|
Chamaeleon
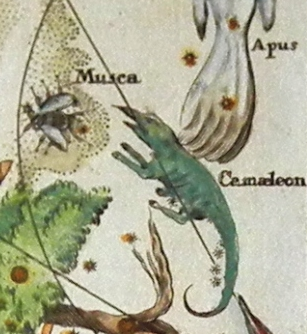
Chamaeleon () is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It is named after the chameleon, a kind of lizard. It was first defined in the 16th century. History Chamaeleon was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. It first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. Johann Bayer was the first uranographer to put Chamaeleon in a celestial atlas. It was one of many constellations created by European explorers in the 15th and 16th centuries out of unfamiliar Southern Hemisphere stars. Features Stars There are four bright stars in Chamaeleon that form a compact diamond-shape approximately 10 degrees from the south celestial pole and about 15 degrees south of Acrux, along the axis formed by Acrux and Gamma Crucis. Alpha Chamaeleontis is a white-hued star of magnitude 4.1, 63 light-years from Earth. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation Chamaeleon
Chamaeleon () is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It is named after the chameleon, a kind of lizard. It was first defined in the 16th century. History Chamaeleon was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. It first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. Johann Bayer was the first uranographer to put Chamaeleon in a celestial atlas. It was one of many constellations created by European explorers in the 15th and 16th centuries out of unfamiliar Southern Hemisphere stars. Features Stars There are four bright stars in Chamaeleon that form a compact diamond-shape approximately 10 degrees from the south celestial pole and about 15 degrees south of Acrux, along the axis formed by Acrux and Gamma Crucis. Alpha Chamaeleontis is a white-hued star of magnitude 4.1, 63 light-years from Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chameleon
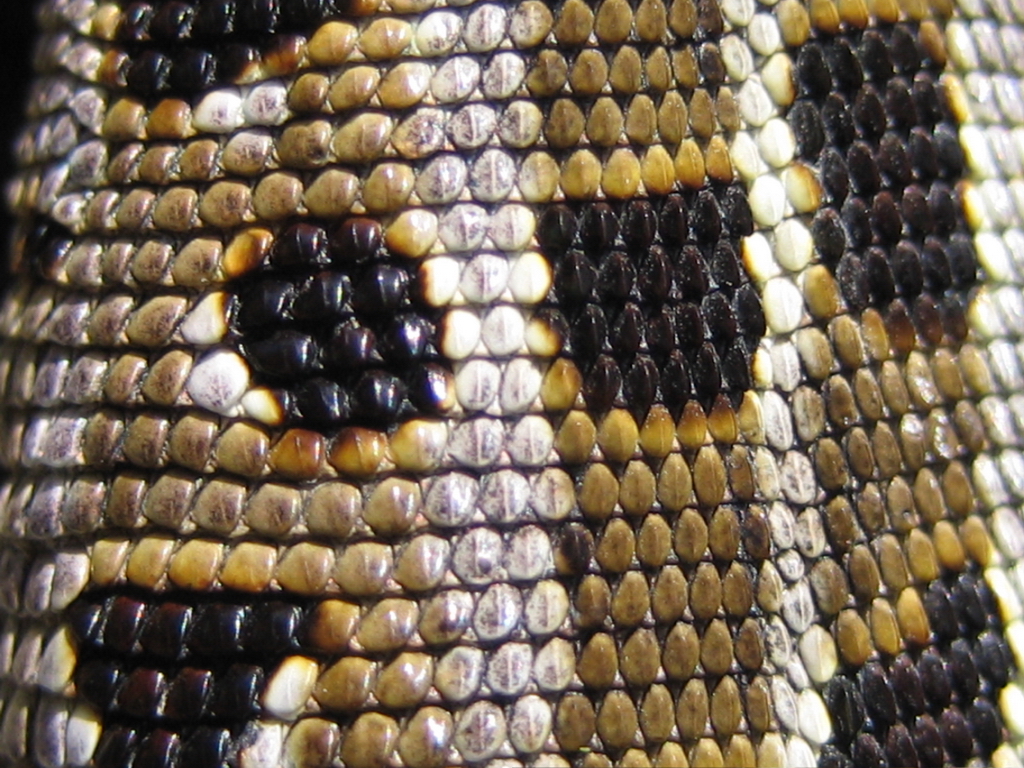
Chameleons or chamaeleons (family Chamaeleonidae) are a distinctive and highly specialized clade of Old World lizards with 202 species described as of June 2015. The members of this family are best known for their distinct range of colors, being capable of shifting to different hues and degrees of brightness. The large number of species in the family exhibit considerable variability in their capacity to change color. For some, it is more of a shift of brightness (shades of brown); for others, a plethora of color-combinations (reds, yellows, greens, blues) can be seen. Chameleons are distinguished by their zygodactylous feet, their prehensile tail, their laterally compressed bodies, their head casques, their projectile tongues, their swaying gait, and crests or horns on their brow and snout. Chameleons' eyes are independently mobile, and because of this there are two separate, individual images that the brain is analyzing of the chameleon’s environment. When hunting prey, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chameleon
Chameleons or chamaeleons (family Chamaeleonidae) are a distinctive and highly specialized clade of Old World lizards with 202 species described as of June 2015. The members of this family are best known for their distinct range of colors, being capable of shifting to different hues and degrees of brightness. The large number of species in the family exhibit considerable variability in their capacity to change color. For some, it is more of a shift of brightness (shades of brown); for others, a plethora of color-combinations (reds, yellows, greens, blues) can be seen. Chameleons are distinguished by their zygodactylous feet, their prehensile tail, their laterally compressed bodies, their head casques, their projectile tongues, their swaying gait, and crests or horns on their brow and snout. Chameleons' eyes are independently mobile, and because of this there are two separate, individual images that the brain is analyzing of the chameleon’s environment. When hunting prey, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chameleon Constellation
Chameleons or chamaeleons (family Chamaeleonidae) are a distinctive and highly specialized clade of Old World lizards with 202 species described as of June 2015. The members of this family are best known for their distinct range of colors, being capable of shifting to different hues and degrees of brightness. The large number of species in the family exhibit considerable variability in their capacity to change color. For some, it is more of a shift of brightness (shades of brown); for others, a plethora of color-combinations (reds, yellows, greens, blues) can be seen. Chameleons are distinguished by their zygodactylous feet, their prehensile tail, their laterally compressed bodies, their head casques, their projectile tongues, their swaying gait, and crests or horns on their brow and snout. Chameleons' eyes are independently mobile, and because of this there are two separate, individual images that the brain is analyzing of the chameleon’s environment. When hunting prey, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Chamaeleontis
Beta Chamaeleontis, Latinized from β Chamaeleontis, is the third-brightest star in the southern constellation of Chamaeleon. A solitary, suspected variable star, it is visible to the naked eye as a faint blue-white point of light with an apparent visual magnitude that has been measured ranging between 4.24 and 4.30. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of 298 light years from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +23 km/s. This is a B-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of B4 V that is generating energy through core hydrogen fusion. It has been catalogued both as a Be star and a normal star. This object is about 23 million years old with a high projected rotational velocity of 255 km/s. The rapid rotation is creating an equatorial bulge that is 12% larger than the polar radius. The star has five times the mass of the Sun and 2.8 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 212 times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Chamaeleontis
Alpha Chamaeleontis, Latinized from α Chamaeleontis, is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Chamaeleon. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.06 and thus is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. With an annual parallax shift of 51.12 mas, it is located 63.8 light years from the Sun. The star is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −13 km/s, and is predicted to come to within in 666,000 years. This is an F-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of , where the 'Fe−0.8' notation indicates an anomalously low abundance of iron. It has an estimated 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, 2.1 times the Sun's radius, and radiates 7.5 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 6,580 K. The star is around 1.8 billion years old with a projected rotational velocity that is too low to be measured. The star has been examined for an infrared excess that would sug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Chamaeleontis
The Bayer designation Delta Chamaeleontis (δ Cha / δ Chamaeleontis) is shared by two star systems, in the constellation Chamaeleon (constellation), Chamaeleon: *Delta1 Chamaeleontis, δ¹ Chamaeleontis *Delta2 Chamaeleontis, δ² Chamaeleontis {{SIA , astronomical objects Bayer objects, Chamaeleontis, Delta Chamaeleon (constellation) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Chamaeleontis
Gamma Chamaeleontis, Latinized from γ Chamaeleontis, is a solitary star located in the southern circumpolar constellation of Chamaeleon. It can faintly be seen with the naked eye on a dark night, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.12. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 7.81 mas, it is located around 418 light years from the Sun. This is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K5 III. The measured angular diameter, after correction for limb darkening, is . At the estimated distance of the star, this yields a physical size of about 67 times the radius of the Sun. It is a suspected variable star, with an amplitude of 0.01 magnitude. The star radiates 864 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere with an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musca
Musca () is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It was one of 12 constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman, and it first appeared on a celestial globe in diameter published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer's ''Uranometria'' of 1603. It was also known as Apis () for 200 years. Musca remains below the horizon for most Northern Hemisphere observers. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appears to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. These include Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Zeta2 and (probably) Eta Muscae, as well as HD 100546, a blue-white Herbig Ae/Be star that is surrounded by a complex debris disk containing a large planet or brown dwarf and possible protoplanet. Two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apus
Apus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky. It represents a bird-of-paradise, and its name means "without feet" in Greek language, Greek because the bird-of-paradise was once wrongly believed to lack feet. First depicted on a celestial globe by Petrus Plancius in 1598, it was charted on a star atlas by Johann Bayer in his 1603 ''Uranometria''. The French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille charted and gave the brighter stars their Bayer designations in 1756. The five brightest stars are all reddish in hue. Shading the others at apparent magnitude 3.8 is Alpha Apodis, an orange giant that has around 48 times the diameter and 928 times the luminosity of the Sun. Marginally fainter is Gamma Apodis, another ageing giant star. Delta Apodis is a double star, the two components of which are 103 Minute and second of arc, arcseconds apart and visible with the naked eye. Two star systems have been found to have exoplanet, planets. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mensa (constellation)
Mensa is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere near the south celestial pole, one of fourteen constellations drawn up in the 18th century by French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille. Its name is Latin for table, though it originally commemorated Table Mountain and was known as "Mons Mensae". One of the eighty-eight constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), it covers a keystone-shaped wedge of sky 153.5 square degrees in area. Other than the south polar constellation of Octans, it is the most southerly of constellations and is observable only south of the 5th parallel of the Northern Hemisphere. One of the faintest constellations in the night sky, Mensa contains no apparently bright stars—the brightest, Alpha Mensae, is barely visible in suburban skies. Part of the Large Magellanic Cloud, several star clusters and a quasar lie in the area covered by the constellation, and at least three of its star systems have been f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia although some lizards are more closely related to these two excluded groups than they are to other lizards. Lizards range in size from chameleons and geckos a few centimeters long to the 3-meter-long Komodo dragon. Most lizards are quadrupedal, running with a strong side-to-side motion. Some lineages (known as "legless lizards"), have secondarily lost their legs, and have long snake-like bodies. Some such as the forest-dwelling ''Draco'' lizards are able to glide. They are often territorial, the males fighting off other males and signalling, often with bright colours, to attract mates and to intimidate rivals. Lizards are mainly carnivorous, often being sit-and-wait predators; many smaller species eat insects, while the Komodo eats mammals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |