|
Constellation Chamaeleon
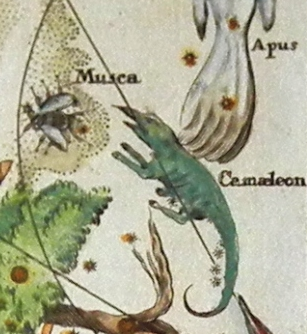
Chamaeleon () is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It is named after the chameleon, a kind of lizard. It was first defined in the 16th century. History Chamaeleon was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. It first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. Johann Bayer was the first uranographer to put Chamaeleon in a celestial atlas. It was one of many constellations created by European explorers in the 15th and 16th centuries out of unfamiliar Southern Hemisphere stars. Features Stars There are four bright stars in Chamaeleon that form a compact diamond-shape approximately 10 degrees from the south celestial pole and about 15 degrees south of Acrux, along the axis formed by Acrux and Gamma Crucis. Alpha Chamaeleontis is a white-hued star of magnitude 4.1, 63 light-years from Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chameleon
Chameleons or chamaeleons (family Chamaeleonidae) are a distinctive and highly specialized clade of Old World lizards with 202 species described as of June 2015. The members of this family are best known for their distinct range of colors, being capable of shifting to different hues and degrees of brightness. The large number of species in the family exhibit considerable variability in their capacity to change color. For some, it is more of a shift of brightness (shades of brown); for others, a plethora of color-combinations (reds, yellows, greens, blues) can be seen. Chameleons are distinguished by their zygodactylous feet, their prehensile tail, their laterally compressed bodies, their head casques, their projectile tongues, their swaying gait, and crests or horns on their brow and snout. Chameleons' eyes are independently mobile, and because of this there are two separate, individual images that the brain is analyzing of the chameleon’s environment. When hunting prey, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrus Plancius
Petrus Plancius (; 1552 – 15 May 1622) was a Dutch-Flemish astronomer, cartographer and clergyman. He was born as Pieter Platevoet in Dranouter, now in Heuvelland, West Flanders. He studied theology in Germany and England. At the age of 24 he became a minister in the Dutch Reformed Church. Plancius fled from Brussels to Amsterdam to avoid religious prosecution by the Inquisition after the city fell into Spanish hands in 1585. In Amsterdam he became interested in navigation and cartography and, having access to nautical charts recently brought from Portugal, he was soon recognized as an expert on safe maritime routes to India and the nearby "spice islands". This enabled colonies and port trade in both, including what would become the Dutch East Indies, named after the Dutch East India Company set up in 1602. He saw strong potential in the little-mapped Arctic Sea and strongly believed in the idea of a Northeast Passage until the failure of Willem Barentsz's third voyage in 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Chamaeleontis
The Bayer designation Delta Chamaeleontis (δ Cha / δ Chamaeleontis) is shared by two star systems, in the constellation Chamaeleon (constellation), Chamaeleon: *Delta1 Chamaeleontis, δ¹ Chamaeleontis *Delta2 Chamaeleontis, δ² Chamaeleontis {{SIA , astronomical objects Bayer objects, Chamaeleontis, Delta Chamaeleon (constellation) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Chamaeleontis
Gamma Chamaeleontis, Latinized from γ Chamaeleontis, is a solitary star located in the southern circumpolar constellation of Chamaeleon. It can faintly be seen with the naked eye on a dark night, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.12. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 7.81 mas, it is located around 418 light years from the Sun. This is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K5 III. The measured angular diameter, after correction for limb darkening, is . At the estimated distance of the star, this yields a physical size of about 67 times the radius of the Sun. It is a suspected variable star, with an amplitude of 0.01 magnitude. The star radiates 864 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere with an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Chamaeleontis
