|
Borane-methyl Sulfide
Borane dimethylsulfide (BMS) is a complexed borane reagent that is used for hydroborations and reductions. The advantages of BMS over other borane reagents, such as borane-tetrahydrofuran, are its increased stability and higher solubility. BMS is commercially available at much higher concentrations than its tetrahydrofuran counterpart (10 M) and does not require sodium borohydride as a stabilizer, which could result in undesired side reactions. In contrast, borane·THF requires sodium borohydride to inhibit reduction of THF to tributyl borate. BMS is soluble in most aprotic solvents. Preparation and structure Although usually purchased, BMS can be prepared by absorbing diborane into dimethyl sulfide Dimethyl sulfide (DMS) or methylthiomethane is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2S. Dimethyl sulfide is a flammable liquid that boils at and has a characteristic disagreeable odor. It is a component of the smell produced from cook ...: :B2H6 + 2 SMe2 → ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroboration
In organic chemistry, hydroboration refers to the addition of a hydrogen-boron bond to certain double and triple bonds involving carbon (, , , and ). This chemical reaction is useful in the organic synthesis of organic compounds. Hydroboration produces organoborane compounds that react with a variety of reagents to produce useful compounds, such as alcohols, amines, or alkyl halides. The most widely known reaction of the organoboranes is oxidation to produce alcohols typically by hydrogen peroxide. This type of reaction has promoted research on hydroboration because of its mild condition and a wide scope of tolerated alkenes. Another research subtheme is metal-catalysed hydroboration. The development of this technology and the underlying concepts were recognized by the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Herbert C. Brown. He shared the prize with Georg Wittig in 1979 for his pioneering research on organoboranes as important synthetic intermediates. Addition of a H-B bond to C-C doubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Redox Reaction
Organic reductions or organic oxidations or organic redox reactions are redox reactions that take place with organic compounds. In organic chemistry oxidations and reductions are different from ordinary redox reactions, because many reactions carry the name but do not actually involve electron transfer.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Instead the relevant criterion for organic oxidation is gain of oxygen and/or loss of hydrogen, respectively.''Organic Redox Systems: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications'', Tohru Nishinaga 2016 Simple functional groups can be arranged in order of increasing oxidation state. The oxidation numbers are only an approximation: When methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide its oxidation number changes from −4 to +4. Classical reductions include alkene reduction to alkanes and classical oxidations include oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes. In oxidations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Preparations And Procedures International
''Organic Preparations and Procedures International'' is a bimonthly scientific journal In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication intended to further the progress of science, usually by reporting new research. Content Articles in scientific journals are mostly written by active scientists such as s ... focusing on organic chemists engaged in synthesis. Topics include original preparative chemistry in association with the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. Organic chemistry journals English-language journals {{chemistry-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Borohydride
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula Na BH4. This white solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution, is a reducing agent that finds application in papermaking and dye industries. It is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis. The compound was discovered in the 1940s by H. I. Schlesinger, who led a team seeking volatile uranium compounds.Hermann I Schlesinger and Herbert C Brown (1945)Preparation of alkali metal compounds. US Patent 2461661. Granted on 1949-02-15; expired on 1966-02-15. Results of this wartime research were declassified and published in 1953. Properties The compound is soluble in alcohols, certain ethers, and water, although it slowly hydrolyzes. Sodium borohydride is an odorless white to gray-white microcrystalline powder that often forms lumps. It can be purified by recrystallization from warm (50 °C) diglyme. Sodium borohydride is soluble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Sulfide
Dimethyl sulfide (DMS) or methylthiomethane is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2S. Dimethyl sulfide is a flammable liquid that boils at and has a characteristic disagreeable odor. It is a component of the smell produced from cooking of certain vegetables, notably maize, cabbage, beetroot, and seafoods. It is also an indication of bacterial contamination in malt production and brewing. It is a breakdown product of dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), and is also produced by the bacterial metabolism of methanethiol. Occurrence and production DMS originates primarily from DMSP, a major secondary metabolite in some marine algae. DMS is the most abundant biological sulfur compound emitted to the atmosphere. Emission occurs over the oceans by phytoplankton. DMS is also produced naturally by bacterial transformation of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) waste that is disposed of into sewers, where it can cause environmental odor problems. DMS is oxidized in the marine atmos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information. Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic, and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among various mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallics
''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is organometallic and organometalloid chemistry. This peer-reviewed journal has an impact factor of 3.837 as reported by the 2021 Journal Citation Reports by Thomson Reuters. Since 2015 Paul Chirik is the editor-in-chief of ''Organometallics''. He is an American chemist and the Edwards S. Sanford Professor of Chemistry at Princeton University, and associate director for external partnerships of the Andlinger Center for Energy and the Environment. He writes about the catalysis of hydrocarbons. Past editors-in-chief are Dietmar Seyferth and John Gladysz. Retrieved on 2014-07-30. This journal is indexed in |
Dimethylsulfide
Dimethyl sulfide (DMS) or methylthiomethane is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2S. Dimethyl sulfide is a flammable liquid that boils at and has a characteristic disagreeable odor. It is a component of the smell produced from cooking of certain vegetables, notably maize, cabbage, beetroot, and seafoods. It is also an indication of bacterial contamination in malt production and brewing. It is a breakdown product of dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), and is also produced by the bacterial metabolism of methanethiol. Occurrence and production DMS originates primarily from DMSP, a major secondary metabolite in some marine algae. DMS is the most abundant biological sulfur compound emitted to the atmosphere. Emission occurs over the oceans by phytoplankton. DMS is also produced naturally by bacterial transformation of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) waste that is disposed of into sewers, where it can cause environmental odor problems. DMS is oxidized in the marine atmosphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
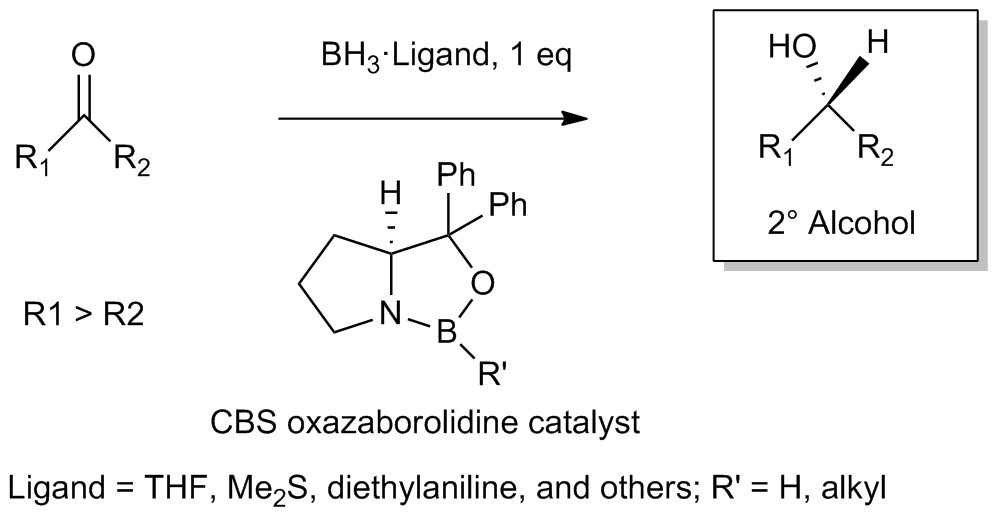
Corey–Itsuno Reduction
The Corey–Itsuno reduction, also known as the Corey–Bakshi–Shibata (CBS) reduction, is a chemical reaction in which an achiral ketone is enantioselectively reduced to produce the corresponding chiral, non-racemic alcohol. The oxazaborolidine reagent which mediates the enantioselective reduction of ketones was previously developed by the laboratory of Itsuno and thus this transformation may more properly be called the Itsuno-Corey oxazaborolidine reduction. History In 1981, Itsuno and coworkers first reported the use of chiral alkoxy-amine-borane complexes in reducing achiral ketones to chiral alcohols enantioselectively and in high yield. Several years later in 1987, E. J. Corey and coworkers developed the reaction between chiral amino alcohols and borane (BH3), generating oxazaborolidine products which were shown to rapidly catalyze the enantioselective reduction of achiral ketones in the presence of BH3•THF. The CBS reduction has since been utilized by organic chemist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boranes
Boranes is the name given to compounds with the formula BxHy and related anions. Many such boranes are known. Most common are those with 1 to 12 boron atoms. Although they have few practical applications, the boranes exhibit structures and bonding that differs strongly from the patterns seen in hydrocarbons. Hybrids of boranes and hydrocarbons, the carboranes are also well developed. History The development of the chemistry of boranes led to innovations in synthetic methods as well as structure and bonding. First, new synthetic techniques were required to handle diborane and many of its derivatives, which are both pyrophoric and volatile. Alfred Stock invented the glass vacuum line for this purpose. The structure of diborane was correctly predicted in 1943 many years after its discovery. The structures of the boron hydride clusters were determined beginning in 1948 with the characterization of decaborane. William Lipscomb was awarded the Nobel prize in Chemistry in 1976 for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


-from-xtal-view-1-tilt-3D-bs-17.png)