|
Battle Of Magnesia
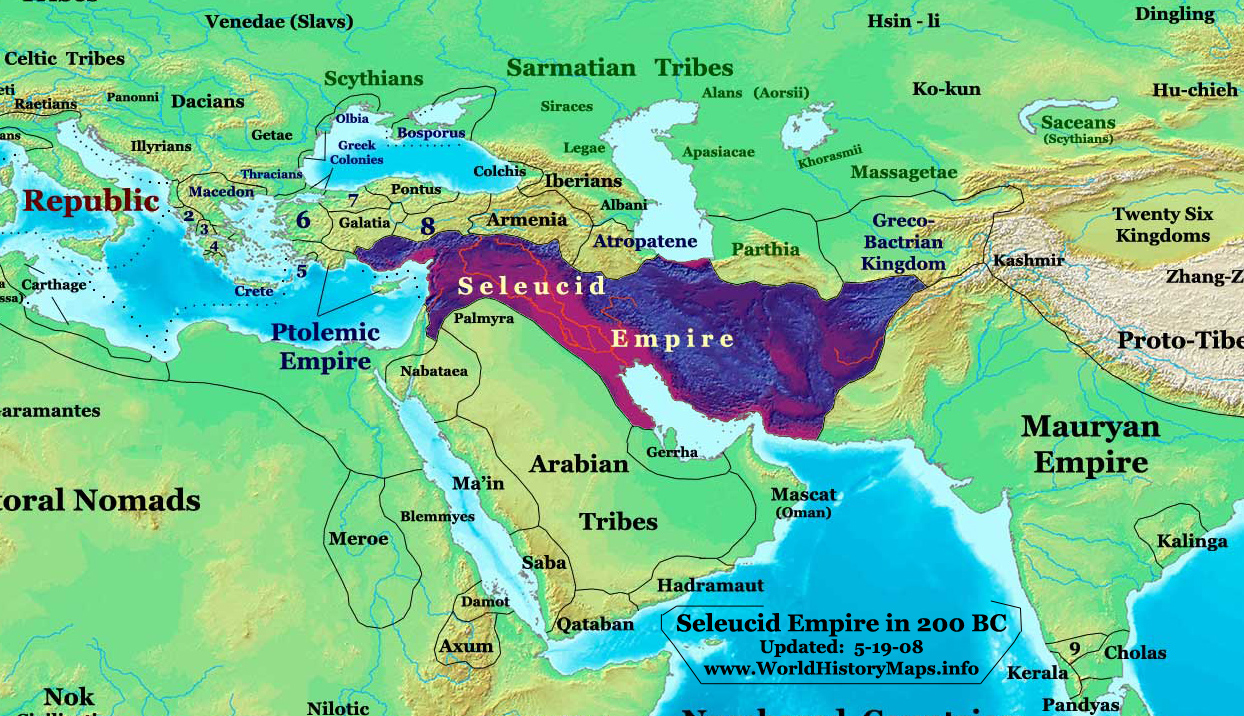
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pergamon under Eumenes II against a Seleucid army of Antiochus III the Great. The two armies initially camped north-east of Magnesia ad Sipylum in Asia Minor (modern-day Manisa, Turkey), attempting to provoke each other into a battle on favorable terrain for several days. When the battle finally began, Eumenes managed to throw the Seleucid left flank into disarray. While Antiochus' cavalry overpowered his adversaries on the right flank of the battlefield, his army's center collapsed before he could reinforce it. Modern estimates give 10,000 dead for the Seleucids and 5,000 killed for the Romans. The battle resulted in a decisive Roman-Pergamene victory, which led to the Treaty of Apamea that ended Seleucid domination in Asia Minor. Backgrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman–Seleucid War
The Seleucid War (192–188 BC), also known as the War of Antiochos or the Syrian War, was a military conflict between two coalitions led by the Roman Republic and the Seleucid Empire. The fighting took place in modern day southern Greece, the Aegean Sea and Asia Minor. The war was the consequence of a "cold war" between both powers, which had started in 196 BC. In this period, the Romans and the Seleucids attempted to settle spheres of influence by forging alliances with the small Greek city-states. The fighting ended with a clear Roman victory. In the Treaty of Apamea, the Seleucids were forced to give up Asia Minor, which fell to Roman allies. As a main result of the war, the Roman Republic gained hegemony over the Greek city-states and Asia Minor and became the only remaining major power around the Mediterranean Sea. Prelude Antiochus III the Great, the Seleucid king, first became involved with Greece when he signed an alliance with King Philip V of Macedon in 203 BC.Green ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip V Of Macedon
Philip V ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 238–179 BC) was king ( Basileus) of Macedonia from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon against Rome in the First and Second Macedonian Wars, losing the latter but allying with Rome in the Roman-Seleucid War towards the end of his reign. Early life Philip was the son of Demetrius II of Macedon and Chryseis. Philip was nine years old when his father died 229 BC. His elder paternal half sister was Apama III. Philips's great-uncle, Antigonus III Doson, administered the kingdom as regent until his death in 221 BC when Philip was seventeen years old. Philip was attractive and charismatic as a young man. A dashing and courageous warrior, he was compared to Alexander the Great and was nicknamed ''beloved of the Hellenes'' () because he became, as Polybius put it, "...the beloved of the Hellenes for his charitable inclination". A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal's father, Hamilcar Barca, was a leading Carthaginian general during the First Punic War. His younger brothers were Mago and Hasdrubal; his brother-in-law was Hasdrubal the Fair, who commanded other Carthaginian armies. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the Mediterranean Basin, triggered by the emergence of the Roman Republic as a great power with its defeat of Carthage in the First Punic War. Revanchism prevailed in Carthage, symbolized by the pledge that Hannibal made to his father to "never be a friend of Rome". In 218 BC, Hannibal attacked Saguntum (modern Sagunto, Spain), an ally of Rome, in Hispania, sparking the Second Pun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Carthage
Carthage () was a settlement in modern Tunisia that later became a city-state and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians in the ninth century BC, Carthage reached its height in the fourth century BC as one of the largest metropolises in the worldGeorge Modelski, ''World Cities: –3000 to 2000'', Washington DC: FAROS 2000, 2003. . Figures in main tables are preferentially cited. Part of former estimates can be read at Evolutionary World Politics Homepage Archived 2008-12-28 at the Wayback Machine and the centre of the Carthaginian Empire, a major power in the ancient world that dominated the western Mediterranean. Following the Punic Wars, Carthage was destroyed by the Romans in 146 BC, who later rebuilt the city lavishly. Carthage was settled around 814 BC by colonists from Tyre, a leading Phoenician city-state located in present-day Lebanon. In the seventh century BC, following Phoenicia's conquest by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Carthage became independent, gradually ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean administrative region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Rhodes. The city of Rhodes had 50,636 inhabitants in 2011. In 2022 the island has population of 124,851 people. It is located northeast of Crete, southeast of Athens. Rhodes has several nicknames, such as "Island of the Sun" due to its patron sun god Helios, "The Pearl Island", and "The Island of the Knights", named after the Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem, who ruled the island from 1310 to 1522. Historically, Rhodes was famous for the Colossus of Rhodes, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The Medieval Old Town of the City of Rhodes has been declared a World Heritage Site. Today, it is one of the most popular tourist destina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus II Theos
Antiochus II Theos ( grc-gre, Ἀντίοχος Θεός, ; 286 – July 246 BC) was a Greek king of the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic Seleucid Empire who reigned from 261 to 246 BC. He succeeded his father Antiochus I Soter in the winter of 262–61 BC. He was the younger son of Antiochus I and princess Stratonice of Syria, Stratonice, the daughter of Demetrius I of Macedon, Demetrius Poliorcetes. Antiochus II was a forceful personality who in his lifetime largely succeeded to hold the sprawling Seleucid realm intact. However his fateful decision to repudiate his first wife Laodice I, Laodice and marry a Ptolemaic dynasty, Ptolemaic princess Berenice (Seleucid queen), Berenice as part of a peace treaty led to a succession struggle after his death that would shake the empire's foundations and cause large territorial losses. Early life Antiochus II was the younger son of Antiochus I Soter and his famous queen Stratonice of Syria, Stratonice. Antiochus was initially not expect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysimachia (Thrace)
Lysimachia ( el, Λυσιμάχεια) was an important Hellenistic Greece, Hellenistic Greek town on the north-western extremity of the Thracian Chersonese (the modern Gallipoli peninsula) in the neck where the peninsula joins the mainland in what is now the Turkish Thrace, European part of Turkey, not far from the bay of Melas (the modern Gulf of Saros). History The city was built by Lysimachus in 309 BC, when he was preparing for war with his Diadochi, rivals; for the new city, being situated on the isthmus, commanded the road from Sestos to the north and the mainland of Thrace. In order to obtain inhabitants for his new city, Lysimachus destroyed the neighbouring town of Cardia (Thrace), Cardia, the birthplace of the historian Hieronymus of Cardia, Hieronymus, and settled the inhabitants of it and other Chersonesean cities here. Lysimachus no doubt made Lysimachia the capital of his kingdom, and it must have rapidly risen to great splendour and prosperity. After his de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellespont
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; grc-x-classical, Ἑλλήσποντος, translit=Hellēspontos, lit=Sea of Helle), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey that forms part of the continental boundary between Asia and Europe and separates Asian Turkey from European Turkey. Together with the Bosporus, the Dardanelles forms the Turkish Straits. One of the world's narrowest straits used for international navigation, the Dardanelles connects the Sea of Marmara with the Aegean and Mediterranean seas while also allowing passage to the Black Sea by extension via the Bosporus. The Dardanelles is long and wide. It has an average depth of with a maximum depth of at its narrowest point abreast the city of Çanakkale. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lampsacus
Lampsacus (; grc, Λάμψακος, translit=Lampsakos) was an ancient Greek city strategically located on the eastern side of the Hellespont in the northern Troad. An inhabitant of Lampsacus was called a Lampsacene. The name has been transmitted in the nearby modern town of Lapseki. Ancient history Originally known as Pityusa or Pityussa ( grc, Πιτυούσ(σ)α), it was colonized from Phocaea and Miletus. In the 6th century BC Lampsacus was attacked by Miltiades the Elder and Stesagoras, the Athenian tyrants of the nearby Thracian Chersonese. During the 6th and 5th centuries BC, Lampsacus was successively dominated by Lydia, Persia, Athens, and Sparta. The Greek tyrants Hippoclus and later his son Acantides ruled under Darius I. Artaxerxes I assigned it to Themistocles with the expectation that the city supply the Persian king with its famous wine. When Lampsacus joined the Delian League after the battle of Mycale (479 BC), it paid a tribute of twelve talents, a testimo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prominence. The name of the city since about 1930 is İzmir. Two sites of the ancient city are today within Izmir's boundaries. The first site, probably founded by indigenous peoples, rose to prominence during the Archaic Period as one of the principal ancient Greek settlements in western Anatolia. The second, whose foundation is associated with Alexander the Great, reached metropolitan proportions during the period of the Roman Empire. Most of the present-day remains of the ancient city date from the Roman era, the majority from after a second-century AD earthquake. In practical terms, a distinction is often made between these. ''Old Smyrna'' was the initial settlement founded around the 11th century BC, first as an Aeolian settlement, and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attalid Dynasty
The Kingdom of Pergamon or Attalid kingdom was a Ancient Greece, Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Anatolia, Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (; grc-x-koine, Δυναστεία των Ατταλιδών, translit=Dynasteía ton Attalidón). The kingdom was a rump state that was created from the territory ruled by Lysimachus, a general of Alexander the Great. Philetaerus, one of Lysimachus' lieutenants, rebelled and took the city of Pergamon and its environs with him; Lysimachus died soon after in 281 BC. The new kingdom was initially in a vassal-like relationship of nominal fealty to the Seleucid Empire, but exercised considerable autonomy and soon became entirely independent. It was a monarchy ruled by Philetaerus's extended family and their descendants. It lasted around 150 years before being eventually absorbed by the Roman Republic during the period from 133–129 BC. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attalus I
Attalus I ( grc, Ἄτταλος Α΄), surnamed ''Soter'' ( el, , "Savior"; 269–197 BC) ruled Pergamon, an Ionian Greek polis (what is now Bergama, Turkey), first as dynast, later as king, from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the first cousin once removed and the adopted son of Eumenes I, whom he succeeded, and was the first of the Attalid dynasty to assume the title of king in 238 BC. He was the son of Attalus and his wife Antiochis. Attalus won Battle of the Caecus River, an important victory over the Galatians, newly arrived Celtic tribes from Thrace, who had been, for more than a generation, plundering and exacting tribute throughout most of Asia Minor without any serious check. This victory, celebrated by the triumphal monument at Pergamon (famous for its ''Dying Gaul'') and the liberation from the Gallic "terror" which it represented, earned for Attalus the name of "Soter", and the title of "basileus, king". A courageous and capable general and loyal ally of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |