Deformation (volcanology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

 In
In volcanology
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geological, geophysical and geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin word ''vulcan''. Vulcan was the anci ...
, deformation is any change in the shape of a volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
or the land surrounding it. This can be in the form of inflation, which is a response to pressurization
{{Wiktionary
Pressurization or pressurisation is the application of pressure in a given situation or environment.
Industrial
Industrial equipment is often maintained at pressures above or below atmospheric.
Atmospheric
This is the process by ...
, or deflation, which is a response to depressurization. Inflation is represented by swelling of the ground surface, a volcanic edifice, or a subsurface magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
body. It can be caused by magma accumulation, exsolution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The wor ...
of volatiles
Volatiles are the group of chemical elements and chemical compounds that can be readily vaporized. In contrast with volatiles, elements and compounds that are not readily vaporized are known as refractory substances.
On planet Earth, the term ' ...
, geothermal processes, heating, and tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents k ...
compression
Compression may refer to:
Physical science
*Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces
*Compression member, a structural element such as a column
*Compressibility, susceptibility to compression
* Gas compression
*Compression ratio, of a ...
. Deflation is represented by shrinking of the ground surface, a volcanic edifice, or a subsurface magma body. It can be caused by magma withdrawal (related to intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
or eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often ...
), volatile escape, thermal contraction Negative thermal expansion (NTE) is an unusual physicochemical process in which some materials contract upon heating, rather than expand as most other materials do. The most well-known material with NTE is water at 0~4 °C. Water's NTE is the r ...
, phase changes during crystallization
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposi ...
, and tectonic extension. Deformation is a key indicator of pre-eruptive unrest at many active volcanoes. The term bradyseism
Bradyseism is the gradual uplift (positive bradyseism) or descent (negative bradyseism) of part of the Earth's surface caused by the filling or emptying of an underground magma chamber or hydrothermal activity, particularly in volcanic calderas. ...
is used in the volcanological literature to mean the vertical ground movements associated with the Phlegraean Fields
The Phlegraean Fields ( it, Campi Flegrei ; nap, Campe Flegree, from Ancient Greek 'to burn') is a large region of supervolcanic calderas situated to the west of Naples, Italy. It was declared a regional park in 2003. The area of the calde ...
volcanic area west of Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
.
Ground deformation measurements are crucial in volcano monitoring as they provide an important indicator about what is happening beneath a volcano. As magma accumulates in an underground reservoir
A salt dome is a type of structural dome formed when salt (or other evaporite minerals) intrudes into overlying rocks in a process known as diapirism. Salt domes can have unique surface and subsurface structures, and they can be discovered using ...
before an eruption, the ground surface typically undergoes inflation. If silicic
Silicic is an adjective to describe magma or igneous rock rich in silica. The amount of silica that constitutes a silicic rock is usually defined as at least 63 percent. Granite and rhyolite are the most common silicic rocks.
Silicic is the grou ...
magma intrudes very near the surface but does not breach to the surface, it may form a bulge on the surface known as a cryptodome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions o ...
. Although deformation is frequently related to subsurface magmatic movements, other processes may contribute as well. This is particularly true for subglacial volcanoes, which may undergo inflation or deflation due to size variations of the overlying ice cap
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets.
Description
Ice caps are not constrained by topographical features ...
. An example of this phenomenon has been demonstrated for Katla, an active volcano under Mýrdalsjökull
Mýrdalsjökull (pronounced , Icelandic for "(the) mire dale glacier" or "(the) mire valley glacier") is an ice cap in the south of Iceland. It is to the north of Vík í Mýrdal and to the east of the smaller ice cap Eyjafjallajökull. Between t ...
in the south of Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
.
GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
, tilt and InSAR Interferometric synthetic aperture radar, abbreviated InSAR (or deprecated IfSAR), is a radar technique used in geodesy and remote sensing. This geodetic method uses two or more synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images to generate maps of surface defo ...
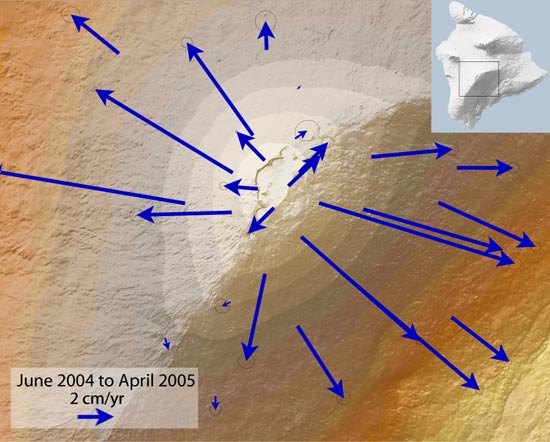
are the primary methods used to track ground movement. GPS measurements can be used to estimate the location and amount of magma accumulating beneath the surface. For example, the Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
an volcano Mauna Loa
Mauna Loa ( or ; Hawaiian: ; en, Long Mountain) is one of five volcanoes that form the Island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The largest subaerial volcano (as opposed to subaqueous volcanoes) in both mass and ...
has experienced multiple episodes of inflation since its 1984 eruption, and it has been well documented since the mid-1990s. Ground tilt is continuously recorded with electronic tiltmeter
A tiltmeter is a sensitive inclinometer designed to measure very small changes from the vertical level, either on the ground or in structures. Tiltmeters are used extensively for monitoring volcanoes, the response of dams to filling, the small ...
s installed in drill holes about beneath the ground surface—a location that insulates the instruments from the effects of environmental (temperature and wind) and cultural noise. Rapid changes in tilt are usually detected in the hours to days before an intrusion or eruption. InSAR uses radar images of the ground that are collected by airplanes or orbiting satellites to make maps of ground deformation. The Group on Earth Observations
The Group on Earth Observations (GEO) coordinates international efforts to build a Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS). It links existing and planned Earth observation systems and supports the development of new ones in cases of p ...
' "Supersite" initiative identified Hawaii as a critical site for regular monitoring, so more satellite InSAR data are available for Kīlauea
Kīlauea ( , ) is an active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands. Located along the southeastern shore of the Big Island of Hawaii, the volcano is between 210,000 and 280,000 years old and emerged above sea level about 100,000 years ago. His ...
and Mauna Loa volcanoes than for any other volcano on Earth. Because InSAR detects deformation over broad areas, it is an excellent tool for mapping both large- and small-scale changes.
References
{{reflist, 30em Volcanology Volcano monitoring