Beta Chamaeleontis, Latinized from β Chamaeleontis, is the third-brightest star in the southern constellation of Chamaeleon. A solitary, suspected variable star, it is visible to the naked eye as a faint blue-white point of light with an apparent visual magnitude that has been measured ranging between 4.24 and 4.30. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of 298 light years from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +23 km/s. This is a B-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of B4 V that is generating energy through core hydrogen fusion. It has been catalogued both as a Be star and a normal star. This object is about 23 million years old with a high projected rotational velocity of 255 km/s. The rapid rotation is creating an equatorial bulge that is 12% larger than the polar radius. The star has five times the mass of the Sun and 2.8 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 212 times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
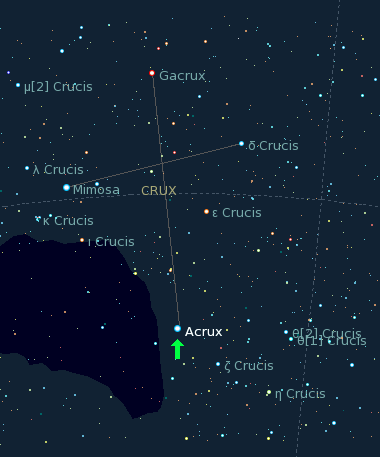
Gamma Crucis
Gacrux it is the third-brightest star in the southern constellation of Crux, the Southern Cross. It has the Bayer designation Gamma Crucis, which is Latinised from γ Crucis and abbreviated Gamma Cru or γ Cru. With an apparent visual magnitude of +1.63, it is the 26th brightest star in the night sky. A line from the two "Pointers", Alpha Centauri through Beta Centauri, leads to within 1° north of this star. Using parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, it is located at a distance of from the Sun. It is the nearest red giant star to the Sun. Nomenclature ''γ Crucis'' (Latinised to ''Gamma Crucis'') is the star's Bayer designation. Since Gacrux is at roughly −60° declination. It was known to the ancient Greeks and Romans, but oddly in the era lacked a traditional name, and was visible north of 40° latitude due to the precession of equinoxes. The astronomer Ptolemy counted it as part of the constellation of Centaurus. The historical name ''Gacru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Crucis
Acrux is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Crux. It has the Bayer designation α Crucis, which is Latinised to Alpha Crucis and abbreviated Alpha Cru or α Cru. With a combined visual magnitude of +0.76, it is the 13th-brightest star in the night sky. It is the most southerly star of the asterism known as the Southern Cross and is the southernmost first-magnitude star, 2.3 degrees more southerly than Alpha Centauri. This system is located at a distance of 321 light-years from the Sun. To the naked eye Acrux appears as a single star, but it is actually a multiple star system containing six components. Through optical telescopes, Acrux appears as a triple star, whose two brightest components are visually separated by about 4 arcseconds and are known as Acrux A and Acrux B, α1 Crucis and α2 Crucis, or α Crucis A and α Crucis B. Both components are B-type stars, and are many times more massive and luminous than the Sun. α1 Crucis is itself a spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
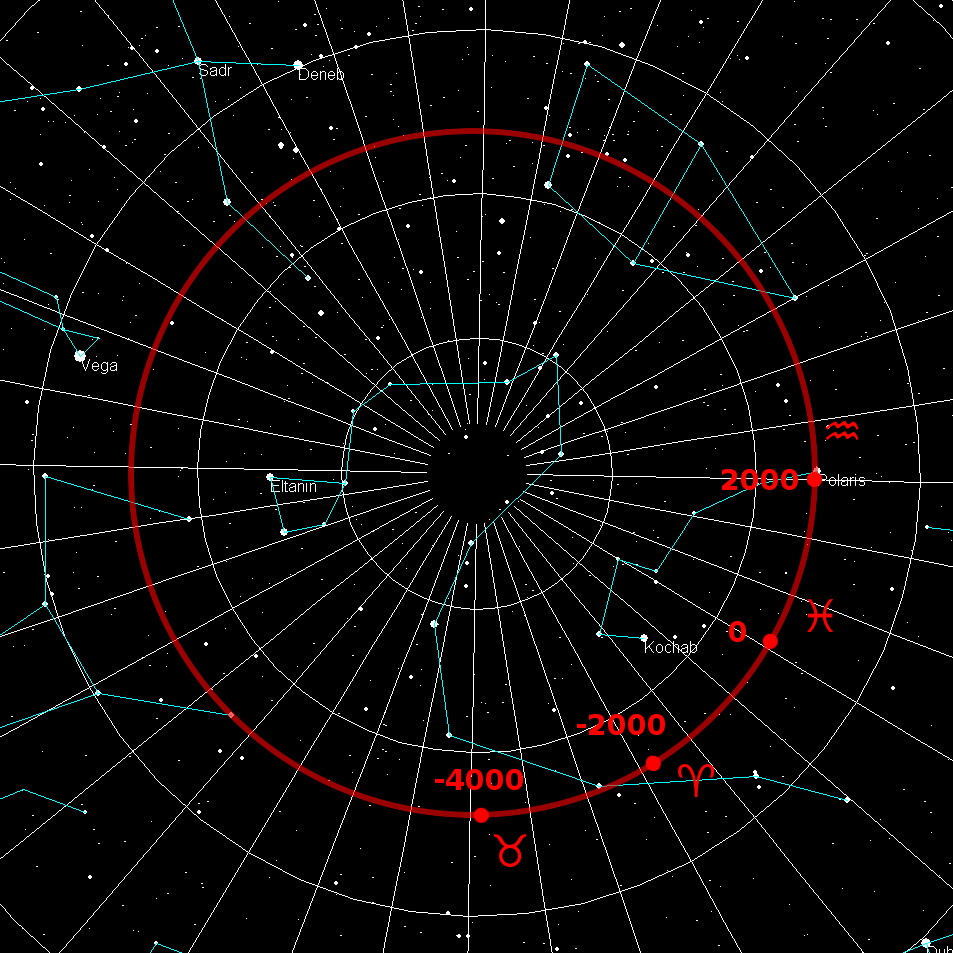
South Celestial Pole
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers at Earth's North Pole and South Pole, respectively. As Earth spins on its axis, the two celestial poles remain fixed in the sky, and all other celestial points appear to rotate around them, completing one circuit per day (strictly, per sidereal day). The celestial poles are also the poles of the celestial equatorial coordinate system, meaning they have declinations of +90 degrees and −90 degrees (for the north and south celestial poles, respectively). Despite their apparently fixed positions, the celestial poles in the long term do not actually remain permanently fixed against the background of the stars. Because of a phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes, the poles trace out circles on the celestial sphere, with a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation Chamaeleon
Chamaeleon () is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It is named after the chameleon, a kind of lizard. It was first defined in the 16th century. History Chamaeleon was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. It first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. Johann Bayer was the first uranographer to put Chamaeleon in a celestial atlas. It was one of many constellations created by European explorers in the 15th and 16th centuries out of unfamiliar Southern Hemisphere stars. Features Stars There are four bright stars in Chamaeleon that form a compact diamond-shape approximately 10 degrees from the south celestial pole and about 15 degrees south of Acrux, along the axis formed by Acrux and Gamma Crucis. Alpha Chamaeleontis is a white-hued star of magnitude 4.1, 63 light-years from Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranography
Celestial cartography, uranography, astrography or star cartography is the aspect of astronomy and branch of cartography concerned with mapping stars, galaxies, and other astronomical objects on the celestial sphere. Measuring the position and light of charted objects requires a variety of instruments and techniques. These techniques have developed from angle measurements with quadrants and the unaided eye, through sextants combined with lenses for light magnification, up to current methods which include computer-automated space telescopes. Uranographers have historically produced planetary position tables, star tables, and star maps for use by both amateur and professional astronomers. More recently, computerized star maps have been compiled, and automated positioning of telescopes uses databases of stars and of other astronomical objects. Etymology The word "uranography" derived from the Greek "ουρανογραφια" (Koine Greek ''ουρανος'' "sky, heave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer (1572 – 7 March 1625) was a German lawyer and uranographer (celestial cartographer). He was born in Rain, Lower Bavaria, in 1572. At twenty, in 1592 he began his study of philosophy and law at the University of Ingolstadt, after which he moved to Augsburg to begin work as a lawyer, becoming legal adviser to the city council in 1612. Bayer had several interests outside his work, including archaeology and mathematics. However, he is primarily known for his work in astronomy; particularly for his work on determining the positions of objects on the celestial sphere. He remained unmarried and died in 1625. Bayer's star atlas '' Uranometria Omnium Asterismorum'' (" Uranometry of all the asterisms") was first published in 1603 in Augsburg and dedicated to two prominent local citizens. This was the first atlas to cover the entire celestial sphere. It was based upon the work of Tycho Brahe and may have borrowed from Alessandro Piccolomini's 1540 star atlas, ''De le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jodocus Hondius
Jodocus Hondius (Latinized version of his Dutch language, Dutch name: ''Joost de Hondt'') (17 October 1563 – 12 February 1612) was a Flemish people, Flemish and Dutch engraving, engraver and cartographer. He is sometimes called Jodocus Hondius the Elder to distinguish him from his son Jodocus Hondius II. Hondius is best known for his early maps of the New World and Europe, for re-establishing the reputation of the work of Gerardus Mercator, Gerard Mercator, and for his portraits of Francis Drake. He inherited and republished the plates of Mercator, thus reviving his legacy, also making sure to include independent revisions to his work. One of the notable figures in the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography, Golden Age of Dutch cartography (c. 1570s–1670s), he helped establish Amsterdam as the center of cartography in Europe in Dutch Golden Age, the 17th century. Biography Hondius was born in Wakken and grew up in Ghent. In his early years he established himself as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |