Boranes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Boranes is the name given to compounds with the formula BxHy and related anions. Many such boranes are known. Most common are those with 1 to 12
Boranes is the name given to compounds with the formula BxHy and related anions. Many such boranes are known. Most common are those with 1 to 12
Image:Borane-3D-balls.png,
BH3 Image:Diborane-3D-balls-A.png, Diborane(6)
B2H6 Image:Tetraborane-3D-balls.png, ''arachno''-Tetraborane(10)
B4H10 Image:Pentaborane(9)-from-xtal-view-1-Mercury-3D-bs.png,
B5H9 Image:Decaborane(14)-from-xtal-view-1-tilt-3D-bs-17.png, Decaborane(14)
B10H14 image:B18H22 from Xray coordinates.tif, B18H22 image:Iso-B18H22 from Xray coordinates.tif, ''iso''-B18H22
File:Hexaborate(6)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Hexaborate(6)
B6H62ŌłÆ File:Heptaborate(7)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Heptaborate(7)
B7H72ŌłÆ File:Octaborate(8)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Octaborate(8)
B8H82ŌłÆ File:Nonaborate(9)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Nonaborate(9)
B9H92ŌłÆ File:Decaborate(10)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Decaborate(10)
B10H102ŌłÆ File:Closo-undecaborate(11)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Undecaborate(11)
B11H112ŌłÆ Image:Dodecaborate(12)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Dodecaborate(12)
B12H122ŌłÆ
The naming of anions is illustrated by
:octahydridopentaborate, B5H8−
The hydrogen count is specified first followed by the boron count. The -ate suffix is applied with
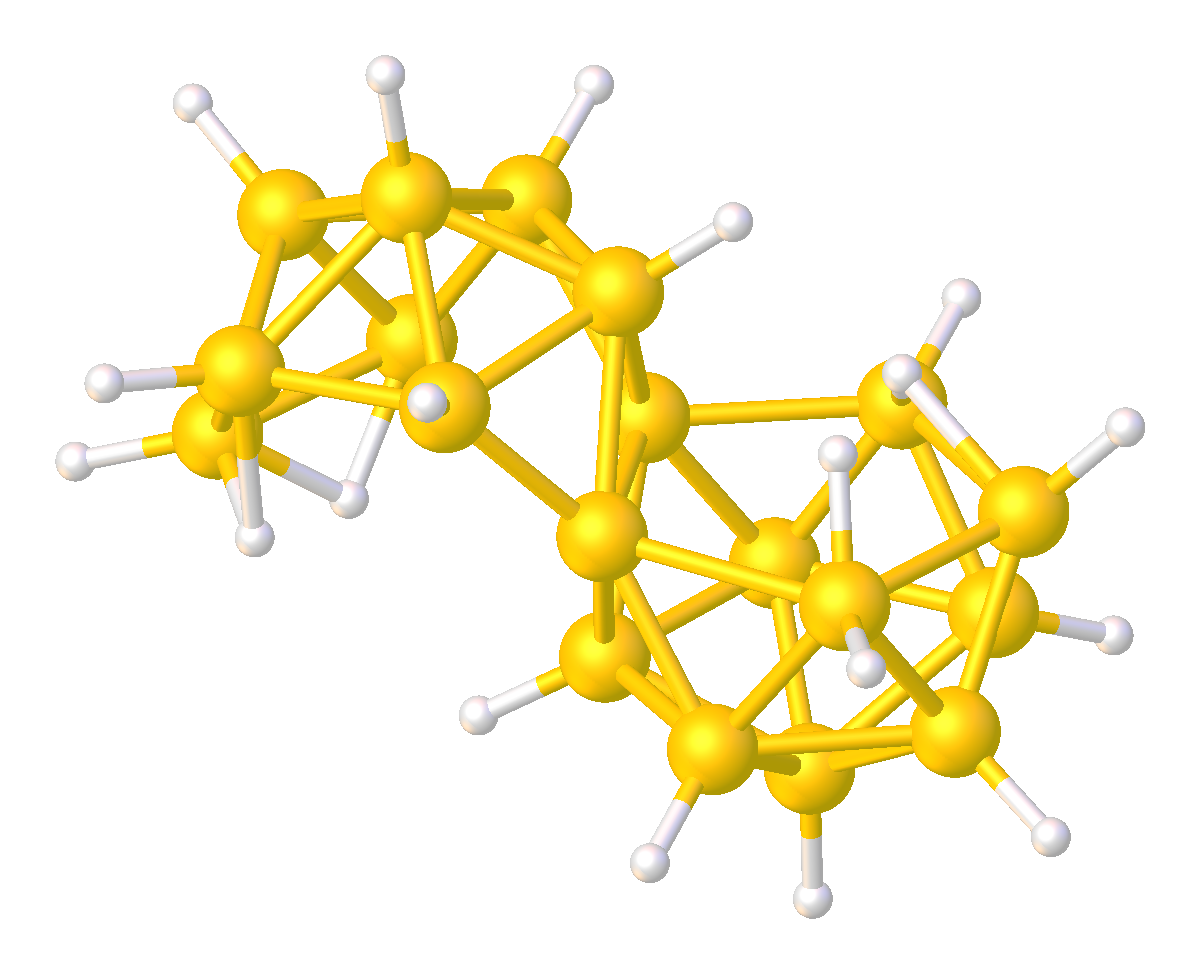 Although relatively rare, several multi-cluster boranes have been characterized. For example, reaction of a borane cluster with B2H6 (as a source of BH3) can lead to the formation of a ''conjuncto''-borane species in which borane cluster sub-units are joined by the sharing of boron atoms.
:B6H10 + (BH3) ŌåÆ B7H11 + H2
:B7H11 + B6H10 ŌåÆ B13H19 + H2
Other ''conjuncto''-boranes, where the sub-units are joined by a B-B bond, can be made by ultra violet irradiation of ''nido''-boranes. Some B-B coupled ''conjuncto''-boranes can be produced using PtBr2 as catalyst.
Analogous to Wade's Rules, electron counting scheme has been developed to predict or rationalize multicluster boranes.
Although relatively rare, several multi-cluster boranes have been characterized. For example, reaction of a borane cluster with B2H6 (as a source of BH3) can lead to the formation of a ''conjuncto''-borane species in which borane cluster sub-units are joined by the sharing of boron atoms.
:B6H10 + (BH3) ŌåÆ B7H11 + H2
:B7H11 + B6H10 ŌåÆ B13H19 + H2
Other ''conjuncto''-boranes, where the sub-units are joined by a B-B bond, can be made by ultra violet irradiation of ''nido''-boranes. Some B-B coupled ''conjuncto''-boranes can be produced using PtBr2 as catalyst.
Analogous to Wade's Rules, electron counting scheme has been developed to predict or rationalize multicluster boranes.
 Boranes is the name given to compounds with the formula BxHy and related anions. Many such boranes are known. Most common are those with 1 to 12
Boranes is the name given to compounds with the formula BxHy and related anions. Many such boranes are known. Most common are those with 1 to 12 boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the '' boron group'' it has t ...
atoms. Although they have few practical applications, the boranes exhibit structures and bonding that differs strongly from the patterns seen in hydrocarbons. Hybrids of boranes and hydrocarbons, the carborane
Carboranes are electron-delocalized (non-classically bonded) clusters composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms.Grimes, R. N., ''Carboranes 3rd Ed.'', Elsevier, Amsterdam and New York (2016), . Like many of the related boron hydrides, these c ...
s are also well developed.
History
The development of the chemistry of boranes led to innovations in synthetic methods as well as structure and bonding. First, new synthetic techniques were required to handle diborane and many of its derivatives, which are bothpyrophoric
A substance is pyrophoric (from grc-gre, ŽĆŽģŽü╬┐ŽåŽīŽü╬┐Žé, , 'fire-bearing') if it ignites spontaneously in air at or below (for gases) or within 5 minutes after coming into contact with air (for liquids and solids). Examples are organolith ...
and volatile. Alfred Stock invented the glass vacuum line for this purpose.
The structure of diborane was correctly predicted in 1943 many years after its discovery. The structures of the boron hydride clusters were determined beginning in 1948 with the characterization of decaborane
Decaborane, also called decaborane(14), is the borane with the chemical formula B10 H14. This white crystalline compound is one of the principal boron hydride clusters, both as a reference structure and as a precursor to other boron hydrides. It ...
. William Lipscomb
William Nunn Lipscomb Jr. (December 9, 1919April 14, 2011) was a Nobel Prize-winning American inorganic and organic chemist working in nuclear magnetic resonance, theoretical chemistry, boron chemistry, and biochemistry.
Biography
Overview
Li ...
was awarded the Nobel prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
in Chemistry in 1976 for this and many subsequent crystallographic investigations. These investigations revealed the prevalence of deltahedral structures, i.e., networks of triangular arrays of BH centers.
The bonding of the clusters ushered in Polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory and Wade's rules, which can be used to predict the structures of boranes. These rules were found to describe structures of many cluster compounds.
Interest in boranes increased during World War II due to the potential of uranium borohydride for enrichment of the uranium isotopes and as a source of hydrogen for inflating weather balloons. In the US, a team led by Schlesinger Schlesinger is a German surname (in part also Jewish) meaning "Silesian" from the older regional term ''Schlesinger''; someone from ''Schlesing'' (Silesia); in modern Standard German (or Hochdeutsch) a '' Schlesier'' is someone from '' Schlesien'' ...
developed the basic chemistry of the anionic boron hydrides and the related aluminium hydrides. Schlesinger's work laid the foundation for a host of boron hydride reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
s for organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
, most of which were developed by his student Herbert C. Brown
Herbert Charles Brown (May 22, 1912 ŌĆō December 19, 2004) was an American chemist and recipient of the 1979 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work with organoboranes.
Life and career
Brown was born Herbert Brovarnik in London, to Ukrainian Jewis ...
. Borane-based reagents are now widely used in organic synthesis. Brown was awarded the Nobel prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
in Chemistry in 1979 for this work.
Chemical formula and naming conventions
Borane clusters are classified as follows, where ''n'' is the number of boron atoms in a single cluster: pp 151-195 The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry rules for systematic naming is based on a prefix denoting a class of compound, followed by the number of boron atoms and finally the number of hydrogen atoms in parentheses. Various details can be omitted if there is no ambiguity about the meaning, for example, if only one structural type is possible. Some examples of the structures are shown below.Borane
Trihydridoboron, also known as borane or borine, is an unstable and highly reactive molecule with the chemical formula . The preparation of borane carbonyl, BH3(CO), played an important role in exploring the chemistry of boranes, as it indicated ...
BH3 Image:Diborane-3D-balls-A.png, Diborane(6)
B2H6 Image:Tetraborane-3D-balls.png, ''arachno''-Tetraborane(10)
B4H10 Image:Pentaborane(9)-from-xtal-view-1-Mercury-3D-bs.png,
Pentaborane(9)
Pentaborane(9) is an inorganic compound with the formula B5H9. It is one of the most common boron hydride clusters, although it is a highly reactive compound. Because of its high reactivity toward oxygen, it was once evaluated as rocket or jet fue ...
B5H9 Image:Decaborane(14)-from-xtal-view-1-tilt-3D-bs-17.png, Decaborane(14)
B10H14 image:B18H22 from Xray coordinates.tif, B18H22 image:Iso-B18H22 from Xray coordinates.tif, ''iso''-B18H22
B6H62ŌłÆ File:Heptaborate(7)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Heptaborate(7)
B7H72ŌłÆ File:Octaborate(8)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Octaborate(8)
B8H82ŌłÆ File:Nonaborate(9)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Nonaborate(9)
B9H92ŌłÆ File:Decaborate(10)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Decaborate(10)
B10H102ŌłÆ File:Closo-undecaborate(11)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Undecaborate(11)
B11H112ŌłÆ Image:Dodecaborate(12)-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png, Dodecaborate(12)
B12H122ŌłÆ
anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s. The ionic charge value is included in the chemical formula but not as part of the systematic name.
Bonding in boranes
Boranes are nonclassicallyŌĆōbonded compounds, that is, there are not enough electrons to form 2-centre, 2-electron bonds between all pairs of adjacent atoms in the molecule. A description of the bonding in the larger boranes was formulated byWilliam Lipscomb
William Nunn Lipscomb Jr. (December 9, 1919April 14, 2011) was a Nobel Prize-winning American inorganic and organic chemist working in nuclear magnetic resonance, theoretical chemistry, boron chemistry, and biochemistry.
Biography
Overview
Li ...
. It involved:
* 3-center 2-electron B-H-B hydrogen bridges
*3-center 2-electron B-B-B bonds
*2-center 2-electron bonds (in B-B, B-H and BH2)
Lipscomb's methodology has largely been superseded by a molecular orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of find ...
approach. This allows the concept of multi-centre bonding to be extended. For example, in the icosahedral ion 12H12sup>2-, the totally symmetric (Ag symmetry) molecular orbital is equally distributed among all 12 boron atoms. Wade's rules
In chemistry the polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory (PSEPT) provides electron counting rules useful for predicting the structures of clusters such as borane and carborane clusters. The electron counting rules were originally formulated by ...
provide a powerful method that can be used to rationalize the structures in terms of the number of atoms and the connectivity between them.
Multicluster boranes
 Although relatively rare, several multi-cluster boranes have been characterized. For example, reaction of a borane cluster with B2H6 (as a source of BH3) can lead to the formation of a ''conjuncto''-borane species in which borane cluster sub-units are joined by the sharing of boron atoms.
:B6H10 + (BH3) ŌåÆ B7H11 + H2
:B7H11 + B6H10 ŌåÆ B13H19 + H2
Other ''conjuncto''-boranes, where the sub-units are joined by a B-B bond, can be made by ultra violet irradiation of ''nido''-boranes. Some B-B coupled ''conjuncto''-boranes can be produced using PtBr2 as catalyst.
Analogous to Wade's Rules, electron counting scheme has been developed to predict or rationalize multicluster boranes.
Although relatively rare, several multi-cluster boranes have been characterized. For example, reaction of a borane cluster with B2H6 (as a source of BH3) can lead to the formation of a ''conjuncto''-borane species in which borane cluster sub-units are joined by the sharing of boron atoms.
:B6H10 + (BH3) ŌåÆ B7H11 + H2
:B7H11 + B6H10 ŌåÆ B13H19 + H2
Other ''conjuncto''-boranes, where the sub-units are joined by a B-B bond, can be made by ultra violet irradiation of ''nido''-boranes. Some B-B coupled ''conjuncto''-boranes can be produced using PtBr2 as catalyst.
Analogous to Wade's Rules, electron counting scheme has been developed to predict or rationalize multicluster boranes.
Reactivity of boranes
The lowest borane, BH3 exists only transiently, dimerizing instantly to form diborane, B2H6. Its adducts BH3┬ĘTHF and BH3┬ĘDMSO are sufficiently stable to be used in hydroboration reactions. Reminiscent of the behavior of diborane, some lower boranes react with air very exothermically, even explosively. By contrast, many ''closo''-borane cluster, such as B12H122ŌłÆ, do not react with air. The boron hydride clusters are so diverse that generalizations on their reactions are not possible.Lewis acid/base behavior
some function as electron donors owing to the relative basic character of the B-Hterminal groups. Boranes can function asligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elect ...
s in coordination compound
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Man ...
s. Hapticities of ╬Ę1 to ╬Ę6 have been found, with electron donation involving bridging H atoms or donation from B-B bonds. For example, ''nido-''B6H10 can replace ethene in Zeise's salt
Zeise's salt, potassium trichloro(ethylene)platinate(II), is the chemical compound with the formula K platinum">PtCl3(C2H4).html" ;"title="platinum.html" ;"title="/nowiki>PtCl3(C2H4)">platinum.html"_;"title="/nowiki>platinum">PtCl3(C2H4)ĘH2O.__Th ...
to produce Fe(╬Ę2-B6H10)(CO)4.
They can also act as Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
s, with concomitant opening of the cluster. An example involving trimethylphosphine:
:B5H9 + 2 PMe3 ŌåÆ B5H9(PMe3)2
Br├Ėnsted acid/base behavior
Some higher boranes, especially those with bridging hydrogen atoms, can be deprotonated with a strong base. An example: :B5H9 + NaH ŌåÆ Na(B5H8) + H2 Acidity increases with the size of the borane. B10H14 has a pK value of 2.7. : B5H9 < B6H10 < B10H14 < B16H20 < B18H22Aufbau reactions
For the boron hydride chemist, one of the most important reactions is the building up process by which smaller boron hydride clusters add borane to give larger clusters.Hydroboration
Reminiscent of the behavior of diborane and its adducts, higher boranes participate in hydroboration. When boron hydrides add analkyne
\ce
\ce
Acetylene
\ce
\ce
\ce
Propyne
\ce
\ce
\ce
\ce
1-Butyne
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbonŌĆöcarbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and n ...
, the carbon becomes incorporated into the cluster, producing carborane
Carboranes are electron-delocalized (non-classically bonded) clusters composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms.Grimes, R. N., ''Carboranes 3rd Ed.'', Elsevier, Amsterdam and New York (2016), . Like many of the related boron hydrides, these c ...
s, e.g. C2B10H12.
Applications
Diborane and its monomeric adductsboraneŌĆōtetrahydrofuran
BoraneŌĆōtetrahydrofuran is a dipolar bond charge-transfer complex composed of borane and tetrahydrofuran (THF). These solutions are used for reductions and hydroboration, reactions that are useful in synthesis of organic compounds.Marek Zaidlew ...
or boraneŌĆōdimethylsulfide are useful reagents. They are often used for hydroboration in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
. Some higher boranes, including anti-B18H22, have demonstrated luminescent properties. Some cobalt derivative of carboranes have been commercialized for sequestering 137Cs from radioactive waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapon ...
.
Aspirational uses
Because boron hydride clusters readily absorb neutrons, their derivatives have often been investigated for applications inNeutron capture therapy of cancer
Neutron capture therapy (NCT) is a type of radiotherapy for treating locally invasive malignant tumors such as primary brain tumors, recurrent cancers of the head and neck region, and cutaneous and extracutaneous melanomas. It is a two-step pro ...
. One favored compound is the Na2 12H11(SH) It makes use of the fact that 10B has a very high neutron-capture cross section, so neutron irradiation is highly selective for the region where the compound resides.
:10B + 1n ŌåÆ (11B*) ŌåÆ 4He + 7Li + ╬│ (2.4 Mev)
Boranes have a high specific energy of combustion compared to hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
s, making them potentially attractive as fuels. Intense research was carried out in the 1950s into their use as jet fuel additives, but the effort did not lead to practical results.
See also
* :Boranes, containing all specific borane-compound articlesReferences
{{Authority control