|
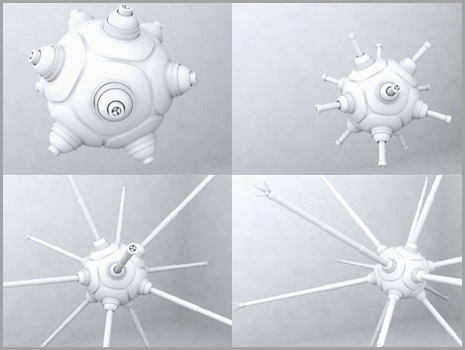
Utility Fog
Utility fog (also referred to as foglets) is a hypothetical collection of tiny nanobots that can replicate a physical structure.LEGOs (TM) to the Stars The Assembler, Volume 4, Number 3 Third Quarter, 1996, Tihamer Toth-Fejel As such, it is a form of ics. Conception The term was coined by John Storrs Hall in 1989. Hall thought of it as a nanotechnological replacement for car[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foglet Stimulacra
Utility fog (also referred to as foglets) is a hypothetical collection of tiny nanobots that can replicate a physical structure.LEGOs (TM) to the Stars The Assembler, Volume 4, Number 3 Third Quarter, 1996, Tihamer Toth-Fejel As such, it is a form of ics. Conception The term was coined by in 1989. Hall thought of it as a nanotechnological replacement for car |
Aluminum Oxide
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide, aloxite, ALOX or alundum in various forms and applications and alumina is refined from bauxite. It occurs naturally in its crystalline polymorphic phase α-Al2O3 as the mineral corundum, varieties of which form the precious gemstones ruby and sapphire,which have an alumina content approaching 100%. Al2O3 is used as feedstock to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point. Natural occurrence Corundum is the most common naturally occurring crystalline form of aluminium oxide. Rubies and sapphires are gem-quality forms of corundum, which owe their characteristic colours to trace impurities. Rubies are given their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a multidisciplinary field of science that focuses on living systems and organisms. It applies engineering principles to develop new biological parts, devices, and systems or to redesign existing systems found in nature. It is a branch of science that encompasses a broad range of methodologies from various disciplines, such as biochemistry, biotechnology, biomaterials, Materials science, material science/engineering, genetic engineering, molecular biology, molecular engineering, systems biology, Model lipid bilayer, membrane science, biophysics, Biological engineering, chemical and biological engineering, Electrical engineering, electrical and computer engineering, control engineering and evolutionary biology. It includes designing and constructing BioBrick, biological modules, biological systems, and biological machines, or re-designing existing biological systems for useful purposes. Additionally, it is the branch of science that focuses on the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Dust
Neural dust is a class of nanometer-sized devices operated as wirelessly powered nerve sensors; it is a type of brain–computer interface. The sensors may be used to study, monitor, or control the nerves and muscles and to remotely monitor neural activity. In practice, a medical treatment could introduce thousands of neural dust devices into human brains. The term is derived from "smart dust", as the sensors used as neural dust may also be defined by this concept. Background The design for neural dust was first proposed in a 2011 presentation by Jan Rabaey from the University of California, Berkeley Wireless Research Center and was subsequently demonstrated by graduate students in his lab. While the history of BCI begins with the invention of the electroencephalogram by Hans Berger in 1924, the term did not appear in scientific literature until the 1970s. The hallmark research of the field came from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), following a research grant fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smartdust
Smartdust is a system of many tiny microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) such as sensors, robots, or other devices, that can detect, for example, light, temperature, vibration, magnetism, or chemicals. They are usually operated on a computer network wirelessly and are distributed over some area to perform tasks, usually sensing through radio-frequency identification. Without an antenna of much greater size the range of tiny smart dust communication devices is measured in a few millimeters and they may be vulnerable to electromagnetic disablement and destruction by microwave exposure. Design and engineering The concepts for Smart Dust emerged from a workshop at RAND in 1992 and a series of DARPA ISAT studies in the mid-1990s due to the potential military applications of the technology. The work was strongly influenced by work at UCLA and the University of Michigan during that period, as well as science fiction authors Stanislaw Lem (in novels ''The Invincible'' in 1964 and ''Peace on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
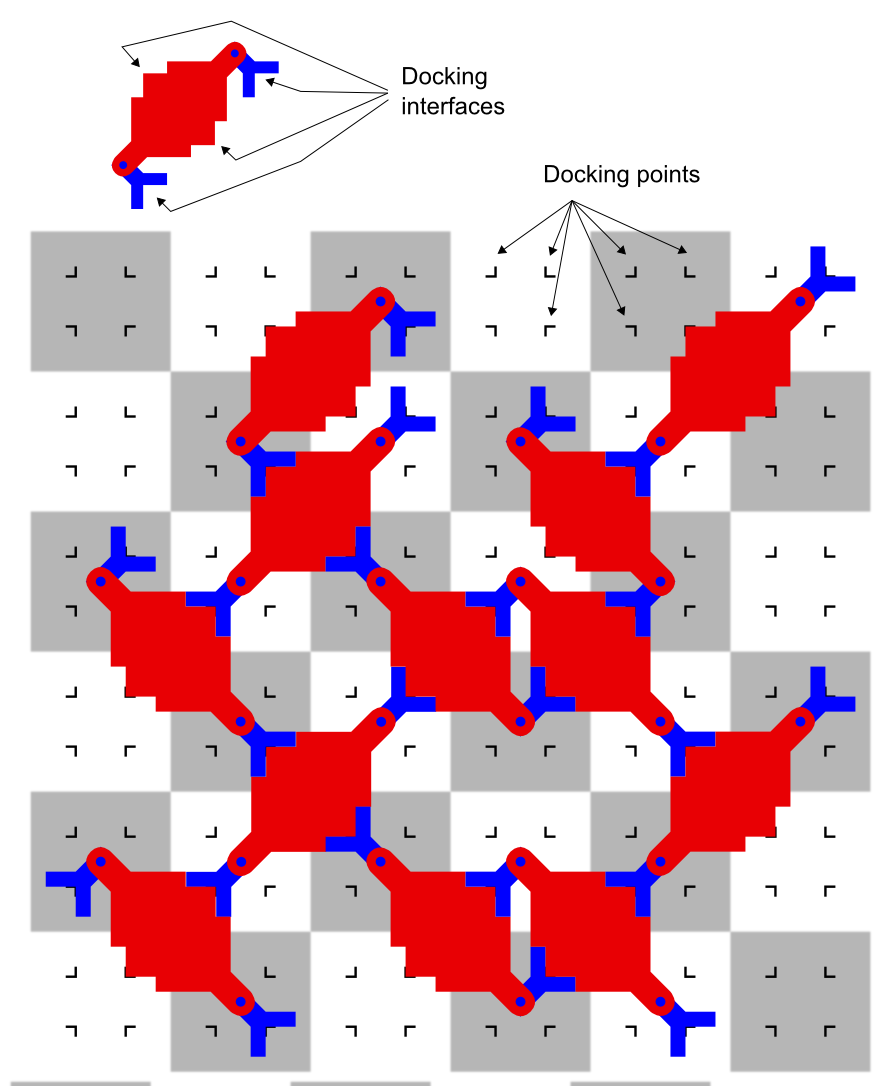
Self-reconfiguring Modular Robot
Modular self-reconfiguring robotic systems or self-reconfigurable modular robots are autonomous kinematic machines with variable morphology. Beyond conventional actuation, sensing and control typically found in fixed-morphology robots, self-reconfiguring robots are also able to deliberately change their own shape by rearranging the connectivity of their parts, in order to adapt to new circumstances, perform new tasks, or recover from damage. For example, a robot made of such components could assume a worm-like shape to move through a narrow pipe, reassemble into something with spider-like legs to cross uneven terrain, then form a third arbitrary object (like a ball or wheel that can spin itself) to move quickly over a fairly flat terrain; it can also be used for making "fixed" objects, such as walls, shelters, or buildings. In some cases this involves each module having 2 or more connectors for connecting several together. They can contain electronics, sensors, computer processo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Matter
Programmable matter is matter which has the ability to change its physical properties (shape, density, moduli, conductivity, optical properties, etc.) in a programmable fashion, based upon user input or autonomous sensing. Programmable matter is thus linked to the concept of a material which inherently has the ability to perform information processing. History Programmable matter is a term originally coined in 1991 by Toffoli and Margolus to refer to an ensemble of fine-grained computing elements arranged in space. Their paper describes a computing substrate that is composed of fine-grained compute nodes distributed throughout space which communicate using only nearest neighbor interactions. In this context, programmable matter refers to compute models similar to cellular automata and lattice gas automata. The CAM-8 architecture is an example hardware realization of this model. This function is also known as "digital referenced areas" (DRA) in some forms of self-replic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanorobotics
