|
Bradyseism
Bradyseism is the gradual uplift (positive bradyseism) or descent (negative bradyseism) of part of the Earth's surface caused by the filling or emptying of an underground magma chamber or hydrothermal activity, particularly in volcanic calderas. It can persist for millennia in between eruptions and each uplift event is normally accompanied by thousands of small to moderate earthquakes. The word derives from the ancient Greek words βραδύς ''bradús'', meaning "slow", and σεισμός ''seismós'' meaning "movement", and was coined by Arturo Issel in 1883. Phlegraean Fields The area of Phlegraean Fields (Campi Flegrei), near Naples, is a collapsed caldera, namely a volcanic area formed by several volcanic edifices, which includes the Solfatara volcano, well known for its fumaroles. The Campi Flegrei area is especially noted for bradyseismic uplift and subsidence. The inflation and deflation of this caldera is especially well documented due to its seaside location and a lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
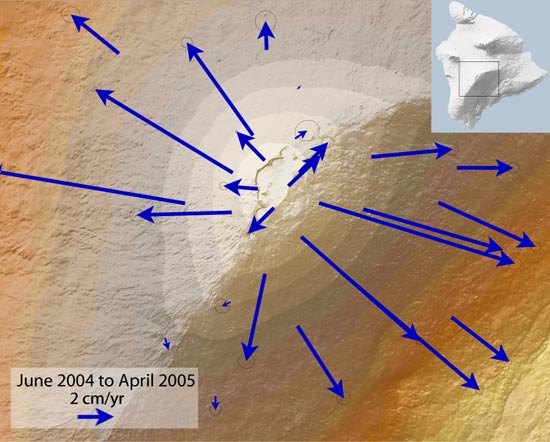
Deformation (volcanology)
In volcanology, deformation is any change in the shape of a volcano or the land surrounding it. This can be in the form of inflation, which is a response to pressurization, or deflation, which is a response to depressurization. Inflation is represented by swelling of the ground surface, a volcanic edifice, or a subsurface magma body. It can be caused by magma accumulation, exsolution of volatiles, geothermal processes, heating, and tectonic compression. Deflation is represented by shrinking of the ground surface, a volcanic edifice, or a subsurface magma body. It can be caused by magma withdrawal (related to intrusion or eruption), volatile escape, thermal contraction, phase changes during crystallization, and tectonic extension. Deformation is a key indicator of pre-eruptive unrest at many active volcanoes. The term bradyseism is used in the volcanological literature to mean the vertical ground movements associated with the Phlegraean Fields volcanic area west of Naples, Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pozzuoli
Pozzuoli (; ; ) is a city and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Naples, in the Italian region of Campania. It is the main city of the Phlegrean Peninsula. History Pozzuoli began as the Greek colony of ''Dicaearchia'' ( el, Δικαιαρχία) founded in about 531 BC with the consent of nearby Cumae when refugees from Samos escaped from the tyranny of Polycrates. The Samnites occupied Dicaearchia in 421 BC after having conquered Cumae and may have changed its name to Fistelia. It enjoyed considerable political and commercial autonomy favoured by the excellent position of its port with the Campanian hinterland. The Roman occupation of Campania after the end of the 1st Samnite War from 341 BC marked the start of the Romanisation of the Greek-Samnite city. During the Second Punic War (218-201 BC), Rome experienced the strategic importance of the port of Puteoli and reinforced the defences and introduced a garrison to protect the town from Hannibal, who failed to capt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serapeum (Pozzuoli) -3
A serapeum is a temple or other religious institution dedicated to the syncretic Greco-Egyptian deity Serapis, who combined aspects of Osiris and Apis in a humanized form that was accepted by the Ptolemaic Greeks of Alexandria. There were several such religious centers, each of which was a ''serapeion'' ( el, Σεραπεῖον) or, in its Latinized form, a ''serapeum''. An Egyptian name for the temple of Osiris-Apis ( , ) was Pr-Wsỉr-Ḥp "House of Osiris-Apis". Egyptian serapea Alexandria The Serapeum of Alexandria in the Ptolemaic Kingdom was an ancient Greek temple built by Ptolemy III Euergetes. There are also signs of Harpocrates. It has been referred to as the daughter of the Library of Alexandria. It existed until the end of the fourth century AD. Saqqara The Serapeum of Saqqara is located north west of the Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara, a necropolis near Memphis in Lower Egypt. It was a burial place of the Apis, sacred bulls that were incarnations of Ptah. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumaroles
A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcanic activity, but fumarole activity can also precede a volcanic eruption and has been used for eruption prediction. Most fumaroles die down within a few days or weeks of the end of an eruption, but a few are persistent, lasting for decades or longer. An area containing fumaroles is known as a fumarole field. The predominant vapor emitted by fumaroles is steam, formed by the circulation of groundwater through heated rock. This is typically accompanied by volcanic gases given off by magma cooling deep below the surface. These volcanic gases include sulfur compounds, such as various sulfur oxides and hydrogen sulfide, and sometimes hydrogen chloride, hydrogen fluoride, and other gases. A fumarole that emits significant sulfur compounds is some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform and terrain history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphologists work within disciplines such as physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology, climatology, and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field. Overview Earth's surface is modified by a combination of surface processes that shape landscapes, and geologic processes that cause tectonic uplift and subsidence, and shape the coastal geography. Surface processes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake Swarm
In seismology, an earthquake swarm is a sequence of seismic events occurring in a local area within a relatively short period. The time span used to define a swarm varies, but may be days, months, or years. Such an energy release is different from the situation when a major earthquake (main shock) is followed by a series of aftershocks: in earthquake swarms, no single earthquake in the sequence is obviously the main shock. In particular, a cluster of aftershocks occurring after a mainshock ''is not'' a swarm. History and generalities In the Ore Mountains (Erzgebirge), which form the border between the Czech Republic and Germany, western Bohemia and the Vogtland region, have been known since the 16th century as prone to frequent earthquake swarms, which typically last a few weeks to a few months. Austrian geologist Josef Knett, while studying in 1899 a swarm of about a hundred events felt in western Bohemia/Vogtland in January-February 1824, coined the noun ''Schwarmbeben'', ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithophaga
''Lithophaga'', the date mussels, are a genus of medium-sized marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae. Some of the earliest fossil ''Lithophaga'' shells have been found in Mesozoic rocks from the Alps and from Vancouver Island.Ludvigsen, Rolf & Beard, Graham. 1997. West Coast Fossils: A Guide to the Ancient Life of Vancouver Island. pg. 102Kleemann, K.H., 1994. Mytilid bivalve ''Lithophaga'' in Upper Triassic coral ''Pamiroseris'' from Zlambach Beds compared with Cretaceous ''Lithophaga alpina''. Facies 30, 151-154. The shells of species in this genus are long and narrow with parallel sides. The animals bore into stone or coral rock with the help of pallial gland secretions,"integument (mollusks)."Encyclopædia Britannica. 2009. Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD hence the systematic name ''Lithophaga'', which means "stone-eater". Their club-shaped borings are given the trace fossil name ''Gastrochaenolites''. Species Species within the genus ''Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrochaenolites
''Gastrochaenolites'' is a trace fossil formed as a clavate (club-shaped) boring in a hard substrate such as a shell, rock or carbonate hardground. The aperture of the boring is narrower than the main chamber and may be circular, oval, or dumb-bell shaped (Kelly and Bromley, 1984). ''Gastrochaenolites'' is most commonly attributed to bioeroding bivalves such as '' Lithophaga'' and ''Gastrochaena'' (Kleeman, 1980). The fossil ranges from the Ordovician The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start ... to the Recent (Taylor and Wilson, 2003; Vinn and Wilson, 2010). The first Lower Jurassic ''Gastrochaenolites'' ichnospecies is ''Gastrochaenolites messisbugi'' Bassi, Posenato, Nebelsick, 2017. This is the first record of boreholes and their producers (mytilid bivalves) in one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macellum Of Pozzuoli
The Macellum of Pozzuoli ( it, Macellum di Pozzuoli) was the macellum or market building of the Roman colony of Puteoli, now the city of Pozzuoli in southern Italy. When first excavated in the 18th century, the discovery of a statue of Serapis led to the building being misidentified as the city's serapeum or Temple of Serapis. A band of borings or ''Gastrochaenolites'' left by marine ''Lithophaga'' bivalve molluscs on three standing marble columns indicated that these columns had remained upright over centuries while the site sank below sea level, then re-emerged. This puzzling feature was the subject of debate in early geology, and eventually led to the identification of bradyseism in the area, showing that the Earth's crust could be subject to gradual movement without destructive earthquakes. Roman origins The city of Dicaearchia, founded by Greek refugees escaping dictatorship on Samos, was integrated into the Roman Empire as the city of Puteoli in 194 BC. The macellum or fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solfatara (volcano)
Solfatara ( it, Solfatara di Pozzuoli) is a shallow volcanic crater at Pozzuoli, near Naples, part of the Phlegraean Fields ( it, Campi Flegrei) volcanic area. It is a dormant volcano, which still emits jets of steam with sulfurous fumes. The name comes from the Latin, ''Sulpha terra'', "land of sulfur", or "sulfur earth". It was formed around 4000 years ago and last erupted in 1198 with what was probably a ''phreatic'' eruption – an explosive steam-driven eruption caused when groundwater interacts with magma. The crater floor was a popular tourist attraction until 2017, as it has many fumaroles and mud pools. The area is well known for its bradyseism. The vapours had been used for medical purposes since Roman times. Solfatara crater.jpg, Panoramic view of the crater towards the southeast Mud pool in Solfatara crater.jpg, Close-up view of a mud pool Medium fumarole in Solfatara crater.jpg, Medium size fumarole in Solfatara Fumarole in Solfatara crater (close up).jpg, Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma Chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it upwards. If the magma finds a path to the surface, then the result will be a volcanic eruption; consequently, many volcanoes are situated over magma chambers. These chambers are hard to detect deep within the Earth, and therefore most of those known are close to the surface, commonly between 1 km and 10 km down. Dynamics of magma chambers Magma rises through cracks from beneath and across the crust because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. When the magma cannot find a path upwards it pools into a magma chamber. These chambers are commonly built up over time, by successive horizontal or vertical magma injections. Influx of new magma causes reaction of pre-existing crystals and the pressure in the chamber to increase. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is gone. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a Volcanic crater, crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur each century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times per century. Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2016. More recently, a caldera collapse occurred at Kīlauea, Hawaii in 2018. Etymology The term ''caldera'' comes from Spanish language, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-3.jpg)

.jpg)



