|
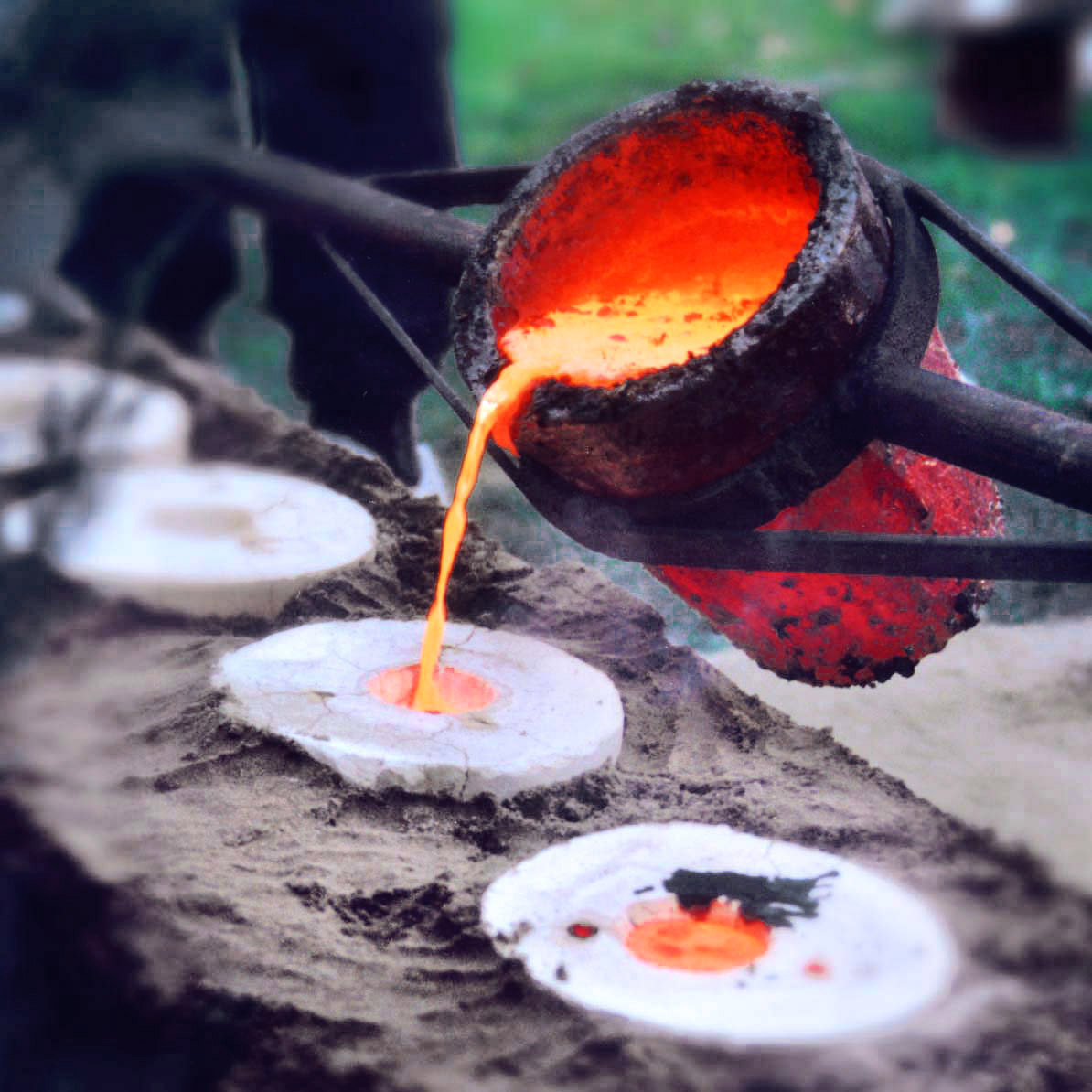
Castings
In metalworking and jewelry making, casting is a process in which a liquid metal is delivered into a Mold (manufacturing), mold (usually by a crucible) that contains a negative impression (i.e., a three-dimensional negative image) of the intended shape. The metal is poured into the mold through a hollow channel called a Sprue (manufacturing), sprue. The metal and mold are then cooled, and the metal part (the ''casting'') is extracted. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Casting processes have been known for thousands of years, and have been widely used for sculpture (especially in bronze), jewelry in precious metals, and weapons and tools. Highly engineered castings are found in 90 percent of durable goods, including cars, trucks, aerospace, trains, mining and construction equipment, oil wells, appliances, pipes, hydrants, wind turbines, nuclear plants, medical devices, defense products, toys, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Casting
Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used. The casting equipment and the metal dies represent large capital costs and this tends to limit the process to high-volume production. Manufacture of parts using die casting is relatively simple, involving only four main steps, which keeps the incremental cost per item low. It is especially suited for a large quantity of small- to medium-sized castings, which is why die casting produces more castings than any other casting process. Die castings are characterized by a very good surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand Casting
Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand as the mold material. The term "sand casting" can also refer to an object produced via the sand casting process. Sand castings are produced in specialized factories called foundries. Over 60% of all metal castings are produced via sand casting process. Molds made of sand are relatively cheap, and sufficiently refractory even for steel foundry use. In addition to the sand, a suitable bonding agent (usually clay) is mixed or occurs with the sand. The mixture is moistened, typically with water, but sometimes with other substances, to develop the strength and plasticity of the clay and to make the aggregate suitable for molding. The sand is typically contained in a system of frames or mold boxes known as a flask. The mold cavities and gate system are created by compacting the sand around models called patterns, by carving directly into the sand, or by 3D printing. Basic pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
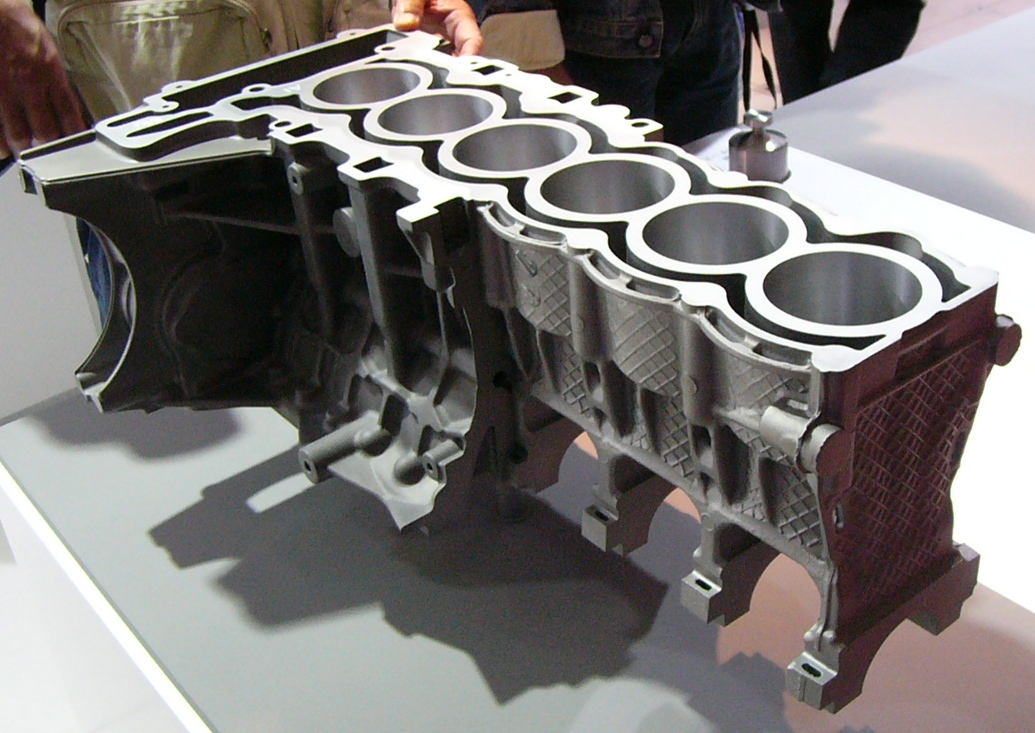
Casting Processes
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a ''casting'', which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting materials are usually metals or various ''time setting'' materials that cure after mixing two or more components together; examples are epoxy, concrete, plaster and clay. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Heavy equipment like machine tool beds, ships' propellers, etc. can be cast easily in the required size, rather than fabricating by joining several small pieces. Casting is a 7,000-year-old process. The oldest surviving casting is a copper frog from 3200 BC. History Throughout history, metal casting has been used to make tools, weapons, and religious objects. Metal casting history and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a ''casting'', which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting materials are usually metals or various ''time setting'' materials that cure after mixing two or more components together; examples are epoxy, concrete, plaster and clay. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Heavy equipment like machine tool beds, ships' propellers, etc. can be cast easily in the required size, rather than fabricating by joining several small pieces. Casting is a 7,000-year-old process. The oldest surviving casting is a copper frog from 3200 BC. History Throughout history, metal casting has been used to make tools, weapons, and religious objects. Metal casting history and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Assist Direct Pour
Investment casting is an industrial process based on lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques. The term "lost-wax casting" can also refer to modern investment casting processes. Investment casting has been used in various forms for the last 5,000 years. In its earliest forms, beeswax was used to form patterns necessary for the casting process. Today, more advanced waxes, refractory materials and specialist alloys are typically used for making patterns. Investment casting is valued for its ability to produce components with accuracy, repeatability, versatility and integrity in a variety of metals and high-performance alloys. The fragile wax patterns must withstand forces encountered during the mould making. Much of the wax used in investment casting can be reclaimed and reused. Lost-foam casting is a modern form of investment casting that eliminates certain steps in the process. Investment casting is so named because the process invests (surrounds) the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost-wax Casting
Lost-wax casting (also called "investment casting", "precision casting", or ''cire perdue'' which has been adopted into English from the French, ) is the process by which a duplicate metal sculpture (often silver, gold, brass, or bronze) is cast from an original sculpture. Intricate works can be achieved by this method. The oldest known examples of this technique are approximately 6,500-year-old (4550–4450 BC) and attributed to gold artefacts found at Bulgaria's Varna Necropolis. A copper amulet from Mehrgarh, Indus Valley civilization, in Pakistan, is dated to circa 4,000 BC. Cast copper objects, found in the Nahal Mishmar hoard in southern Israel, which belong to the Chalcolithic period (4500–3500 BC), are estimated, from carbon-14 dating, to date to circa 3500 BC. In Other examples from somewhat later periods are from Mesopotamia in the third millennium BC. Lost-wax casting was widespread in Europe until the 18th century, when a piece-moulding process came to predomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cast Iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impurities which allow cracks to pass straight through, grey cast iron has graphite flakes which deflect a passing crack and initiate countless new cracks as the material breaks, and ductile cast iron has spherical graphite "nodules" which stop the crack from further progressing. Carbon (C), ranging from 1.8 to 4 wt%, and silicon (Si), 1–3 wt%, are the main alloying elements of cast iron. Iron alloys with lower carbon content are known as steel. Cast iron tends to be brittle, except for malleable cast irons. With its relatively low melting point, good fluidity, castability, excellent machinability, resistance to deformation and wear resistance, cast irons have become an engineering material with a wide range of applications and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaster Mold Casting
Plaster mold casting is a metalworking casting process similar to sand casting except the molding material is plaster of Paris instead of sand. Like sand casting, plaster mold casting is an expendable mold process, however it can only be used with non-ferrous materials. It is used for castings as small as to as large as . Generally, the form takes less than a week to prepare. Production rates of 1–10 units/hr can be achieved with plaster molds.. Parts that are typically made by plaster casting are lock components, gears, valves, fittings, tooling, and ornaments. Details The plaster is not pure plaster of Paris, but rather has additives to improve green strength, dry strength, permeability, and castability. For instance, talc or magnesium oxide are added to prevent cracking and reduce setting time; lime and cement limit expansion during baking; glass fibers increase strength; sand can be used as a filler. The ratio of ingredients is 70–80% gypsum and 20–30% additives.. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size.The elements are from different metal groups. See periodic table. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near Net Shape
Near-net-shape is an industrial manufacturing technique. As the name implies, the initial production of the item is very close to the final, or ''net'', shape. This reduces the need for surface finishing. By minimizing the use of finishing methods like machining or grinding, near-net-shape production eliminates more than two-thirds of the production costs in some industries. Processes The following are various near-net-shape processes categorized by material. Ceramics * Gelcasting * Ceramic injection molding *Spray forming *Structural ceramic production Composites * Lanxide process Plastics *Injection moulding *Rapid prototyping Metals *Casting **Permanent mold casting *Powder metallurgy * Linear friction welding *Friction welding *Metal injection molding *Rapid prototyping *Spray forming * Superplastic forming *Cold forming *Semi-solid metal casting *Photochemical machining Photochemical machining (PCM), also known as photochemical milling or photo etching, is a chemical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table) it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and it almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explode as supernovas, much of the magnesium is expelled into the interstellar medium where it ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |