaining a degree of predictability required for collaboration (e.g. human-robot collaboration). The degree of adaptability is demonstrated in the way these can be moved around and used in different tasks. Unlike static or factory robots, which have pre-defined way of operating, adaptable robots can function even if a component breaks, making them useful in cases like caring for the elderly, doing household tasks, and rescue work. The kits come with an open software platform tailored to a range of common robotic functions. The kits also come with common robotics hardware that connects easily with the software (infrared sensors, motors, microphone and video camera), which add to the capabilities of the robot. The process of modifying a robot to achieve varying capabilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitous Computing
Ubiquitous computing (or "ubicomp") is a concept in software engineering, hardware engineering and computer science where computing is made to appear anytime and everywhere. In contrast to desktop computing, ubiquitous computing can occur using any device, in any location, and in any format. A user interacts with the computer, which can exist in many different forms, including laptop computers, tablets, smart phones and terminals in everyday objects such as a refrigerator or a pair of glasses. The underlying technologies to support ubiquitous computing include Internet, advanced middleware, operating system, mobile code, sensors, microprocessors, new I/O and user interfaces, computer networks, mobile protocols, location and positioning, and new materials. This paradigm is also described as pervasive computing, ambient intelligence, or "everyware". Each term emphasizes slightly different aspects. When primarily concerning the objects involved, it is also known as physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |