|
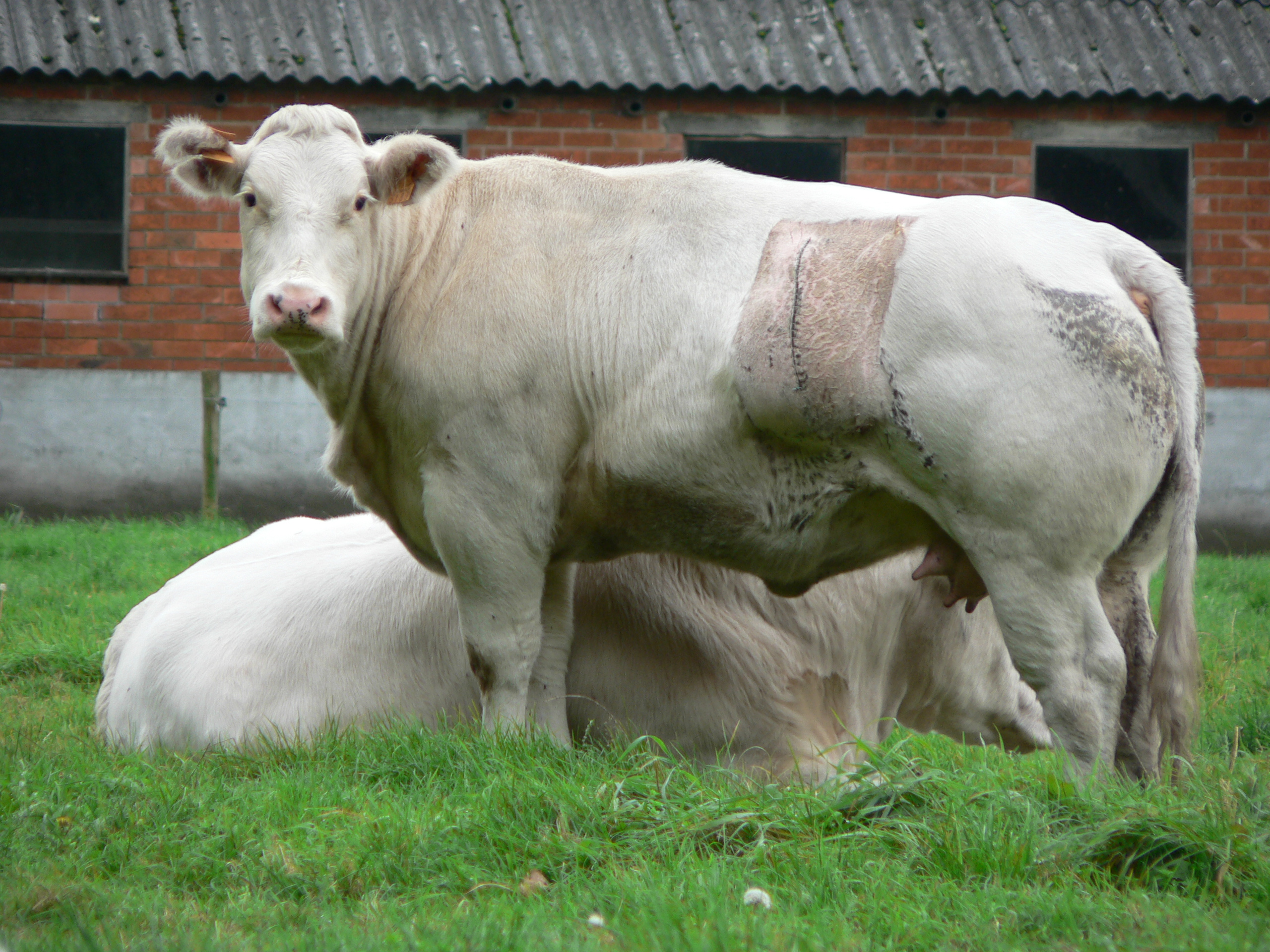
Broodstock
Broodstock, or broodfish, are a group of mature individuals used in aquaculture for breeding purposes. Broodstock can be a population of animals maintained in captivity as a source of replacement for, or enhancement of, seed and fry numbers.Waples, R.S., and C. Do. 1994. Genetic risk associated with supplementation of Pacific salmonids: Captive broodstock programs. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science,51(1), 310–329. These are generally kept in ponds or tanks in which environmental conditions such as photoperiod, temperature and pH are controlled. Such populations often undergo conditioning to ensure maximum fry output. Broodstock can also be sourced from wild populations where they are harvested and held in maturation tanks before their seed is collected for grow-out to market sizeFast, A. W. (1994). Effects of broodstock size and source on ovarian maturation and spawning on ''Penaeus monodon'' Fabricius from the Gulf of Thailand. Journal of the World Aquaculture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lotus). Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, refers specifically to aquaculture practiced in seawater habitats and lagoons, opposed to in freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain fish products as food. Aquaculture can also be defined as the breeding, growing, and harvesting of fish and other aquatic plants, also known as farming in water. It is an environmental source of food and commercial product which help to improve healthier habitats and used to recon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Stocks
Fish stocks are subpopulations of a particular species of fish, for which intrinsic parameters (growth, recruitment, mortality and fishing mortality) are traditionally regarded as the significant factors determining the stock's population dynamics, while extrinsic factors (immigration and emigration) are traditionally ignored. Concepts The stock concept All species have geographic limits to their distribution, which are determined by their tolerance to environmental conditions, and their ability to compete successfully with other species. In marine environments this may be less evident than on land because there are fewer topographical boundaries, however, discontinuities still exist, produced for example by mesoscale and sub-mesoscale circulations that minimize long-distance dispersal of fish larvae. For fish, it is rare for an individual to reproduce randomly with all other individuals of that species within its biological range. There is a tendency to form a structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
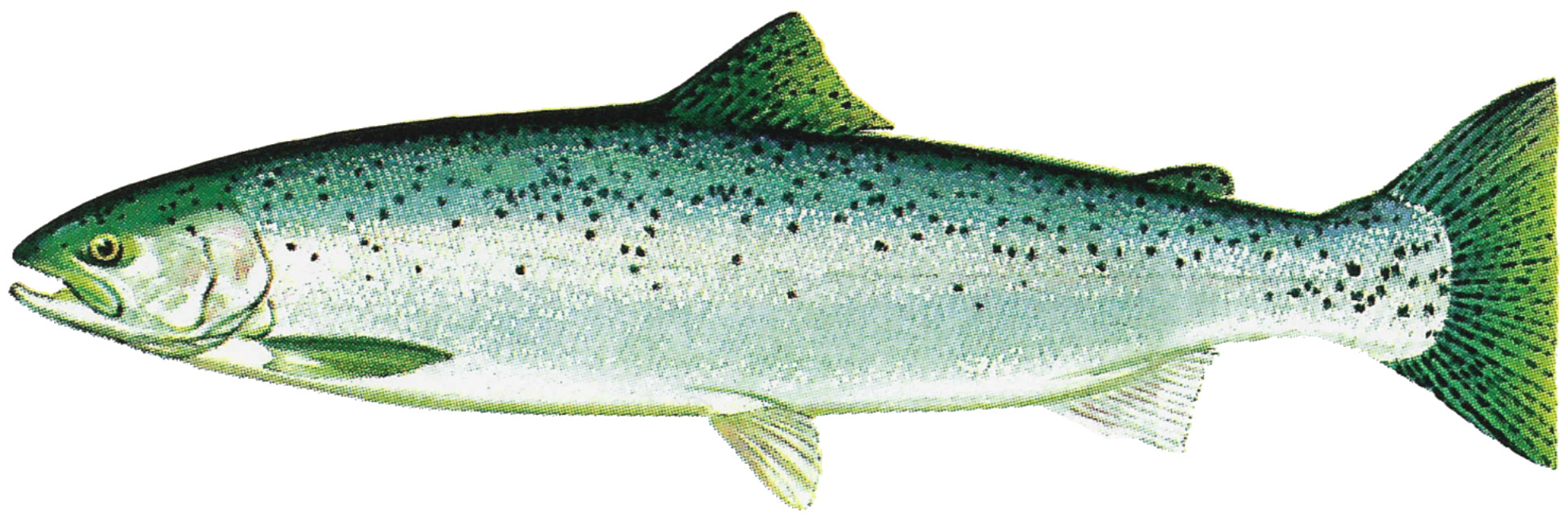
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Freshwater forms that have been introduced into the Great Lakes and migrate into tributaries to spawn are also called steelhead. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Larva
Ichthyoplankton (from Greek: ἰχθύς, , "fish"; and πλαγκτός, , "drifter") are the eggs and larvae of fish. They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epipelagic or photic zone. Ichthyoplankton are planktonic, meaning they cannot swim effectively under their own power, but must drift with the ocean currents. Fish eggs cannot swim at all, and are unambiguously planktonic. Early stage larvae swim poorly, but later stage larvae swim better and cease to be planktonic as they grow into juveniles. Fish larvae are part of the zooplankton that eat smaller plankton, while fish eggs carry their own food supply. Both eggs and larvae are themselves eaten by larger animals. Fish can produce high numbers of eggs which are often released into the open water column. Fish eggs typically have a diameter of about . The newly hatched young of oviparous fish are called larvae. They are usually poorly formed, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
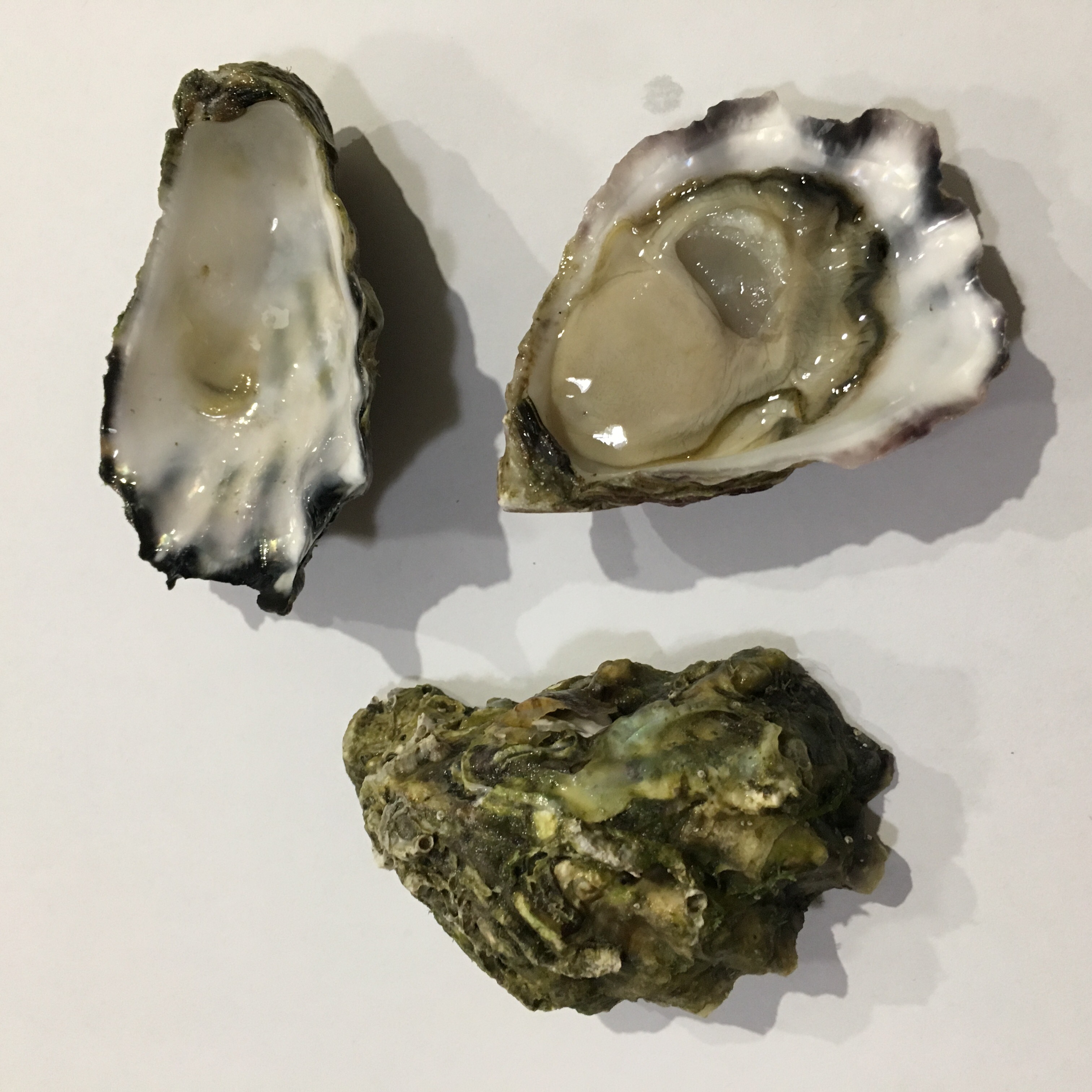
Sydney Rock Oyster
''Saccostrea glomerata'', is an oyster species belonging to the family Ostreidae.MolluscaBase eds. (2022). MolluscaBase. Saccostrea Dollfus & Dautzenberg, 1920. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=138300 on 2022-04-27 It is endemic to Australia and New Zealand. In Australia, it is known as the Sydney rock oyster and is commercially farmed. In New Zealand, where the species is not farmed, it is known as the New Zealand rock oyster or Auckland oyster. The species is closely related to ''Saccostrea cucullata'', the hooded oyster, which is common on Indo-Pacific rocky shores. Sydney rock oysters are capable of tolerating a wide range of salinities (halotolerant). They are usually found in the intertidal zone to below the low-water mark. Taxonomy The Sydney rock oyster and New Zealand rock oyster have previously been classified as two separate species: ''Saccostrea commercialis'' and ''S. glomerata'', resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penaeidae
Penaeidae is a family of marine crustaceans in the suborder Dendrobranchiata, which are often referred to as penaeid shrimp or penaeid prawns. The Penaeidae contain many species of economic importance, such as the tiger prawn, whiteleg shrimp, Atlantic white shrimp, and Indian prawn. Many prawns are the subject of commercial fishery, and farming, both in marine settings, and in freshwater farms. Lateral line–like sense organs on the antennae have been reported in some species of Penaeidae. At , the myelinated giant interneurons of pelagic penaeid shrimp have the world record for impulse conduction speed in any animal. Genera Of the 48 recognised genera in the family Penaeidae, 23 are known only from the fossil record (marked †): * † '' Albertoppelia'' Schweigert & Garassino, 2004 * † ''Ambilobeia'' Garassino & Pasini, 2002 * † ''Antrimpos'' Münster, 1839 * '' Artemesia'' Bate, 1888 * '' Atypopenaeus'' Alcock, 1905 * † '' Bombur'' Münster, 1839 * † ''Bylgia'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-salmonid fish such as ''Cynoscion nebulosus'', the spotted seatrout or speckled trout. Trout are closely related to salmon and char (or charr): species termed salmon and char occur in the same genera as do fish called trout (''Oncorhynchus'' – Pacific salmon and trout, ''Salmo'' – Atlantic salmon and various trout, ''Salvelinus'' – char and trout). Lake trout and most other trout live in freshwater lakes and rivers exclusively, while there are others, such as the steelhead, a form of the coastal rainbow trout, that can spend two or three years at sea before returning to fresh water to spawn (a habit more typical of salmon). Arctic char and brook trout are part of the char genus. Trout are an important food source for humans and wildlife, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Mortality
Fish mortality is a parameter used in fisheries population dynamics to account for the loss of fish in a fish stock through death. The mortality can be divided into two types: * Natural mortality: the removal of fish from the stock due to causes not associated with fishing. Such causes can include disease, competition, cannibalism, old age, predation, pollution or any other natural factor that causes the death of fish. In fisheries models natural mortality is denoted by (M).Sparre, P.; Ursin E.and Venema S. C. (1989). Introduction to tropical fish stock assessment. Part 1- Manual. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper No. 3061. Rome, FAO. p. 337. * Fishing mortality: the removal of fish from the stock due to fishing activities using any fishing gear. It is denoted by (F) in fisheries models. (M) and (F) are additive instantaneous rates that sum up to (Z), the instantaneous total mortality coefficient; that is, Z=M+F.Gulland, J.A. (1969). Manual of Methods for fish stock assessment. Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selective Breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together. Domesticated animals are known as breeds, normally bred by a professional breeder, while domesticated plants are known as varieties, cultigens, cultivars, or breeds. Two purebred animals of different breeds produce a crossbreed, and crossbred plants are called hybrids. Flowers, vegetables and fruit-trees may be bred by amateurs and commercial or non-commercial professionals: major crops are usually the provenance of the professionals. In animal breeding, techniques such as inbreeding, linebreeding, and outcrossing are utilized. In plant breeding, similar methods are used. Charles Darwin discussed how selective breeding had been successful in producing change over time in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as diges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juvenile Fish
Fish go through various life stages between fertilization and adulthood. The life of a fish start as spawned eggs which hatch into immotile larvae. These larval hatchlings are not yet capable of feeding themselves and carry a yolk sac which provides stored nutrition. Before the yolk sac completely disappears, the young fish must mature enough to be able to forage independently. When they have developed to the point where they are capable of feeding by themselves, the fish are called fry. When, in addition, they have developed scales and working fins, the transition to a juvenile fish is complete and it is called a fingerling, so called as they are typically about the size of human fingers. The juvenile stage lasts until the fish is fully grown, sexually mature and interacting with other adult fish. Growth stages Ichthyoplankton ''(planktonic or drifting fish)'' are the eggs and larvae of fish. They are usually found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


_with_its_prey.jpg)


