|
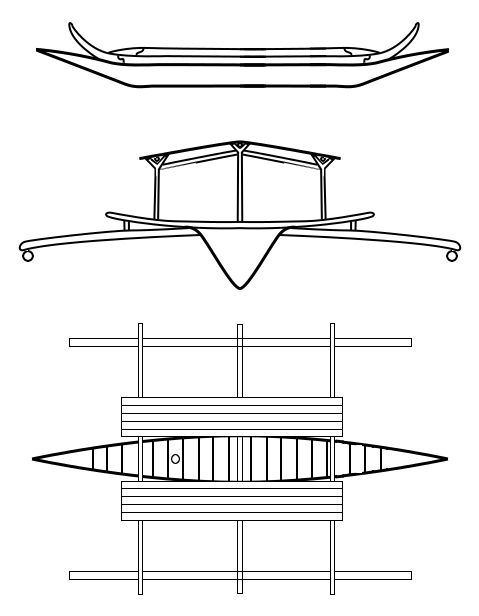
Baloto
A Balangay, or barangay is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The oldest known balangay are the Butuan boats, which have been carbon-dated to 320 AD and were recovered from several sites in Butuan, Agusan del Norte. Balangay were the first wooden watercraft excavated in Southeast Asia. Balangay are celebrated annually in the Balanghai Festival of Butuan City. Names ''Balangay'' was one of the first native words the Europeans learned in the Philippines. The Venetian chronicler Antonio Pigafetta, who was with Ferdinand Magellan when setting foot in the Philippines in 1521 called the native boats ''balangai'' or ''balanghai''. This word appears as either ''balangay'' or ''barangay'', with the same meaning, in all the major languages of the Philippines. Early colonial Spanish dictionaries make it clear t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibanag People
The Ibanag (also Ybanag and Ybanak or Ibanak) are an ethnolinguistic minority numbering a little more than half a million people, who inhabit the provinces of Cagayan, Isabela, and Nueva Vizcaya. They are one of the largest ethnolinguistic minorities in the Philippines. Etymology The endonym "Ibanag" comes from the prefix ''I-'' which means "people of", and ''bannag'', meaning river. This toponym-based name is similar to the unrelated etymology for the Tagalog people, which is derived from ''taga-'' ("person from") and ''ilog'' ("river") Language The Ibanag language (also Ybanag) is spoken by about 500,000 speakers in two of the northeasternmost provinces of the Philippines, Isabela, and Cagayan. It is closely related to Gaddang, Itawis, Agta, Atta, Yogad, Isneg, and Malaweg. It is spoken especially in Tuguegarao City, Solana, Cabagan, San Pablo, Tumauini, Sta. Maria, Sto. Tomas, Ilagan, Gamu, Naguilian, and Reina Mercedes, San Mariano, Isabela. There are also severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou, while its largest city by population is Quanzhou, both located near the coast of the Taiwan Strait in the east of the province. While its population is predominantly of Chinese ethnicity, it is one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse provinces in China. The dialects of the language group Min Chinese were most commonly spoken within the province, including the Fuzhou dialect of northeastern Fujian and various Hokkien dialects of southeastern Fujian. Hakka Chinese is also spoken, by the Hakka people in Fujian. Min dialects, Hakka and Mandarin Chinese are mutually unintelligible. Due to emigration, a sizable amount of the ethnic Chinese populations of Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, and the Philippines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangayaw
The ''Timawa'' were the feudal warrior class of the ancient Visayan societies of the Philippines. They were regarded as higher than the ''uripon'' (commoners, serfs, and slaves) but below the ''Tumao'' (royal nobility) in the Visayan social hierarchy. They were roughly similar to the Tagalog ''maharlika'' caste. The term later lost its military and nobility connotations and was demoted to mean "freemen" during the Spanish conquest of the Philippines. During which, the word was also introduced to the Tagalogs, who incorrectly used the term to refer to freed ''uripon'' (more correctly the ''matitimawa'' or ''tinimawa'' in Visayan) and commoners in general ( ''tuhay'' or ''mamahay'' in Visayan). Eventually, the meaning of ''timawa'' in modern Visayan languages was reduced to an adjective for "impoverished". Overview History The ''Timawa'' were the privileged intermediate class of ancient Visayan society, in between the ''uripon'' (commoners, serfs, and slaves) and the ''tumao' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outrigger
An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts heavy loads. Powered vessels and sailboats An outrigger describes any contraposing float rigging beyond the side (gunwale) of a boat to improve the vessel's stability. If a single outrigger is used it is usually but not always windward. The technology was originally developed by the Austronesian people. There are two main types of boats with outriggers: double outriggers (prevalent in maritime Southeast Asia) and single outriggers (prevalent in Madagascar, Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia). Multihull ships are also derived from outrigger boats. In an outrigger canoe and in sailboats such as the proa, an outrigger is a thin, long, solid, hull used to stabilise an inherently unstable main hull. The outrigger is positioned rigidly and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraw
Paraw (also spelled ''parao'') are various double outrigger sail boats in the Philippines. It is a general term (similar to the term '' bangka'') and thus can refer to a range of ship types, from small fishing canoes to large merchant lashed-lug plank boats (''balangay'' or ''baloto'') with two outriggers (''katig'') propelled by sails (usually a large crab-claw sail opposite a smaller triangular foresail) Etymology The word ''paraw'' (also spelled ''parao'') is a cognate of the terms ''proa'' of the Pacific Islands, and ''perahu'' or ''prau'' of Malay-Indonesia. It refers to outrigger boats propelled by sails (''layag''). It is a type of '' bangka'', the wider term used for boats (with or without outriggers) in the Philippines. Characteristics The paraw has three major elements that make it a paraw: the ''bangka'' (canoe or main hull), the ''katig'' (outriggers), and the ''layag'' (sails). Motorized versions of bangkas (with outriggers) are commonly known as pump boats and ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups In The Philippines
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous People groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither indigenous nor moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history. The Muslim-majority ethnic groups ethnolinguistic groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan are collectively referred to as the Moro people, a broad category which includes some indigenous people groups and some non-indigenous people groups. With a population of over 5 million people, they comprise about 5% of the country's total population, or 5 million people. The Spanish called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Barangayan Boat In The Cagayan River
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish it f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yami Balangays
Yamuna is a sacred river in Hinduism and the main tributary of the Ganges River. The river is also worshipped as a Hindu goddess called Yamuna. Yamuna is known as Yami in early texts, while in later literature, she is called Kalindi. In Hindu scriptures, she is the daughter of Surya, the sun god, and Sanjna, cloud goddess. She is also the twin sister of Yama, god of death. She is associated with the deity Krishna as one of his consorts, or Ashtabharya. Yamuna plays an important role in Krishna's early life as a river. According to Hindu scriptures, bathing in or drinking Yamuna's waters removes sin. Iconography Yamuna's iconographic depiction is seen on temple doorjambs, paired with that of Ganga (the goddess of the Ganges), since the Gupta era. The ''Agni Purana'' describes Yamuna as black in complexion, standing on her mount, the tortoise, and holding a water pot in her hand. In an ancient painting she is shown as a beautiful maiden standing on the banks of the river. Family a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakoa
''Karakoa'' were large outrigger warships from the Philippines. They were used by native Filipinos, notably the Kapampangans and the Visayans, during seasonal sea raids. ''Karakoa'' were distinct from other traditional Philippine sailing vessels in that they were equipped with platforms for transporting warriors and for fighting at sea. During peacetime, they were also used as trading ships. Large ''karakoa'', which could carry hundreds of rowers and warriors, were known as ''joangas'' (also spelled '' juangas'') by the Spanish. Panday Piray of Pampanga, Philippines was also known for forging heavy bronze lantaka to be mounted on Lakan's (Naval Chief/Commander) ships called 'caracoas' doing battle against the Spanish invaders and cannons were also commissioned by Rajah Sulayman for the fortification of Maynila. By the end of the 16th century, the Spanish denounced ''karakoa'' ship-building and its usage. It later led to a total ban of the ship and the traditions assigned to it. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balutu
Djenging is a type of large double-outrigger plank boat built by the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. It is typically used as a houseboat, though it can be converted to a sailing ship. It was the original type of houseboat used by the Sama-Bajau before it was largely replaced by the lepa after World War II. Larger versions of djenging were also known as balutu or kubu, often elaborately carved with bifurcated extensions on the prow and stern. Description The djenging is made from a dugout keel (''baran balutu'') built up at the sides with two planks (''tapid'' and ''lingkam'') attached by dowels. It is usually around long, though it can commonly reach up to in length. It is usually equal-ended, with the prow and the stern indistinguishable from each other. It has two to four outrigger booms (''batangan'') attached to bamboo floats (''katig'') which are parallel to the main hull. The tips of the floats do not extend beyond the prow and stern. Secondary booms (''sa'am'') als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
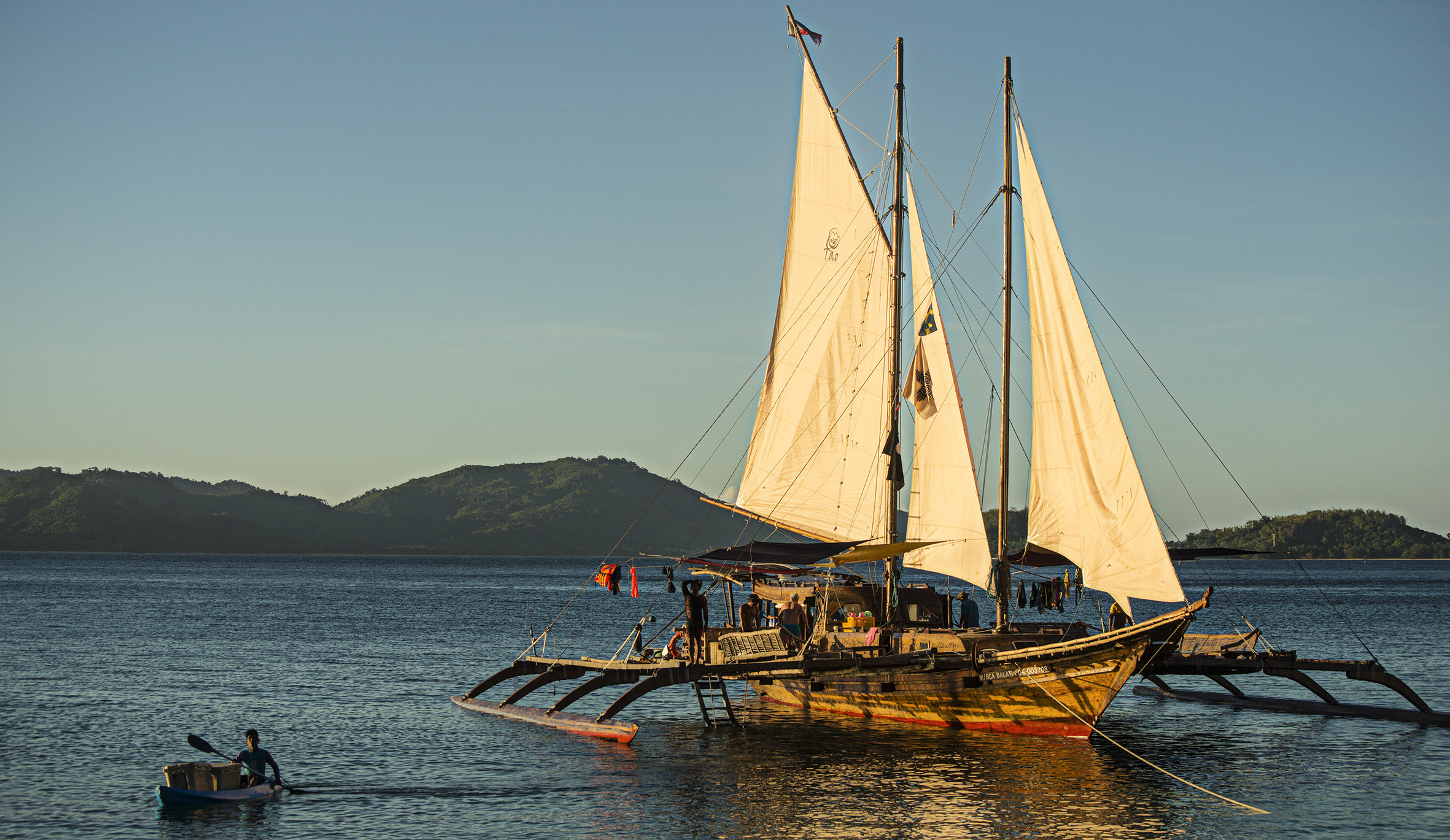



.jpg)