Nanoid robotics, or for short, nanorobotics or nanobotics, is an emerging technology field creating machines or robots, which are called nanorobots or simply nanobots, whose components are at or near the scale of a nanometer (10−9 meters). More specifically, nanorobotics (as opposed to microrobotics) refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building nanorobots with devices ranging in size from 0.1 to 10 micrometres and constructed of nanoscale or molecular components. The terms ''nanobot'', ''nanoid'', ''nanite'', ''nanomachine'' and ''nanomite'' have also been used to describe such devices currently under research and development. Nanomachines are largely in the research and development phase, but some primitive molecular machines and nanomotors have been tested. An example is a sensor having a switch approximately 1.5 nanometers across, able to count specific molecules in the chemical sample. The first useful applications of nanomachines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Machines
Molecular machines are a class of molecules typically described as an assembly of a discrete number of molecular components intended to produce mechanical movements in response to specific stimuli, mimicking macromolecule, macromolecular devices such as switches and motors. Naturally occurring or biological molecular machines are responsible for vital Biological process, living processes such as DNA replication and ATP synthase, ATP synthesis. Kinesins and ribosomes are examples of molecular machines, and they often take the form of Protein complex, multi-protein complexes. For the last several decades, scientists have attempted, with varying degrees of success, to miniaturize machines found in the macroscopic world. The first example of an artificial molecular machine (AMM) was reported in 1994, featuring a rotaxane with a ring and two different possible binding sites. In 2016 the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jean-Pierre Sauvage, Fraser Stoddart, Sir J. Fraser Stoddar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Goo
Gray goo (also spelled as grey goo) is a hypothetical global catastrophic scenario involving molecular nanotechnology in which out-of-control self-replicating machines consume all biomass (and perhaps also everything else) on Earth while building many more of themselves, a scenario that has been called '' ecophagy'' . The original idea assumed machines were designed to have this capability, while popularizations have assumed that machines might somehow gain this capability by accident. Self-replicating machines of the macroscopic variety were originally described by mathematician John von Neumann, and are sometimes referred to as von Neumann machines or clanking replicators. The term ''gray goo'' was coined by nanotechnology pioneer K. Eric Drexler in his 1986 book '' Engines of Creation''. In 2004, he stated "I wish I had never used the term 'gray goo'." ''Engines of Creation'' mentions "gray goo" as a thought experiment in two paragraphs and a note, while the popularized i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Air Explosive
A thermobaric weapon, also called an aerosol bomb, or a vacuum bomb, is a type of explosive munition that works by dispersing an aerosol cloud of gas, liquid or powdered explosive. The fuel is usually a single compound, rather than a mixture of multiple substances. Many types of thermobaric weapons can be fitted to hand-held launchers, and can also be launched from airplanes. Terminology The term ''thermobaric'' is derived from the Greek words for 'heat' and 'pressure': ''thermobarikos'' (θερμοβαρικός), from ''thermos'' (θερμός) 'hot' + ''baros'' (βάρος) 'weight, pressure' + suffix ''-ikos'' (-ικός) '-ic'. Other terms used for the family of weapons are high-impulse thermobaric weapons, heat and pressure weapons, vacuum bombs, and fuel-air explosives (FAE). Mechanism File:Dust explosion 00.jpg, Experimental setup File:Dust explosion 01.jpg, Finely-ground flour is dispersed File:Dust explosion 02.jpg, Cloud of flour is ignited File:Dust explosion 03. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |